|
Morocco–Romania Relations
Morocco is a member of the United Nations and belongs to the African Union, Arab League, Arab Maghreb Union (UMA), Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), the Non-Aligned Movement and the Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD). Morocco's relationships vary greatly between African, Arab, United States, United Kingdom, Australia, and Western states. Morocco has had strong ties with the West in order to gain economic and political benefits. France and Spain remain the primary trade partners, as well as the primary creditors and foreign investors in Morocco. From the total foreign investments in Morocco, the European Union invests approximately 73.5%, whereas the Arab world invests only 19.3%. As of 2009, many countries from the Persian Gulf and Maghreb regions are also becoming more involved in large-scale development projects in Morocco. Foreign relations have had a significant impact on economic and social development in Morocco. Certain evidence of foreign influence is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan II Of Morocco
Hassan II (; 9 July 1929 – 23 July 1999) was King of Morocco from 1961 until his death in 1999. A member of the Alawi dynasty, he was the eldest son of King Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V, and his second wife Princess Lalla Abla bint Tahar, Abla bint Tahar. He was named crown prince in 1957 and was the first commander-in-chief of the Royal Moroccan Armed Forces, Royal Armed Forces. He was enthroned as king in 1961 following his father's death. His reign was marked by the start of the Western Sahara conflict and the Sand War, as well as two failed coup attempts against him 1971 Moroccan coup attempt, in 1971 and 1972 Moroccan coup attempt, in 1972. Hassan's conservative approach reportedly strengthened his rule over Morocco and the Western Sahara. He was accused of Authoritarianism, authoritarian practices, as well as human rights and civil rights abuses, particularly during the Years of Lead (Morocco), Years of Lead. A Equity and Reconciliation Commission, truth c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
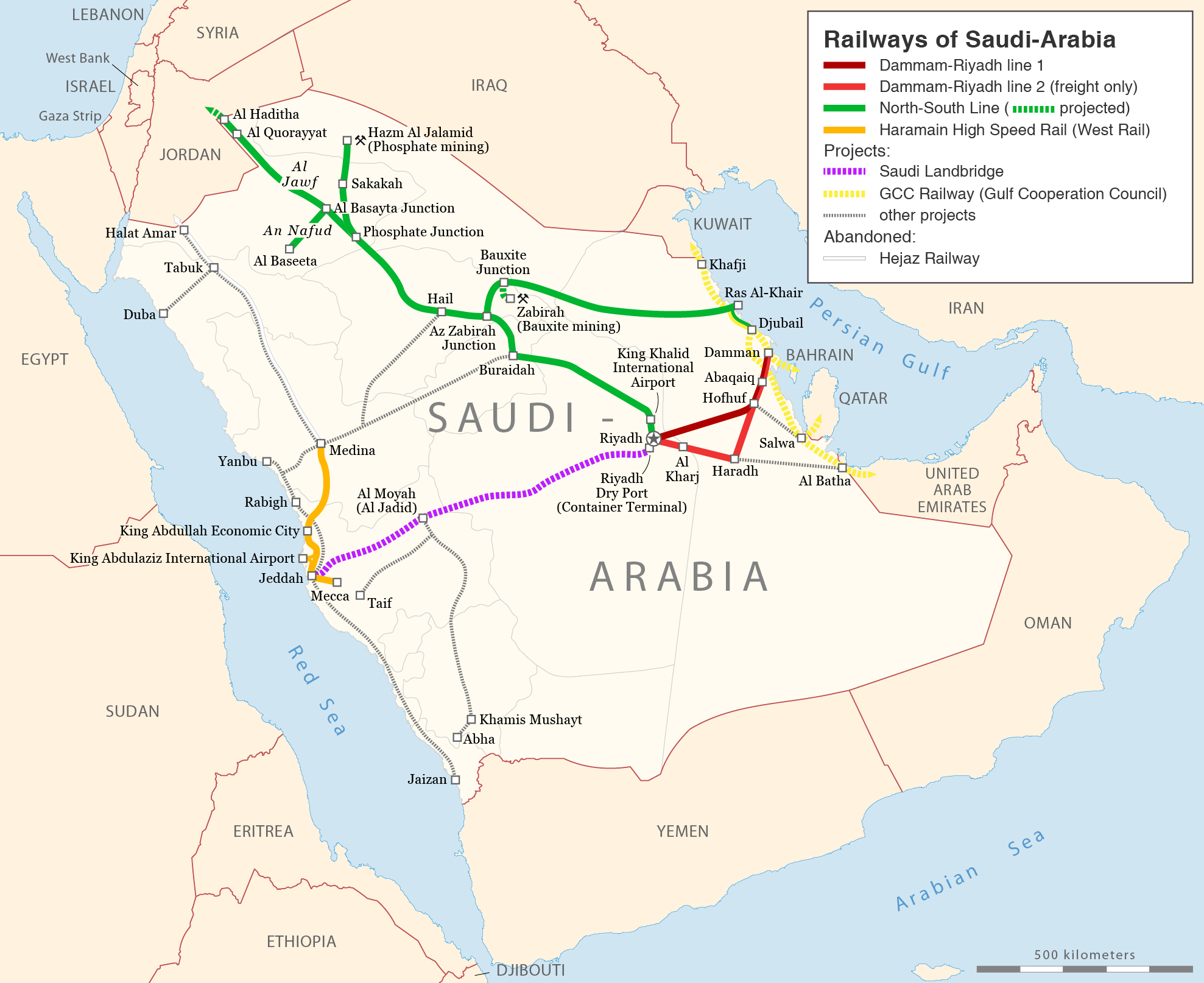
Cooperation Council For The Arab States Of The Gulf
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (), also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC; ), is a regional, intergovernmental, political, and economic union comprising Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The council's main headquarters is located in Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia. The Charter of the GCC was signed on 25 May 1981, formally establishing the institution. All current member states are monarchies, including three constitutional monarchies (Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain), two absolute monarchies (Saudi Arabia and Oman), and one federal monarchy (the United Arab Emirates, which is composed of seven member states, each of which is an absolute monarchy with its own emir). There have been discussions regarding the future membership of Jordan, Morocco, and Yemen. Iraq is the only Gulf Arab state that is not a GCC member. During the Arab Spring in 2012, Saudi Arabia proposed to transform the GCC into a "Gulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Protectorate In Morocco
The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when List of rulers of Morocco, Sultan Abd al-Hafid of Morocco, Abd al-Hafid signed the Treaty of Fez, though the French French conquest of Morocco, military occupation of Morocco had begun with the invasion of Oujda and the Bombardment of Casablanca (1907), bombardment of Casablanca in 1907. The French protectorate lasted until the dissolution of the Treaty of Fez on 2 March 1956, with the Franco-Moroccan Joint Declaration. Morocco's independence movement, described in Moroccan historiography as the Revolution of the King and the People, restored the exiled Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V but it did not end the French presence in Morocco. France preserved its influence in the country, including a right to station French troops and to have a say in Morocco's foreign policy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |