|
Multidrug Efflux Pumps
Multidrug resistance pumps (MDR pumps) also known Multidrug efflux pumps are a type of efflux pump and P-glycoprotein. MDR pumps in the cell membrane extrudes many foreign substances out of the cells and some pumps can have a broad specificity. MDR pumps exist in animals, fungi, and bacteria and likely evolved as a defense mechanism against harmful substances. There are seven families of MDRs and are grouped by homology, energy source, and overall structure. There are five major classes of efflux pumps in bacteria: the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily, the resistance nodulation division (RND) superfamily, the major facilitator superfamily (MFS), the small multidrug resistance (SMR) superfamily, and the multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family. There are also two minor classes: the proteobacterial antimicrobial compound efflux (PACE) family, and the p-aminobenzoyl-glutamate transporter (AbgT) family. The ABC superfamily uses ATP as an energy source for export whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal and parasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
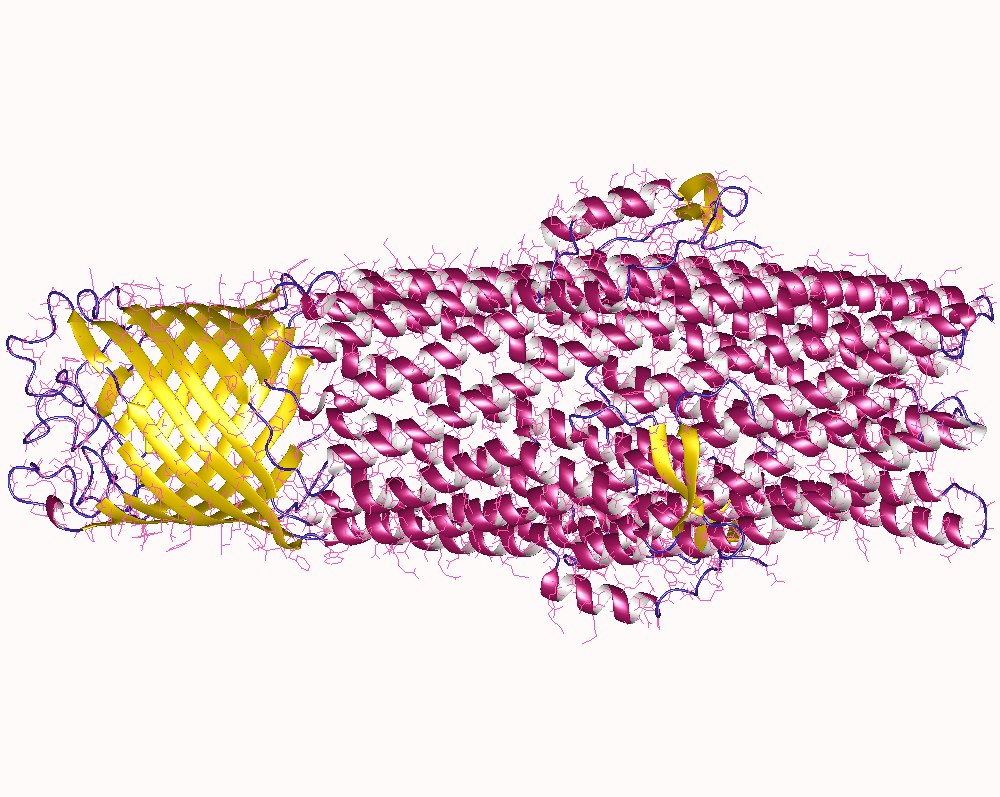
Efflux (microbiology)
An efflux pump is an Active transport, active transporter in cells that moves out unwanted material. Efflux pumps are an important component in bacteria, particularly in their ability to remove antibiotics. The efflux process can also involve the movement of heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites, and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that encode efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species, the most concerning being antibiotic resistance, as microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media. Efflux systems function via an energy-dependent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein 1 (permeability glycoprotein, abbreviated as P-gp or Pgp) also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) or cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243) is an important protein of the cell membrane that pumps many foreign substances out of cells. More formally, it is an ATP-dependent efflux pump with broad substrate specificity. It exists in animals, fungi, and bacteria, and it likely evolved as a defense mechanism against harmful substances. P-gp is extensively distributed and expressed in the intestinal epithelium where it pumps xenobiotics (such as toxins or drugs) back into the intestinal lumen, in liver cells where it pumps them into bile ducts, in the cells of the proximal tubule of the kidney where it pumps them into urinary filtrate (in the proximal tubule), and in the capillary endothelial cells composing the blood–brain barrier and blood–testis barrier, where it pumps them back into the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), Parasitic disease, parasites (antiparasitic resistance), and fungi (antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide. Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes. Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options. Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and increased selective pressure from Antibiotic misuse, antibiotic overuse, both in medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Metabolite
Secondary metabolites, also called ''specialised metabolites'', ''secondary products'', or ''natural products'', are organic compounds produced by any lifeform, e.g. bacteria, archaea, fungi, animals, or plants, which are not directly involved in the normal cell growth, growth, Biological development, development, or reproduction of the organism. Instead, they generally mediate ecological biological interaction, interactions, which may produce a Natural selection, selective advantage for the organism by increasing its survivability or fecundity. Specific secondary metabolites are often restricted to a narrow set of species within a phylogenetic group. Secondary metabolites often play an important role in plant defense against herbivory and other interspecies defenses. Humans use secondary metabolites as medicines, flavourings, pigments, and recreational drugs. The term secondary metabolite was first coined by Albrecht Kossel, the 1910 Nobel Prize laureate for medicine and physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Molecule
In molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs are small molecules; the terms are equivalent in the literature. Larger structures such as nucleic acids and proteins, and many polysaccharides are not small molecules, although their constituent monomers (ribo- or deoxyribonucleotides, amino acids, and monosaccharides, respectively) are often considered small molecules. Small molecules may be used as research tools to probe biological function as well as leads in the development of new therapeutic agents. Some can inhibit a specific function of a protein or disrupt protein–protein interactions. Pharmacology usually restricts the term "small molecule" to molecules that bind specific biological macromolecules and act as an effector, altering the activity or function of the target. Small molecules can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Families
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. Sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence) is one of the most common indicators of homology, or common evolutionary ancestry. Some frameworks for evaluating the significance of similarity between sequences use sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein families. Families are sometimes grouped together into larger clades called superfamilies based on stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |