|
Mygurudu
Mygurudu is a Malayalam-based secret language developed in Northern Kerala during the Malabar Rebellion of 1921. Prisoners used this coded language to pass messages without getting leaked. Concepts The fundamental idea behind Mygurudu involves the swapping of Malayalam alphabets. For example, Mygurudu uses ‘Ra’ instead of ‘Cha’, and ‘Pa’ instead of ‘Na’. Current State Mygurudu had about 400 speakers before 2020, however, the number of speakers has reached 900, and 2,500+ people are learning right now. This is mostly due to online platforms increasing accessibility to language learning resourcesThe Speech Science Research Forum of the Department of Linguistics of Kerala University has digitized and documented the structure of Mygurudu and other dying languages. The scheme The following tables give the transposition scheme used in the ''Mygurudu'' code. Vowels Consonants Mnemonic The users had developed a mnemonic to learn and remember this language. The m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 Languages with official status in India, scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was designated a "Classical Languages of India, Classical Language of India" in 2013. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé, Puducherry, Mahé), and is also the primary spoken language of Lakshadweep. Malayalam is spoken by 35.6 million people in India. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with a significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Kanyakumari district, Kanyakumari, Coimbatore district, Coimbatore and Nilgiris district, Nilgiris district of Tamil Nadu. It is also spoken by the Malayali diaspora, Malayali Diaspora wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beary Dialect
Byari or Beary (ಬ್ಯಾರಿ) is a geographically isolated dialect of Malayalam spoken by the Byaris who are part of the Muslim community in Tulu Nadu region of Coastal Karnataka and Northern Kerala (Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, and Kasargod districts). The community is often recognized as Beary or Byari Muslims., p. ix Byari is influenced by Tulu phonology and grammar. Due to the trading role of the community, the language acquired loan words from other languages of Tulu and Arabic sources., p. ix Etymology See Beary#Etymology. Features The language uses the Arabic and Kannada alphabets for writing. Being a distant cousin of other dialects of Malayalam and surrounded by other linguistic groups for centuries, mainly Tulu, the dialect exhibits ancient features as well as modern innovations not seen in other well-known dialects of Malayalam. Surrounded by Tulu-speaking populations, the impact of Tulu on the phonological, morphological and syntactic structure of the dial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayalam Language
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry ( Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was designated a " Classical Language of India" in 2013. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, Lakshadweep and Puducherry ( Mahé), and is also the primary spoken language of Lakshadweep. Malayalam is spoken by 35.6 million people in India. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with a significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Kanyakumari, Coimbatore and Nilgiris district of Tamil Nadu. It is also spoken by the Malayali Diaspora worldwide, especially in the Persian Gulf countries, due to the large populations of Malayali expatriates there. They are a significant population in each city in India including Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai, De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cant (language)
A cant is the jargon or language of a group, often employed to exclude or mislead people outside the group.McArthur, T. (ed.) ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (1992) Oxford University Press It may also be called a cryptolect, argot, pseudo-language, anti-language or secret language. Each term differs slightly in meaning; their uses are inconsistent. Etymology There are two main schools of thought on the origin of the word ''cant'': * In linguistics, the derivation is normally seen to be from the Irish word (older spelling ), "speech, talk", or Scottish Gaelic . It is seen to have derived amongst the itinerant groups of people in Ireland and Scotland, who hailed from both Irish/Scottish Gaelic and English-speaking backgrounds, ultimately developing as various creole languages. However, the various types of cant (Scottish/Irish) are mutually unintelligible. The Irish creole variant is termed " the cant". Its speakers from the Irish Traveller community know it as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
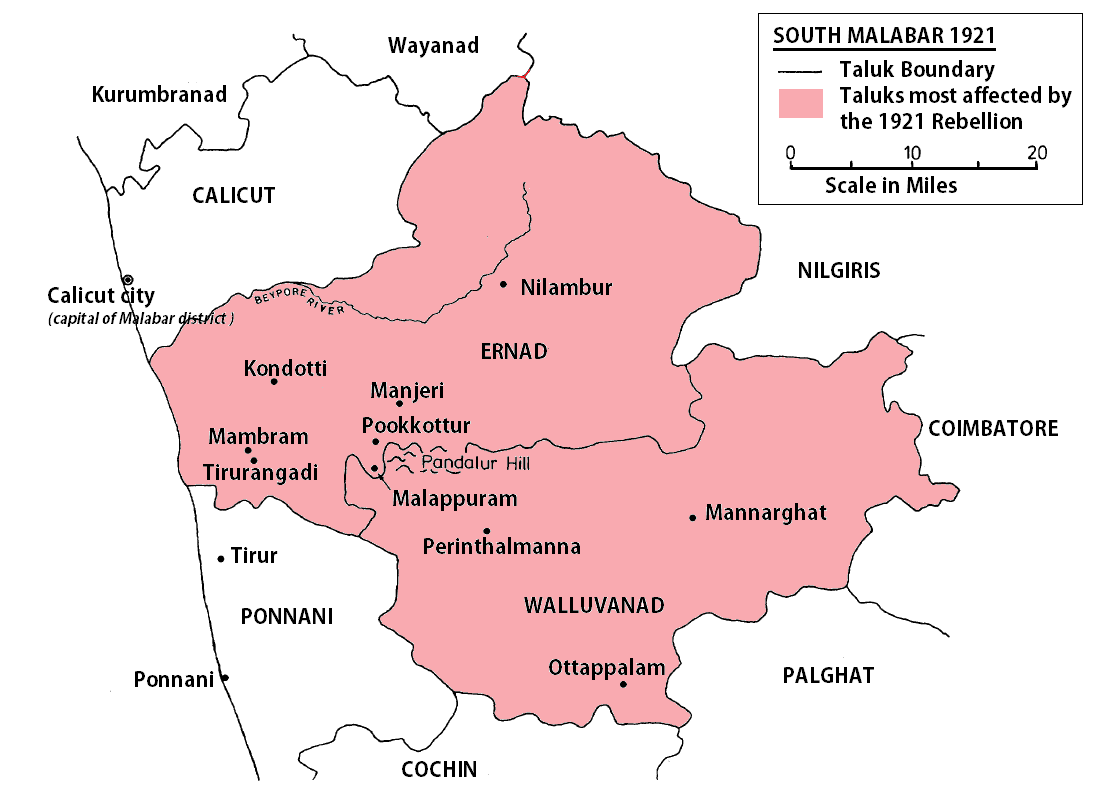
Malabar Rebellion
The Malabar rebellion of 1921 (also called Moplah rebellion, and Mappila rebellion, Malayalam: ''malabār kalāpam'') started as a resistance against the British colonial rule in certain places in the southern part of old Malabar district of present-day Kerala. The popular uprising was also against the prevailing feudal system controlled by Hindus. For the mappila side, the rebellion was primarily a peasant revolt against the colonial government. During the uprising, the rebels attacked various symbols and institutions of the colonial state, such as telegraph lines, train stations, courts and post offices. There were also a series of clashes between the Mappila Muslims, Mappila Muslims and the Hindu landlords, the latter supported by the British colonial government, throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries. The heavy-handed suppression of the Khilafat Movement by the colonial government was met by resistance in the Eranad and Perinthalmanna taluk, Valluvanad ''taluks'' of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala University
University of Kerala (formerly known as University of Travancore) is a state-run public university in Thiruvananthapuram, the state capital of Kerala, India. It was established in 1937 by a promulgation of the Maharajah of Travancore, Chithira Thirunal Balarama Varma who was also the first Chancellor of the university. C. P. Ramaswamy Iyer, the then Diwan (Prime Minister) of the State was the first Vice-Chancellor. It was the first university in Kerala, and among the first in the country. It is accredited by NAAC with highest grade of 'A++' and scored 3.67 points out of 4. The university has over 150 affiliated colleges and has sixteen faculties and 43 Departments of teaching and research. The Governor of Kerala serves as the Chancellor of university. History The history of the University of Kerala is integral to the history of the state itself. One of the first 16 Universities in India, the University of Kerala was founded in 1937. It was formerly called the University of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear Text
In cryptography, plaintext usually means unencrypted information pending input into cryptographic algorithms, usually encryption algorithms. This usually refers to data that is transmitted or stored unencrypted. Overview With the advent of computing, the term ''plaintext'' expanded beyond human-readable documents to mean any data, including binary files, in a form that can be viewed or used without requiring a key or other decryption device. Information—a message, document, file, etc.—if to be communicated or stored in an unencrypted form is referred to as plaintext. Plaintext is used as input to an encryption algorithm; the output is usually termed ciphertext, particularly when the algorithm is a cipher. Codetext is less often used, and almost always only when the algorithm involved is actually a code. Some systems use multiple layers of encryption, with the output of one encryption algorithm becoming "plaintext" input for the next. Secure handling Insecure handling of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cipher Text
In cryptography, ciphertext or cyphertext is the result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm, called a cipher. Ciphertext is also known as encrypted or encoded information because it contains a form of the original plaintext that is unreadable by a human or computer without the proper cipher to decrypt it. This process prevents the loss of sensitive information via hacking. Decryption, the inverse of encryption, is the process of turning ciphertext into readable plaintext. Ciphertext is not to be confused with codetext because the latter is a result of a code, not a cipher. Conceptual underpinnings Let m\! be the plaintext message that Alice wants to secretly transmit to Bob and let E_k\! be the encryption cipher, where _k\! is a cryptographic key. Alice must first transform the plaintext into ciphertext, c\!, in order to securely send the message to Bob, as follows: : c = E_k(m). \! In a symmetric-key system, Bob knows Alice's encryption key. Once the mes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic
A mnemonic device ( ), memory trick or memory device is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval in the human memory, often by associating the information with something that is easier to remember. It makes use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues and imagery as specific tools to encode information in a way that allows for efficient storage and retrieval. It aids original information in becoming associated with something more accessible or meaningful—which in turn provides better retention of the information. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often used for lists and in auditory system, auditory form such as Acrostic, short poems, acronyms, initialisms or memorable phrases. They can also be used for other types of information and in visual or kinesthetic forms. Their use is based on the observation that the human mind more easily remembers spatial, personal, surprising, physical, sexual, humorous and otherwise "relatable" information rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shloka
Shloka or śloka ( , from the root , Macdonell, Arthur A., ''A Sanskrit Grammar for Students'', Appendix II, p. 232 (Oxford University Press, 3rd edition, 1927).) in a broader sense, according to Monier-Williams's dictionary, is "any verse or stanza; a proverb, saying"; but in particular it refers to the 32- syllable verse, derived from the Vedic '' anuṣṭubh'' metre, used in the '' Bhagavad Gita'' and many other works of classical Sanskrit literature. In its usual form it consists of four '' pādas'' or quarter-verses, of eight syllables each, or (according to an alternative analysis) of two half-verses of 16 syllables each. The metre is similar to the Vedic '' anuṣṭubh'' metre, but with stricter rules. The ''śloka'' is the basis for Indian epic poetry, and may be considered the Indian verse form ''par excellence'', occurring as it does far more frequently than any other metre in classical Sanskrit poetry. The ''śloka'' is the verse-form generally used in the '' Maha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulabhadra
Mūlabhadra (മൂലഭദ്ര) aka Mūlabhadri ( :ml:മൂലഭദ്രി) was a secret method of communication employed by the royal spies of the erstwhile Travancore Kingdom during the medieval period. The scheme was also colloquially referred to as Mūlapatra. It was essentially a cryptographic scheme involving a partial transposition of the letters of the Malayalam alphabet. The scheme had been extensively used by King Marthanda Varma (1706–1758) of Travancore Kingdom and his spies both for oral and written communication of messages. It was a fixed one-time unchangeable code in as much as it did not employ any key in its implementation in contrast to modern methods of substitution ciphers involving the utilisation of a key for generating a system of codes. The scheme The following tables give the transposition scheme used in the ''Mulabhadra'' code. Vowels Consonants Chillus Mnemonic The users had developed a mnemonic to learn and remember this la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |