|
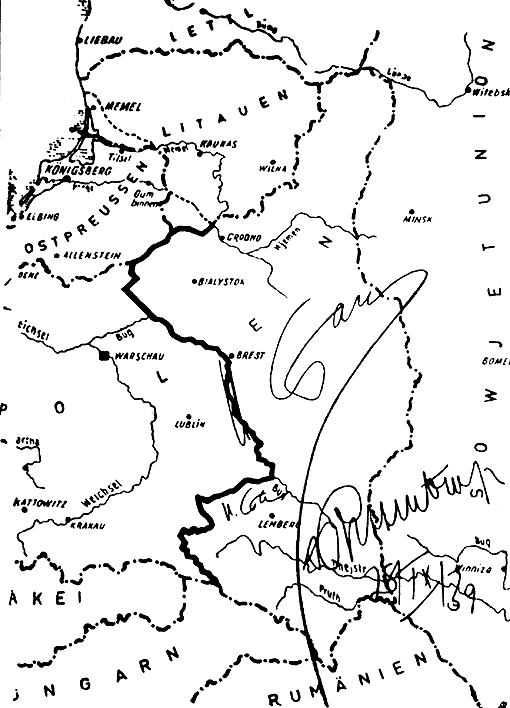
Morzewo, Greater Poland Voivodeship
Morzewo is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kaczory, within Piła County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately south of Kaczory, south-east of Piła, and north of the regional capital Poznań. The village has a population of 620. History Morzewo was a private village of Polish nobility, administratively located in the Nakło County in the Kalisz Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province of the Kingdom of Poland. During the German occupation of Poland ( World War II), on November 7, 1939, the German police carried out a massacre of 41 Poles in the village as part of the '' Intelligenzaktion''. Among the victims were teachers, school principals, priests, policemen, local officials including mayor of the nearby town of Chodzież, merchants, craftsmen, farmers and former insurgents of the Greater Poland uprising from various nearby towns and villages. In 1943, the Germans burned the bodies of the victims in attempt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Academy Of Sciences
The Polish Academy of Sciences ( pl, Polska Akademia Nauk, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society of distinguished scholars and a network of research institutes. It was established in 1951, during the early period of the Polish People's Republic following World War II. History The Polish Academy of Sciences is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning, headquartered in Warsaw, that was established by the merger of earlier science societies, including the Polish Academy of Learning (''Polska Akademia Umiejętności'', abbreviated ''PAU''), with its seat in Kraków, and the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning (Science), which had been founded in the late 18th century. The Polish Academy of Sciences functions as a learned society acting through an elected assembly of leading scholars and research institutions. The Academy h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Piła County
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperial Germany in World War I (1914–1918), as the core element of the of territorial expansion. The most extreme form of this ideology was supported by the Nazi Party and Nazi Germany. was a leading motivation of Nazi Germany to initiate World War II, and it would continue this policy until the end of World War II.Woodruff D. Smith. The Ideological Origins of Nazi Imperialism. Oxford University Press. p. 84. Following Adolf Hitler's rise to power, became an ideological principle of Nazism and provided justification for the German territorial expansion into Central and Eastern Europe. The Nazi policy () was based on its tenets. It stipulated that Germany required a ' necessary for its survival and that most of the indigenous populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Labour Under German Rule During World War II
The use of slave and forced labour in Nazi Germany (german: Zwangsarbeit) and throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II took place on an unprecedented scale. It was a vital part of the German economic exploitation of conquered territories. It also contributed to the mass extermination of populations in occupied Europe. The Germans abducted approximately 12 million people from almost twenty European countries; about two thirds came from Central Europe and Eastern Europe.Part1 an Part 2 . Many workers died as a result of their living conditionsextreme mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion Of Poles By Nazi Germany
The Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany during World War II was a massive operation consisting of the forced resettlement of over 1.7 million Poles from the territories of German-occupied Poland, with the aim of their Germanization (see Lebensraum) between 1939 and 1944. The German Government had plans for the extensive colonisation of territories of occupied Poland, which were annexed directly into Nazi Germany in 1939. Eventually these plans grew bigger to include parts of the General Government. The region was to become a "purely German area" within 15–20 years, as explained by Adolf Hitler in March 1941. By that time the General Government was to be cleared of 15 million Polish nationals, and resettled by 4–5 million ethnic Germans. The operation was the culmination of the expulsion of Poles by Germany carried out since the 19th century, when Poland was partitioned among foreign powers including Germany. Racial policies Following the German invasion of the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Poland Uprising (1918–19)
Greater Poland Uprising (also Wielkopolska Uprising or Great Poland Uprising) may refer to a number of armed rebellions in the region of Greater Poland Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city ...: * Greater Poland Uprising (1794) * Greater Poland Uprising (1806) * Greater Poland Uprising (1846) * Greater Poland Uprising (1848) * Greater Poland Uprising (1918–1919) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chodzież
Chodzież (german: Kolmar in Posen) is a town in northwestern Poland with 17,976 inhabitants as of December 2021. Situated in the Chodzież County, Greater Poland Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Piła Voivodeship (1975–1998). Geography Chodzież is located in the northern part of Greater Poland (western Poland), in the Chodzieskie lakelands. The most important characteristics of this lakeland area are its typical postglacial landforms, forests of pines and mixed woodlands, and lakes. For this reason, the city's surroundings are known as "the Switzerland of Chodzież". Five kilometers west of Chodzież, at the edge of the Chodzieskie lakelands, Mt. Gontyniec rises 192 meters above sea level as the highest peak in a chain of moraine hills; at the same time it has the highest elevation in northern Poland. Deep valleys and ridges covered with a 100-year-old beech forest ensure diversified surroundings. Within the five square miles (13 km2) of city area, there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of National Remembrance
The Institute of National Remembrance – Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation ( pl, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej – Komisja Ścigania Zbrodni przeciwko Narodowi Polskiemu, abbreviated IPN) is a Polish state research institute in charge of education and archives with investigative and lustration powers. The IPN was established by the Polish parliament by the Act on the Institute of National Remembrance of 18 December 1998, which incorporated the earlier Main Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation of 1991. IPN itself had replaced a body on Nazi crimes established in 1945. In 2018, IPN's mission statement was amended by the controversial Amendment to the Act on the Institute of National Remembrance to include "protecting the reputation of the Republic of Poland and the Polish Nation". The IPN investigates Nazi and Communist crimes committed between 1917 and 1990, documents its findings, and disseminates them to the publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligenzaktion
The ''Intelligenzaktion'' (), or the Intelligentsia mass shootings, was a series of mass murders which was committed against the Polish intelligentsia (teachers, priests, physicians, and other prominent members of Polish society) early in the Second World War (1939–45) by Nazi Germany. The Germans conducted the operations in accordance with their plan to Germanize the western regions of occupied Poland, before their territorial annexation to the German Reich. The mass murder operations of the ''Intelligenzaktion'' resulted in the killing of 100,000 Polish people; by way of forced disappearance, the Germans imprisoned and killed select members of Polish society, identified as enemies of the Reich before the war; they were buried in mass graves which were dug in remote places. In order to facilitate the depopulation of Poland, the Germans terrorised the general populace by carrying out public, summary executions of select intellectuals and community leaders, before they effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |