|
Mount Shadow
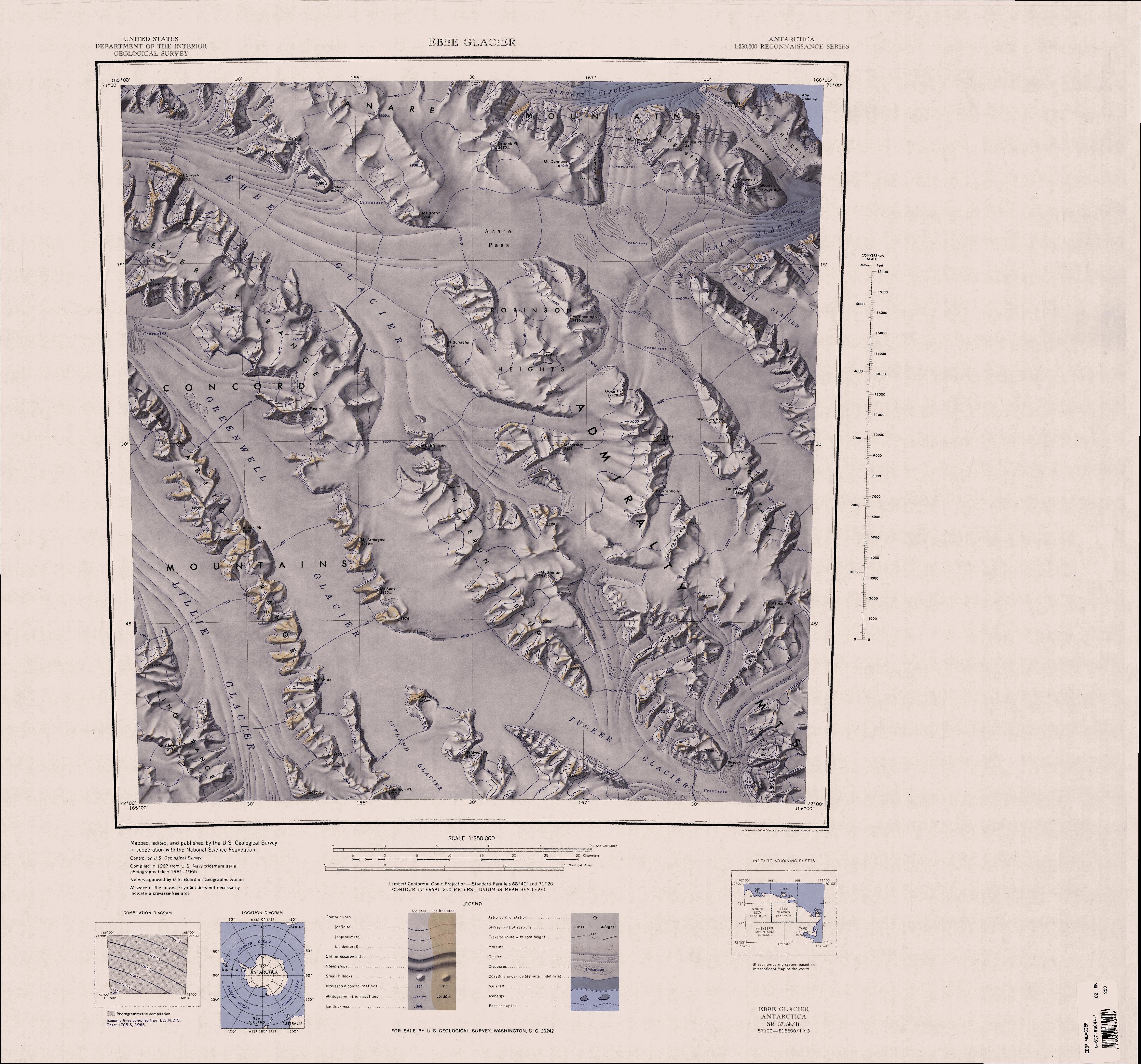
The McGregor Range () is a mountain range long in the south-central Admiralty Mountains, Antarctica. The range is circumscribed by the flow of the Tucker Glacier, Leander Glacier, Fitch Glacier and Man-o-War Glacier. Exploration and naming The McGregor Range was partially mapped by the NZGSAE, 1957–58. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy aerial photography, 1960–63. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Cdr. Ronald K. McGregor, United States Navy, leader of Antarctic Support Activities at McMurdo Station, winter party 1962. Location The McGregor Range extends north–south to the west of Fitch Glacier, which runs south to join Man-o-War Glacier, which in turn runs southwest to join Tucker Glacier. On its east the range is bounded by Leander Glacier, which runs along its north and west sides to join Tucker Glacier. Mount Brazil is in the south of the range. Features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty Mountains
The Admiralty Mountains (alternatively Admiralty Range) is a large group of high mountains and individually named ranges and ridges in northeastern Victoria Land, Antarctica. This mountain group is bounded by the sea (Ross Sea and Southern Ocean), and by the Dennistoun Glacier, Ebbe Glacier, and Tucker Glacier. Discovery and naming The Admiralty Mountains were discovered in January 1841 by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, who named them for the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty under whose orders he served. Location The Admiralty Mountains lie to the east of the Concord Mountains and the Victory Mountains, separated from them by the Ebbe Glacier in the north and the Tucker Glacier further south, which flows into the Ross Sea. They are to the south of the Anare Mountains, separated from them by the Anare Pass and the Dennistoun Glacier, which flow east to the Southern Ocean. To their east they are bounded by the Southern Ocean, Robertson Bay, the Adare Peninsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tucker Glacier
Tucker Glacier () is a major valley glacier of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about long, flowing southeast between the Admiralty Mountains and the Victory Mountains to the Ross Sea. There is a snow saddle at the glacier's head, just west of Homerun Range, from which the Ebbe Glacier flows northwestward. Exploration and naming Explored by New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1957–58, and named by them after Tucker Inlet, the ice-filled coastal indentation at the mouth of this glacier named by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841. Geography The upper reaches of the Tucker Glacier south of the Homerun Range saddle with the Greenwell Glacier and Jutland Glacier, in the Lillie Glacier basin. The Tucker Glacier is fed by the Rastorfer Glacier from the left (north) and then by the Leander Glacier after it has been joined by the Church Glacier. South of the McGregor Range the Man-O-War Glacier enters from the northeast, combined with the Freimanis Glacier from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,500 residents, though the population fluctuates seasonally; during the antarctic night, there are fewer than two hundred people. It serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. Personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station usually first pass through McMurdo, either by flight or by the McMurdo to South Pole Traverse; it is a hub for activities and science projects in Antarctica. McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott, and Palmer are the three non-seasonal United States stations on the continent, though by the Antarctic Treaty System the bases are not a legal claim (though the right is not forfeited); they are dedicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition
The New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) describes a series of scientific explorations of the continent Antarctica. The expeditions were notably active throughout the 1950s and 1960s. Features named by the expeditions 1957–1958 expedition The 1957–1958 expedition went to the Ross Dependency and named the Borchgrevink Glacier. Other features named include: * Carter Ridge * Felsite Island * Halfway Nunatak * Hedgehog Island * Moraine Ridge 1958–1959 expedition * Cadwalader Beach * Cape Hodgson * Carter Ridge * Isolation Point * Mountaineer Range * Mount Aurora * Mount Hayward * Mount Henderson (White Island) * Mount Bird. 1960–1961 expedition * Deverall Island * Lonewolf Nunataks 1961–1962 expedition * Aurora Heights * The Boil * Ford Spur * Graphite Peak * Half Century Nunatak * Half Dome Nunatak * Hump Passage * Last Cache Nunatak * Lookout Dome * Montgomerie Glacier * Mount Fyfe * Mount Macdonald * Sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |