|
Myanmar Nationality Law
The Nationality law of Myanmar currently recognises three categories of citizens, namely citizen, associate citizen and naturalised citizen, according to the 1982 Citizenship Law. Citizens, as defined by the 1947 Constitution, are persons who belong to an "indigenous race", have a grandparent from an "indigenous race", are children of citizens, or lived in British Burma prior to 1942. Under the Burma Residents Registration Act of 1949 and the 1951 Resident Registration Rules, Burmese citizens are required to obtain a National Registration Card (, NRC), while non-citizens are given a Foreign Registration Card (, FRC). Citizens whose parents hold FRCs are not allowed to run for public office. In 1989, the government conducted a nationwide citizenship scrutiny process to replace NRCs with citizenship scrutiny cards (CSCs) to certify citizenship. Myanmar has a stratified citizenship system. Burmese citizens' rights are distinctively different depending on the category they belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domicile (law)
In law and conflict of laws, domicile is relevant to an individual's "personal law", which includes the law that governs a person's status and their property. It is independent of a person's nationality. Although a domicile may change from time to time, a person has only one domicile, or residence, at any point in their life, no matter what their circumstances. Domicile is distinct from habitual residence, where there is less focus on future intent. As domicile is one of the connecting factors ordinarily used in common law legal systems, a person can never be left without a domicile and a domicile is acquired by everyone at birth. Generally domicile can be divided into domicile of origin, domicile of choice, and domicile by operation of law (also known as domicile of dependency). When determining the domicile of an individual, a court applies its own law and understanding of what domicile is. In some common-law countries, such as Australia and New Zealand, the concept of domic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Myanmar
Burmese law is based on common law, and is characterised by significant legal pluralism, with state law coexisting with various customary justice systems across the diverse nation. The legal system of Myanmar (formerly Burma) is a complex, due to significant historical influences, including ancient customary laws, British colonial imprints, and post-independence legislative and judicial developments. Myanmar stands out as the only majority Buddhist country to have developed and maintained a court-enforced system of family law (called Burmese customary law) for Buddhists. Decades of Socialist and military rule has eroded the country's legal institutions. Myanmar's legal system has been characterised by a severe and systematic absence of the rule of law, rampant corruption, and human rights abuses, particularly since the 2021 Myanmar coup. In 2024, it ranked 138th across 142 countries, in the World Justice Project's Rule of Law Index. Beyond state law, ethnic armed organisatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visa Requirements For Myanmar Citizens
Visa requirements for Myanmar citizens are administrative entry restrictions by the authorities of other states placed on citizens of Myanmar. As of 2025, Myanmar citizens have visa-free or visa on arrival access to 45 countries and territories, ranking the Myanmar passport 92nd in the world according to the Henley & Partners Passport Index, Henley Passport Index. Visa requirements map Visa requirements See also * Visa policy of Myanmar * Myanmar passport * Foreign relations of Myanmar References Notes {{Visa policy by country Visa requirements by nationality, Myanmar Foreign relations of Myanmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visa Policy Of Myanmar
Any foreign national who wishes to enter Myanmar must obtain a visa (document), visa unless they are a citizen of one of the designated visa-exempt countries. All visitors to Myanmar must hold a passport valid for at least 6 months. Visa policy map Visa exemption Ordinary passports ;Restricted visa-free access Nationals of the following eight countries do not require a visa to enter Myanmar for Tourism in Myanmar, tourism visits up to the duration listed below. However, to qualify for visa-free entry, they must enter and leave Myanmar through one of the following ports of entry: * Yangon International Airport * Nay Pyi Taw International Airport * Mandalay International Airport # - Temporary visa exemption policy from 1 July 2024 until 30 June 2025. Non-ordinary passports Holders of diplomatic and official / service passports of the following countries do not require a visa to enter Myanmar for stays up to the duration listed below: D - Diplomatic passports only. 1 - 90 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stateless Nation
A stateless nation is an ethnicity, ethnic group or nation that does not possess its own sovereign state.''Dictionary Of Public Administration'', U.C. Mandal, Sarup & Sons 2007, 505 p. Use of the term implies that such ethnic groups have the right to self-determination, to establish an independent nation-state with its own government. Members of stateless nations may be citizens of the country in which they live, or they may be denied citizenship by that country. Stateless nations are usually not represented in international sports or in international organisations such as the United Nations. Nations without a state are classified as Fourth World, fourth-world nations. Some stateless nations have a history of Sovereignty, statehood, while some were always stateless. History The term was coined in 1983 by political scientist Jacques Leruez in his book ''L'Écosse, une nation sans État'' about the position of Scotland within the United Kingdom. It was later adopted and popularized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Bangladesh
The government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh () is the central government of Bangladesh. The government was constituted by the Constitution of Bangladesh comprising the executive (the president, prime minister and cabinet), the legislature (the Jatiya Sangsad), and the judiciary (the Supreme Court). Bangladesh is a unitary state and the central government has the authority to govern over the entirety of the nation. The seat of the government is located in Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh. The executive government is led by the prime minister, who selects all the remaining ministers. The prime minister and the other most senior ministers belong to the supreme decision-making committee, known as the Cabinet. After the resignation of Sheikh Hasina in August 2024, the current interim government is led by Dr. Muhammad Yunus as chief adviser. Head of state The president serves as the head of state, primarily fulfilling ceremonial duties, while the prime m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south along with the Riau Islands in Indonesia, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor along with the State of Johor in Malaysia to the north. In its early history, Singapore was a maritime emporium known as '' Temasek''; subsequently, it was part of a major constituent part of several successive thalassocratic empires. Its contemporary era began in 1819, when Stamford Raffles established Singapore as an entrepôt trading post of the British Empire. In 1867, Singapore came under the direct control of Britain as part of the Straits Settlements. During World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British newspaper published weekly in printed magazine format and daily on Electronic publishing, digital platforms. It publishes stories on topics that include economics, business, geopolitics, technology and culture. Mostly written and edited in London, it has other editorial offices in the United States and in major cities in continental Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. The newspaper has a prominent focus on data journalism and interpretive analysis over News media, original reporting, to both criticism and acclaim. Founded in 1843, ''The Economist'' was first circulated by Scottish economist James Wilson (businessman), James Wilson to muster support for abolishing the British Corn Laws (1815–1846), a system of import tariffs. Over time, the newspaper's coverage expanded further into political economy and eventually began running articles on current events, finance, commerce, and British politics. Throughout the mid-to-late 20th century, it greatl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
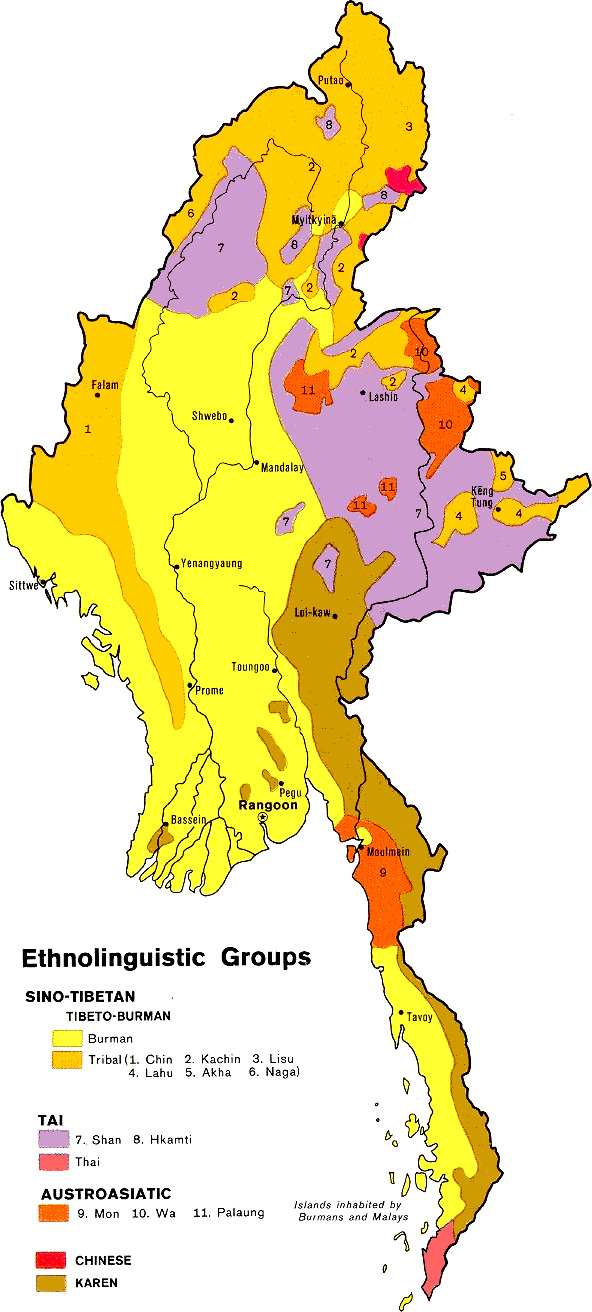
Ethnic Groups Of Myanmar
Myanmar (Burma) is an ethnically diverse nation with 135 distinct ethnic groups officially recognised by the Burmese government, which are grouped into eight "major national ethnic races" — the Bamar, Kayin, Arakanese, Shan, Mon, Chin, Kachin, and Karenni. The Bamar (Burman) comprise about 68% of the population, and the rest belonging to numerous major and minor ethnic and language groups. The "major national ethnic races" are grouped primarily according to geographic region rather than ethnolinguistic affiliation. For example, the Shan national race includes 33 ethnic groups that live in Shan State and speak languages in at least four language families. Myanmar's contemporary politics around ethnicity surround treating ethnicity as a minoritising discourse, pitting a "pan-ethnic" national identity against minority groups. Often ethnicity identities in practice are flexible — sometimes as flexible as simply changing clothes — in part due to a lack of religious or et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohingya People
The Rohingya people (; ; ) are a stateless nation, stateless Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who predominantly follow Islam from Rakhine State, Myanmar. Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an estimated 1.4 million Rohingya lived in Myanmar.UNHCR news briefing, 20 October 2020, https://www.unhcr.org/news/briefing/2020/10/5f8d7c004/unhcr-calls-solidarity-support-solutions-rohingya-refugees-ahead-urgent.html,accessed 20 December 2020 Described by journalists and news outlets as one of the most persecuted minorities in the world, the Rohingya are denied citizenship under the Myanmar nationality law, 1982 Myanmar nationality law. There are also restrictions on their freedom of movement, access to state education and civil service jobs. The legal conditions faced by the Rohingya in Myanmar have been compared to apartheidIbrahim, Azeem (fellow at Mansfield College, Oxford, and 2009 Yale World Fellow"War of Words: What's in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
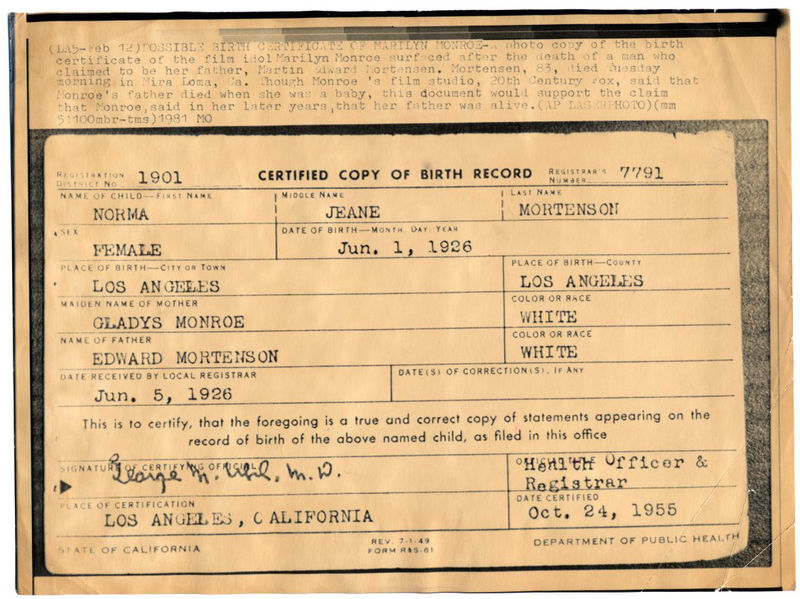
Birth Certificate
A birth certificate is a vital record that documents the Childbirth, birth of a person. The term "birth certificate" can refer to either the original document certifying the circumstances of the birth or to a certified copy of or representation of the ensuing registration of that birth. Depending on the jurisdiction, a record of birth might or might not contain verification of the event by a healthcare professional such as a midwife or doctor. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 17, an integral part of the Sustainable Development Goals, 2030 Agenda, has a target to increase the timely availability of data regarding age, gender, race, ethnicity, and other relevant characteristics which documents like a birth certificate have the capacity to provide. History and contemporary times The documentation of births is a practice widely held throughout human civilization. The original purpose of vital statistics was for tax purposes and for the determination of available mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |