|
Mount Pew
Mount Francis () is a massive, ridgelike mountain, high, that overlooks Tucker Glacier from the north, standing between Tyler Glacier and Staircase Glacier in the Admiralty Mountains of Antarctica. Exploration and name Mount Francis was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–62. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Henry S. Francis, Jr., Director of the International Cooperation and Information Program at the Office of Antarctic Programs, National Science Foundation. Francis wintered-over at Little America V Station in 1958 and made visits to Antarctica in other seasons. Location Mount Francis is in the center of a linear group of mountains and glaciers on the east side of the lower Tucker Glacier. Freimanis Glacier runs west to the north of the group. Features are, from northwest to southeast, Mount Greene, Mount Lozen, Tocci Glacier, Mount Gleaton, Helman Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
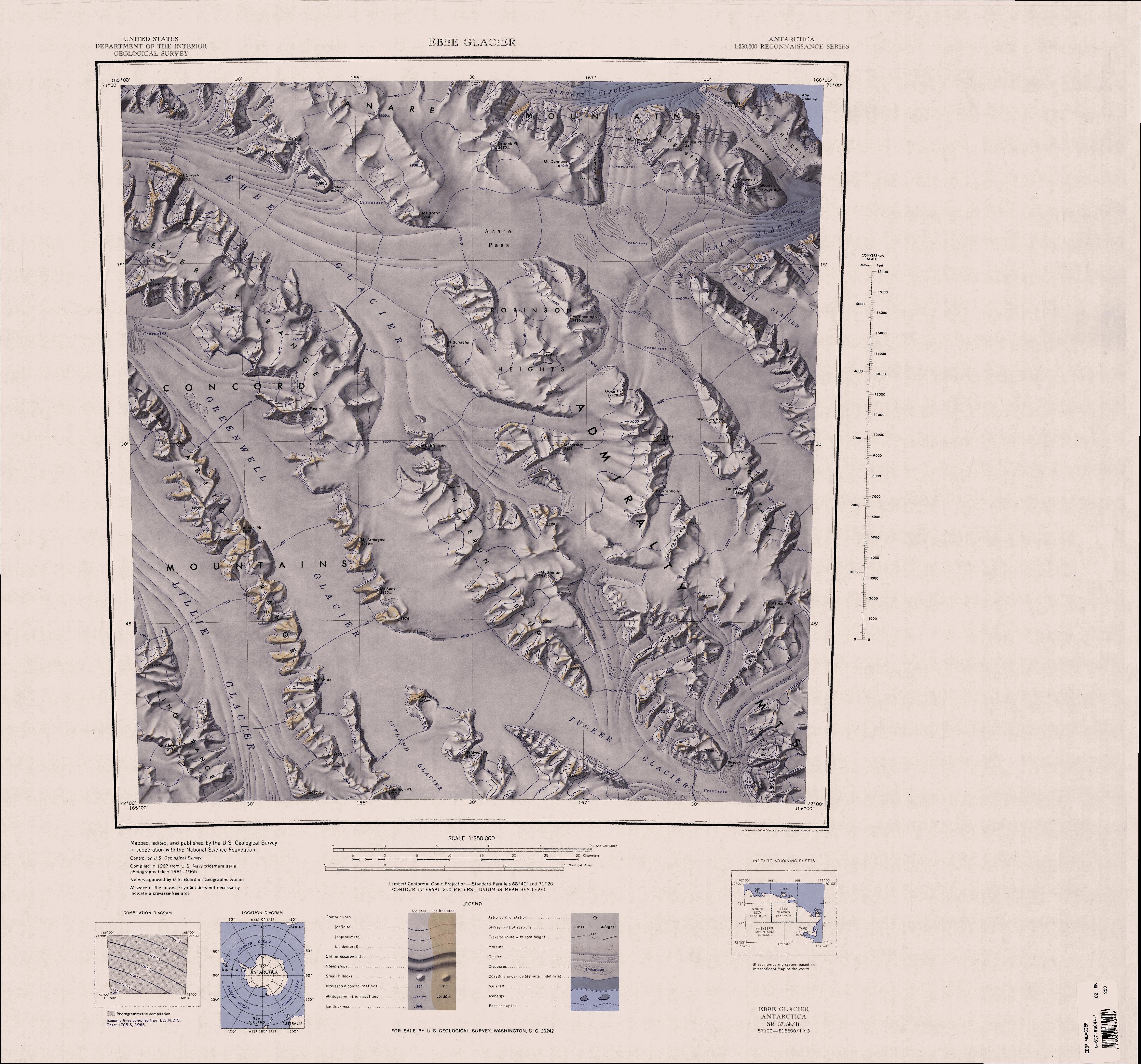
Admiralty Mountains
The Admiralty Mountains (alternatively Admiralty Range) is a large group of high mountains and individually named ranges and ridges in northeastern Victoria Land, Antarctica. This mountain group is bounded by the sea (Ross Sea and Southern Ocean), and by the Dennistoun Glacier, Ebbe Glacier, and Tucker Glacier. Discovery and naming The Admiralty Mountains were discovered in January 1841 by Captain James Clark Ross, Royal Navy, who named them for the Lords Commissioners of the Admiralty under whose orders he served. Location The Admiralty Mountains lie to the east of the Concord Mountains and the Victory Mountains, separated from them by the Ebbe Glacier in the north and the Tucker Glacier further south, which flows into the Ross Sea. They are to the south of the Anare Mountains, separated from them by the Anare Pass and the Dennistoun Glacier, which flow east to the Southern Ocean. To their east they are bounded by the Southern Ocean, Robertson Bay, the Adare Peninsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C72189s1 Ant
C7, C07 or C-7 may refer to: Vehicles (including military) * C-7 Caribou, a military transport aircraft * AEG C.VII, a World War I German armed reconnaissance aircraft * AGO C.VII, a World War I German reconnaissance aircraft * Albatros C.VII, a World War I German military reconnaissance aircraft * C-7, a United States Navy C class blimp and the first airship inflated with helium * Chevrolet Corvette (C7), the seventh generation of a sports car made by General Motors * Fokker C.VII, a 1928 Dutch reconnaissance seaplane * HMS ''C7'', a British Royal Navy C-class submarine * Sauber C7, a 1983 Group C prototype race car * USS ''Cincinnati'' (C-7), a United States Navy protected cruiser Science * Caldwell 7 (NGC 2403), a spiral galaxy in Camelopardalis Technology * Nokia C7-00, a touch screen mobile from Nokia * VIA C7, an IA-32 central processing unit by VIA Technologies * C7, an incandescent light bulb of the size typically used in nightlights and Christmas lighting usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition
The New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) describes a series of scientific explorations of the continent Antarctica. The expeditions were notably active throughout the 1950s and 1960s. Features named by the expeditions 1957–1958 expedition The 1957–1958 expedition went to the Ross Dependency and named the Borchgrevink Glacier. Other features named include: * Carter Ridge * Felsite Island * Halfway Nunatak * Hedgehog Island * Moraine Ridge 1958–1959 expedition * Cadwalader Beach * Cape Hodgson * Carter Ridge * Isolation Point * Mountaineer Range * Mount Aurora * Mount Hayward * Mount Henderson (White Island) * Mount Bird. 1960–1961 expedition * Deverall Island * Lonewolf Nunataks 1961–1962 expedition * Aurora Heights * The Boil * Ford Spur * Graphite Peak * Half Century Nunatak * Half Dome Nunatak * Hump Passage * Last Cache Nunatak * Lookout Dome * Montgomerie Glacier * Mount Fyfe * Mount Macdonald * Sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
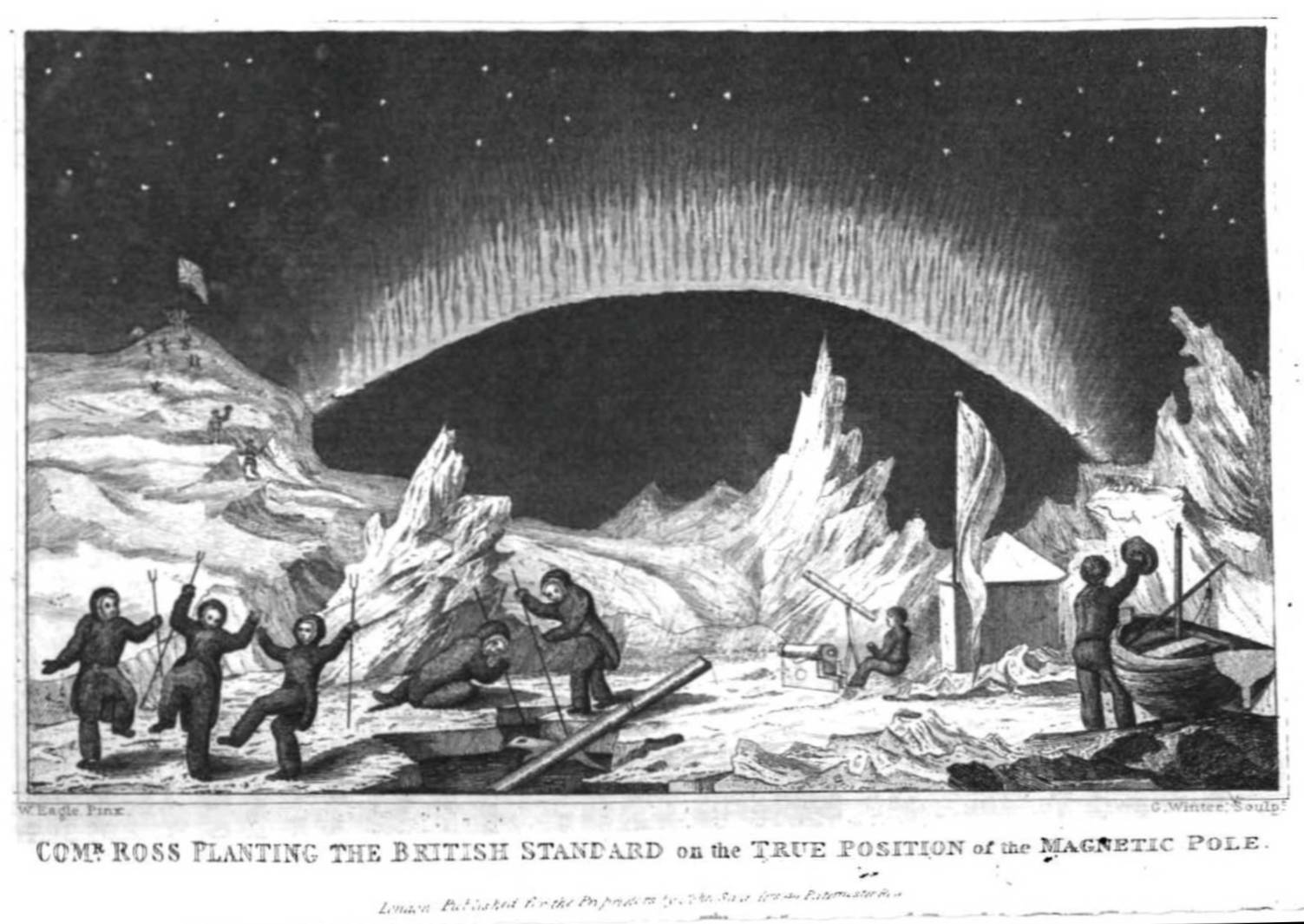
James Clark Ross
Sir James Clark Ross (15 April 1800 – 3 April 1862) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer of both the northern and southern polar regions. In the Arctic, he participated in two expeditions led by his uncle, Sir John Ross, John Ross, and in four led by Sir William Parry, William Edward Parry: in the Antarctic, he led Ross expedition, his own expedition from 1839 to 1843. Biography Early life Ross was born in London, the son of George Ross and nephew of Sir John Ross, John Ross, under whom he entered the Royal Navy on 5 April 1812. Ross was an active participant in the Napoleonic Wars, being present at an action where HMS Briseis (1808), HMS ''Briseis'', commanded by his uncle, captured ''Le Petit Poucet'' (a French privateer) on 9 October 1812. Ross then served successively with his uncle on HMS Acteon (1805), HMS ''Actaeon'' and HMS Driver (1840), HMS ''Driver''. Arctic exploration Ross participated in John's unsuccessful first Arctic voyage in search o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towles Glacier
Tucker Glacier () is a major valley glacier of Victoria Land, Antarctica, about long, flowing southeast between the Admiralty Mountains and the Victory Mountains to the Ross Sea. There is a snow saddle at the glacier's head, just west of Homerun Range, from which the Ebbe Glacier flows northwestward. Exploration and naming Explored by New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE), 1957–58, and named by them after Tucker Inlet, the ice-filled coastal indentation at the mouth of this glacier named by Captain James Clark Ross in 1841. Geography The upper reaches of the Tucker Glacier south of the Homerun Range saddle with the Greenwell Glacier and Jutland Glacier, in the Lillie Glacier basin. The Tucker Glacier is fed by the Rastorfer Glacier from the left (north) and then by the Leander Glacier after it has been joined by the Church Glacier. South of the McGregor Range the Man-O-War Glacier enters from the northeast, combined with the Freimanis Glacier from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little America V Station
Little America was a series of Antarctic exploration bases from 1929 to 1958, located on the Ross Ice Shelf, south of the Bay of Whales. They were built on ice that is moving very slowly, the relative location on the ice sheet, has moved and eventually breaks off into an iceberg. The geographic location has new ice that has shifted to this location, and is technically over the open water. The coordinates are approximate. Little America I The first base in the series was established in January 1929 by Richard Byrd, and was abandoned in 1930. This was where the film ''With Byrd at the South Pole'' (1930), about Byrd's trip to the South Pole, was filmed. Little America II Little America II was established in 1934, some above the site of the original base, with some of the original base accessed via tunnel. This base was briefly set adrift in 1934, but the iceberg fused to the main glacier. During the 1934–1935 expedition, many souvenir letters were sent from Little Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Science Foundation
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is an Independent agencies of the United States government#Examples of independent agencies, independent agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $9.9 billion (fiscal year 2023), the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the List of American institutions of higher education, United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing. NSF's director and deputy director are appointed by the president of the United States and Advice and consent, confirmed by the United States Senate, whereas the 24 president-appointed members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |