|
Mount Aniakchak
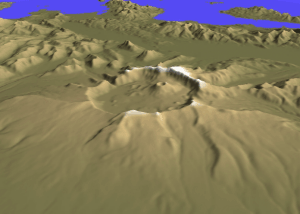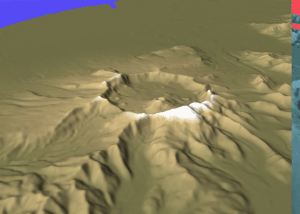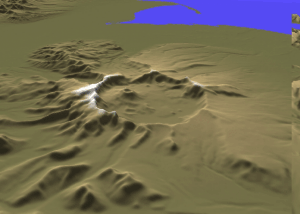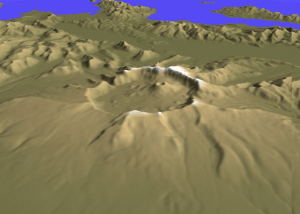
Mount Aniakchak () is a volcano on the western Alaska Peninsula. Part of the Aleutian Volcanic Arc, it was formed by the subduction of the oceanic Pacific Plate under the North American Plate. Aniakchak is a wide caldera with a break to the northeast. The caldera contains Surprise Lake and many volcanic cones, maars and craters, including Vent Mountain. The volcano has erupted mainly calc-alkaline rocks ranging from basalt to rhyolite. Activity began in the Pleistocene. Aniakchak is one of the most active volcanoes in Alaska and underwent several significant caldera-forming eruptions. The largest eruption is known as Aniakchak II and took place in 1628/1627 BCE. During this eruption, pyroclastic flows swept all the flanks of the volcano and caused a tsunami in Bristol Bay. Tephra from the eruption rained down over Alaska, with noticeable deposits being left as far as northern Europe. The eruption depopulated the central Alaska Peninsula and caused cultural changes in Alaska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniakchak National Monument And Preserve
Aniakchak National Monument and Preserve is a U.S. National Monument and National Preserve, consisting of the region around the Aniakchak volcano on the Aleutian Range of south-western Alaska. It has erupted at least 40 times over the last 10,000 years. The monument is one of the least-visited places in the National Park System due to its remote location and difficult weather. The area was proclaimed a National Monument on December 1, 1978, and established as a National Monument and Preserve on December 2, 1980. The National Monument encompasses and the preserve . Visitation to Aniakchak is the lowest of all areas of the U.S. National Park System, according to the NPS, with only 100 documented recreational visits in 2017. Most visitors fly into Surprise Lake inside Aniakchak Crater, but the frequent fog and other adverse weather conditions make landing in the lake difficult. It is also possible to fly into the nearby village of Port Heiden and proceed overland to the Aniakch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matrix (geology), groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent of granite. Its high silica content makes rhyolitic magma extremely viscosity, viscous. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been used extensively for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Heiden
Port Heiden (Alutiiq: ) is a city in Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city is 100, slightly down from 102 in 2010. Geography and climate Port Heiden is located at (56.948949, -158.655745). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which, of it is land and of it (1.28%) is water. Port Heiden has a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc''). Demographics Port Heiden first appeared on the 1880 U.S. Census as the unincorporated Aleut village of "Mashikh." Some maps erroneously placed it at the latter settlement of Port Moller instead of at Port Heiden. In 1890, it returned as "Meshik." It next reported in 1920 as Port Heiden, and again in 1930. It did not appear again until 1960, but has appeared in every subsequent census. It was formally incorporated in 1972. As of the census of 2000, there were 119 people, 41 households, and 23 families residing in the city. The population den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bering Sea
The Bering Sea ( , ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre, p=ˈbʲerʲɪnɡəvə ˈmorʲe) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and the Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelf, continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named after Vitus Bering, a Denmark, Danish-born Russia, Russian navigator, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean. The Bering Sea is separated from the Gulf of Alaska by the Alaska Peninsula. It covers over and is bordered on the east and northeast by Alaska, on the west by the Russian Far East and the Kamchatka Peninsula, on the south by the Alaska Peninsula and the Aleutian Islands and on the far north by the Bering Strait, which connects the Berin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Bay Borough
Bristol Bay Borough is a borough of the U.S. state of Alaska on Bristol Bay. As of the 2020 census the borough population was 844, down from 997 in 2010, the second-least populated borough in Alaska. The borough seat is Naknek. There are no incorporated settlements. Incorporated in 1962, Bristol Bay was the first of Alaska's boroughs. It is also among the smallest, consisting of little more than the rectangle of land around Naknek on the coast and King Salmon (which, uniquely, serves as the borough seat for the neighboring Lake and Peninsula Borough) inland. Geography The borough has a total area of , of which is land and (43.2%) is water. Adjacent boroughs and census areas * Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska (east, north and south) * Dillingham Census Area, Alaska (west) National protected area * Katmai National Park and Preserve Katmai National Park and Preserve is a List of national parks of the United States, United States national park and National preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchorage, Alaska
Anchorage, officially the Municipality of Anchorage, is the List of cities in Alaska, most populous city in the U.S. state of Alaska. With a population of 291,247 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it contains nearly 40 percent of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska, Matanuska-Susitna Borough, had a population of 398,328 in 2020, accounting for more than half the state's population. At of land area, the city is the List of cities in the United States by area, fourth-largest by area in the U.S. Anchorage is in Southcentral Alaska, at the terminus of the Cook Inlet, on a peninsula formed by the Knik Arm to the north and the Turnagain Arm to the south. First settled as a tent city near the mouth of Ship Creek, Alaska, Ship Creek in 1915 when construction on the Alaska Railroad began, Anchorage was incorporated as a city in November 1920. In September 1975, the City of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List of national parks of the United States, national parks; most National monument (United States), national monuments; and other natural, historical, and recreational properties, with various title designations. The United States Congress created the agency on August 25, 1916, through the National Park Service Organic Act. Its headquarters is in Washington, D.C., within the main headquarters of the Department of the Interior. The NPS employs about 20,000 people in units covering over in List of states and territories of the United States, all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and Territories of the United States, US territories. In 2019, the service had more than 279,000 volunteers. The agency is charged with preserving the ecological a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Volcano Observatory
The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) is a joint program of the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the Geophysical Institute of the University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAFGI), and the State of Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys (ADGGS). AVO was formed in 1988, and uses federal, state, and university resources to monitor and study Alaska's volcanology, hazardous volcanoes, to predict and record eruptive activity, and to mitigate volcanic hazards to life and property. The Observatory website allows users to monitor active volcanoes, with seismographs and webcameras that update regularly. AVO monitors more than 20 volcanoes in Cook Inlet, which is close to Alaskan population centers, and the Aleutian Arc due to the hazard that plumes of ash pose to aviation. AVO operates out of two locations. One is at the U.S. Geological Survey office on the campus of Alaska Pacific University in Anchorage. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava Dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular, mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on Earth form lava domes. The geochemistry of lava domes can vary from basalt (e.g. Semeru, 1946) to rhyolite (e.g. Chaiten, 2010) although the majority are of intermediate composition (such as Santiaguito, dacite-andesite, present day). The characteristic dome shape is attributed to high viscosity that prevents the lava from flowing very far. This high viscosity can be obtained in two ways: by high levels of silica in the magma, or by degassing of fluid magma. Since viscous basaltic and andesitic domes weather fast and easily break apart by further input of fluid lava, most of the preserved domes have high silica content and consist of rhyolite or dacite. Existence of lava domes has been suggested for some domed structures on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater Lake
A volcanic crater lake is a lake in a volcanic crater, crater that was formed by explosive eruption, explosive activity or a caldera, collapse during a types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruption. Formation Lakes in calderas fill large craters formed by the collapse of a volcano during an eruption. Lakes in maars fill medium-sized craters where an eruption deposited debris around a vent. Crater lakes form as the created depression, within the Rim (craters), crater rim, is filled by water. The water may come from Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, groundwater circulation (often Hot Spring, hydrothermal fluids in the case of volcanic craters) or melted ice. Its level rises until an equilibrium is reached between the rates of incoming and outgoing water. Sources of water loss singly or together may include evaporation, subsurface seepage, and, in places, surface leakage or overflow when the lake level reaches the lowest point on its rim. At such a saddle location, the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which Paleoecology, paleoenvironmental or Archaeology, archaeological records can be placed. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow into the bay, including the Cinder River, Cinder, Egegik River, Egegik, Igushik River, Igushik, Kvichak River, Kvichak, Meshik River, Meshik, Nushagak River, Nushagak, Naknek River, Naknek, Togiak River, Togiak, and Ugashik River, Ugashik. Upper reaches of Bristol Bay experience some of the highest tides in the world. One such reach, the Nushagak Bay near Dillingham, Alaska, Dillingham and another near Naknek, Alaska, Naknek in Kvichak Bay have tidal extremes in excess of 10 m (30 ft), ranking them — and the area — as eighth highest in the world. Coupled with the extreme number of shoals, sandbars, and shallows, it makes navigation troublesome, especially during the area's frequently strong winds. As the shallowest pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |