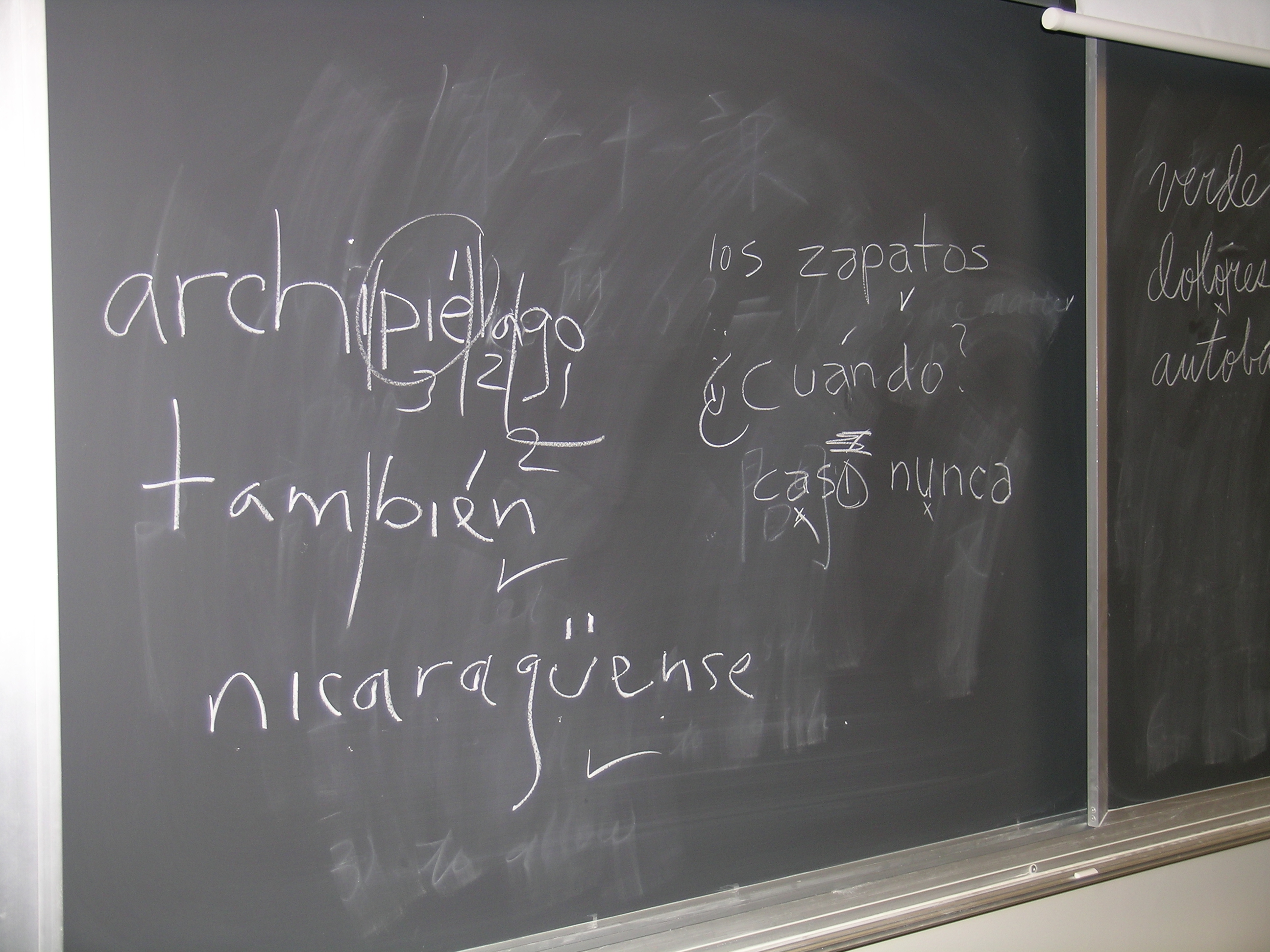|
Multi-competence
Multi-competence is a concept in second language acquisition formulated by Vivian Cook that refers to the knowledge of more than one language in one person's mind.. From the multicompetence perspective, the different languages a person speaks are seen as one connected system, rather than each language being a separate system. People who speak a second language are seen as unique multilingual individuals, rather than people who have merely attached another language to their repertoire. The concept has been backed up by studies showing how the different languages a person learns affect each other. The phenomenon of language transfer, or the first language affecting the second, has long been known. More recent research has also shown that the second language also affects the first in various subtle ways. There is also evidence that people who learn other languages gain general cognitive benefits. Under multi-competence, the second language speaker is seen as more than the sum of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivian Cook (academic)
Prof. Vivian James Cook (13 June 1940 – 10 December 2021) was a British linguist who was Emeritus Professor of Applied Linguistics at Newcastle University. He was known for his work on second-language acquisition and second-language teaching, and for writing textbooks and popular books about linguistics. He worked on a number of topics such as bilingualism, EFL ( English as a foreign language), first-language acquisition, second-language teaching, linguistics, and the English writing system. He published more than 20 books and 100 papers. He was founder and first President of the European Second Language Association (EuroSLA), and co-founder of the Oxford University Press journal '' Writing Systems Research''. He died in December 2021 at the age of 81 and was survived by his wife Pam. Early and personal life Cook's interest in second languages began in childhood when he was sent to a Swiss sanatorium to medicate his asthma, where he met speakers of French, It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Language Acquisition
Second-language acquisition (SLA), sometimes called second-language learning—otherwise referred to as L2 (language 2) acquisition, is the process of learning a language other than one's native language (L1). SLA research examines how learners develop their knowledge of second language, focusing on concepts like ''interlanguage'', a transitional linguistic system with its own rules that evolves as learners acquire the target language. SLA research spans cognitive, social, and linguistic perspectives. Cognitive approaches investigate memory and attention processes; sociocultural theories emphasize the role of social interaction and immersion; and linguistic studies examine the innate and learned aspects of language. Individual factors like age, motivation, and personality also influence SLA, as seen in discussions on the critical period hypothesis and learning strategies. In addition to acquisition, SLA explores language loss, or second-language attrition, and the impact of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing system, writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of Productivity (linguistics), productivity and Displacement (linguistics), displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind
The mind is that which thinks, feels, perceives, imagines, remembers, and wills. It covers the totality of mental phenomena, including both conscious processes, through which an individual is aware of external and internal circumstances, and unconscious processes, which can influence an individual without intention or awareness. The mind plays a central role in most aspects of human life, but its exact nature is disputed. Some characterizations focus on internal aspects, saying that the mind transforms information and is not directly accessible to outside observers. Others stress its relation to outward conduct, understanding mental phenomena as dispositions to engage in observable behavior. The mind–body problem is the challenge of explaining the relation between matter and mind. Traditionally, mind and matter were often thought of as distinct substances that could exist independently from one another. The dominant philosophical position since the 20th century has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Language
A second language (L2) is a language spoken in addition to one's first language (L1). A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a foreign language. A speaker's dominant language, which is the language a speaker uses most or is most comfortable with, is not necessarily the speaker's first language. For example, the Canadian census defines first language for its purposes as "What is the language that this person first learned at home in childhood and still understands?", recognizing that for some, the earliest language may be lost, a process known as language attrition. This can happen when young children start school or move to a new language environment. Second-language acquisition The distinction between acquiring and learning was made by Stephen Krashen as part of his monitor theory. According to Krashen, the ''acquisition'' of a language is a natural process; whereas ''learning'' a language is a conscious one. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Transfer
Language transfer is the application of linguistic features from one language to another by a bilingual or multilingual speaker. Language transfer may occur across both languages in the acquisition of a simultaneous bilingual. It may also occur from a mature speaker's first language (L1) to a second language (L2) they are acquiring, or from an L2 back to the L1. Language transfer (also known as L1 interference, linguistic interference, and crosslinguistic influence) is most commonly discussed in the context of English language learning and teaching, but it can occur in any situation when someone does not have a native-level command of a language, as when translating into a second language. Language transfer is also a common topic in bilingual child language acquisition as it occurs frequently in bilingual children especially when one language is dominant. Types of language transfer When the relevant unit or structure of both languages is the same, linguistic interference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Language
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period hypothesis, critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers to the language of one's ethnic group rather than the individual's actual first language. Generally, to state a language as a mother tongue, one must have full native fluency in that language. The first language of a child is part of that child's personal, social and cultural identity. Another impact of the first language is that it brings about the reflection and learning of successful social patterns of acting and speaking. Research suggests that while a non-native speaker may develop fluency in a targeted language after about two years of immersion, it can take between five and seven years for that child to be on the same working level as their native speaking counterparts. On 17 November 1999, UNESCO design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalinguistic Awareness
Metalinguistic awareness, also known as metalinguistic ability, refers to the ability to consciously reflect on the nature of language and to use metalanguage to describe it. The concept of metalinguistic awareness is helpful in explaining the execution and transfer of linguistic knowledge across languages (e.g. code-switching as well as translation among bilinguals). Metalinguistics expresses itself in ways such as: * an awareness that language has the potential to go beyond the literal meaning, to further include multiple or implied meanings, formal structures like phonemes, syntax, etc. * an awareness, therefore, of the flexibility of language through irony, sarcasm and other forms of word play * an awareness, therefore, too, that language has a structure that can be manipulated * an awareness that a word is separable from its referent (meaning resides in the mind, not in the name, i.e. Sonia is Sonia, and I will be the same person even if somebody calls me another name) Metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlanguage
An interlanguage is an idiolect developed by a learner of a second language (L2) which preserves some features of their first language (L1) and can overgeneralize some L2 writing and speaking rules. These two characteristics give an interlanguage its unique linguistic organization. It is idiosyncratically based on the learner's experiences with L2. An interlanguage can fossilize, or cease developing, in any of its developmental stages. Several factors can shape interlanguage rules, including L1 transfer, previous learning strategies, strategies of L2 acquisition, L2 communication strategies, and the overgeneralization of L2 language patterns. Interlanguage theory posits that a dormant psychological framework in the human brain is activated with study of a second language. The theory is credited to Larry Selinker, who coined the terms ''interlanguage'' and ''fossilization''. Uriel Weinreich is credited with providing the basis for Selinker's research. Selinker noted in 1972 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Period Hypothesis
The critical period hypothesis is a hypothesis within the field of linguistics and second language acquisition that claims a person can only achieve native-like fluency in a language before a certain age. It is the subject of a long-standing debate in linguistics. and language acquisition over the extent to which the ability to acquire language is biologically linked to developmental stages of the brain. The critical period hypothesis was first proposed by Montreal neurologist Wilder Penfield and co-author Lamar Roberts in their 1959 book ''Speech and Brain Mechanisms'', and was popularized by Eric Lenneberg in 1967 with ''Biological Foundations of Language.'' The critical period hypothesis states that the first few years of life is the crucial time in which an individual can acquire a first language if presented with adequate stimuli, and that first-language acquisition relies on neuroplasticity of the brain. If language input does not occur until after this time, the individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Transfer
Language transfer is the application of linguistic features from one language to another by a bilingual or multilingual speaker. Language transfer may occur across both languages in the acquisition of a simultaneous bilingual. It may also occur from a mature speaker's first language (L1) to a second language (L2) they are acquiring, or from an L2 back to the L1. Language transfer (also known as L1 interference, linguistic interference, and crosslinguistic influence) is most commonly discussed in the context of English language learning and teaching, but it can occur in any situation when someone does not have a native-level command of a language, as when translating into a second language. Language transfer is also a common topic in bilingual child language acquisition as it occurs frequently in bilingual children especially when one language is dominant. Types of language transfer When the relevant unit or structure of both languages is the same, linguistic interference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |