|
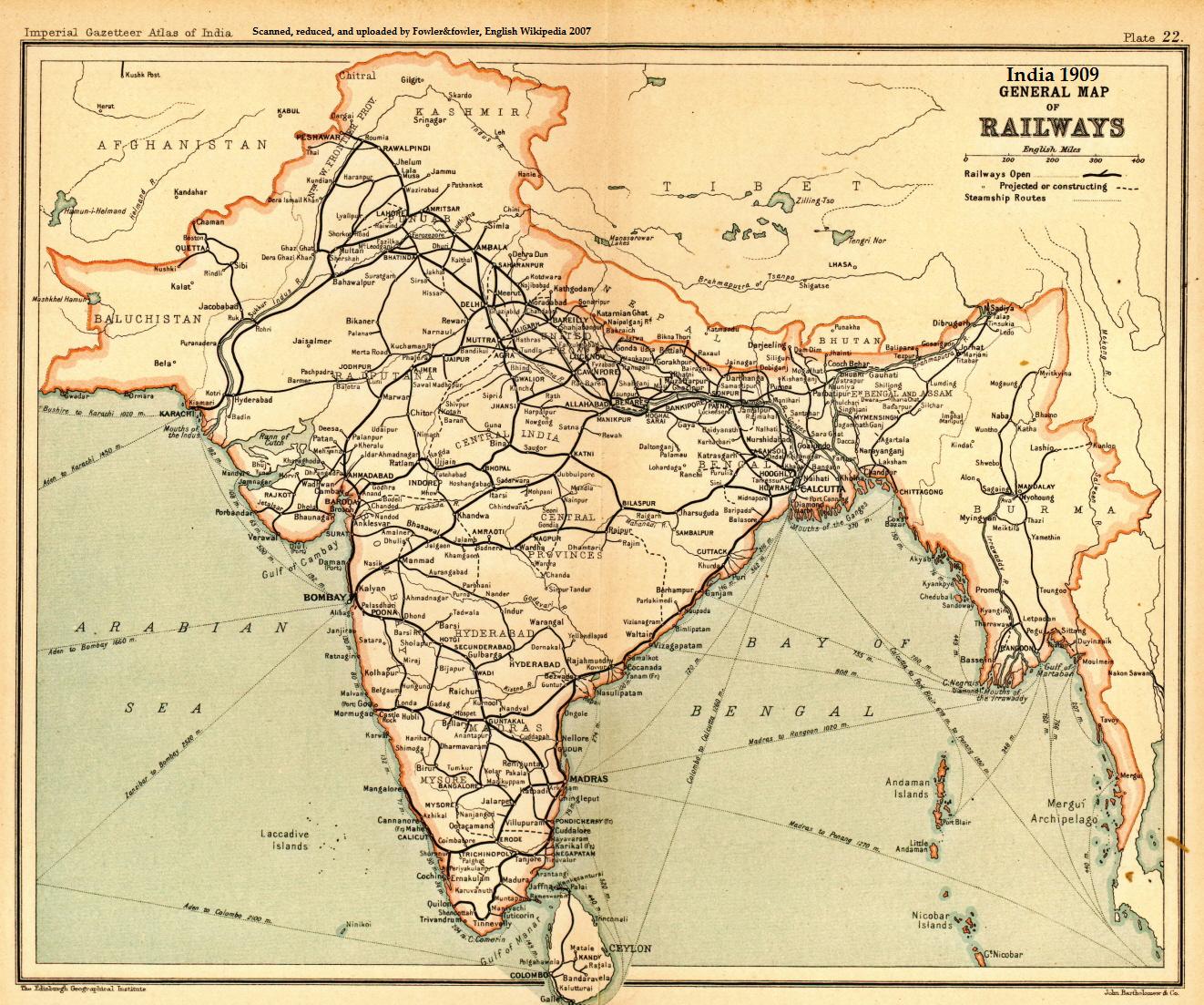
Moradabad–Ambala Line
The Moradabad–Ambala line (also known as Moradabad–Ambala main line) is a railway line connecting in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and in Haryana. The line is under the administrative jurisdiction of Northern Railway. History The Scinde, Punjab & Delhi Railway completed the –Ambala–– line in 1870 connecting Multan (now in Pakistan) with Delhi. The Varanasi–Lucknow– main line of Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway was extended to in 1886. Electrification The Ambala– sector was electrified in 1996–98 and –Roorkee in 2003–04. The Roorkee–Mordabad sector was electrified around 2005–06. The Ambala–Laksar– sector is an electrified double-line. Sheds and workshops Ambala has an outstation shed for Shakurbasti WDS-4 locos. Jagadhari has a carriage and wagon workshop and a bridge workshop. Speed limit The Ambala Cantonment to moradabad jn line is classified as a "Group D " line and can take speeds up to 110 km/ h. Passenger movement and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
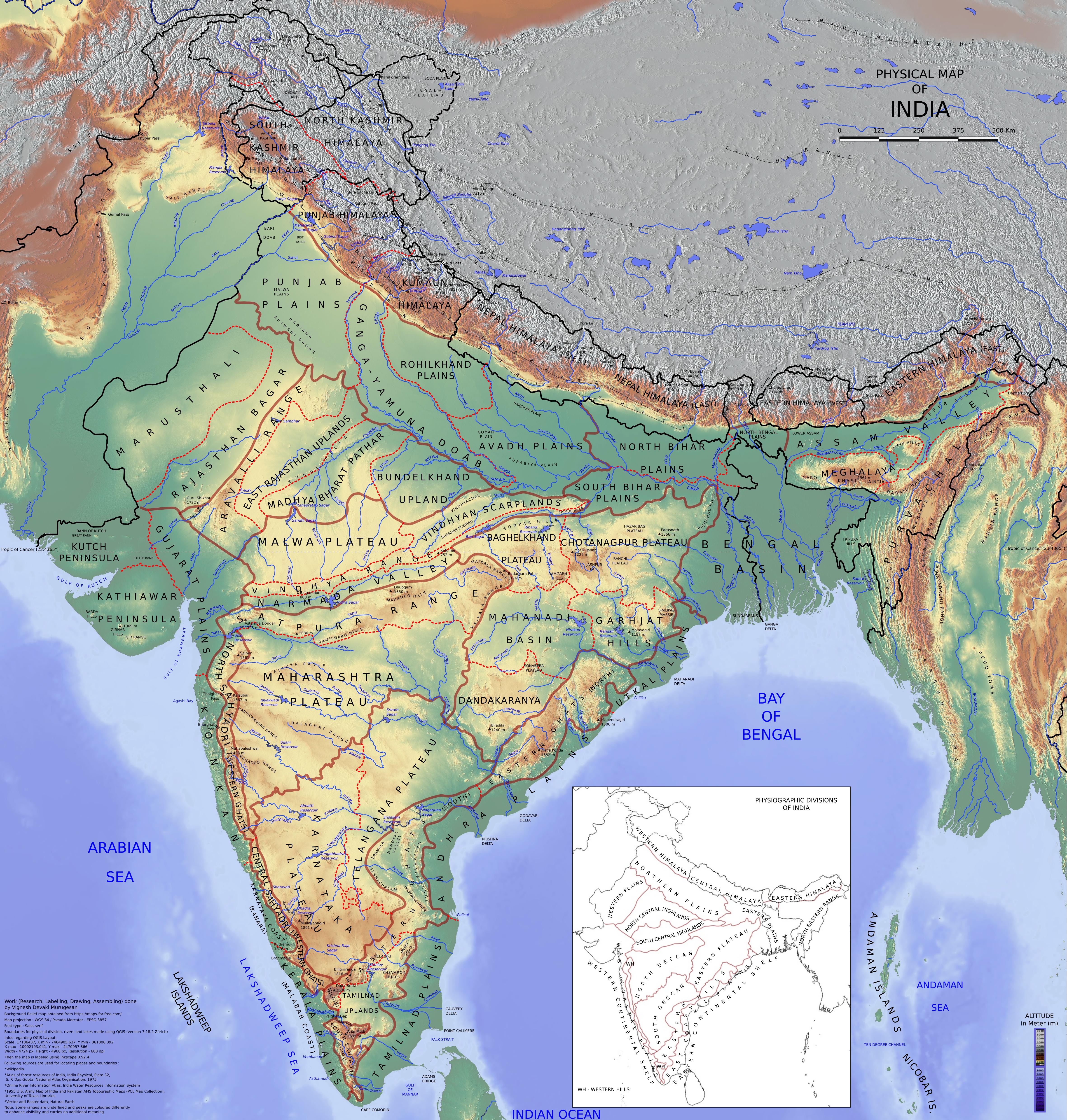
Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, eastern India, eastern Pakistan, southern Nepal, and almost all of Bangladesh. It is named after the two major river systems that drain the region–Indus River, Indus and Ganges. It stretches from the Himalayas in the north to the northern edge of the Deccan plateau in the south, and extends from North East India in the east to the Iranian border in the west. The region is home to many major cities and nearly one-seventh of the world's population. As the region was formed by the deposits of the three major rivers–Indus, Ganges and Brahmaputra, the plains consists of the world's largest expanse of uninterrupted alluvial soil, alluvium. Due to its rich water resources, it is one of the world's most densely populated and intensely farmed areas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamunanagar-Jagadhri Railway Station
Yamunanagar-Jagadhri railway station is a station on the Moradabad–Ambala line. It is located in the Indian state of Haryana. History The Scinde, Punjab & Delhi Railway completed the -long Amritsar–Ambala–Jagadhri–– line in 1870 connecting Multan (now in Pakistan) with Delhi. Electrification Ambala–Jagadhri– sector in 1996–98. Important trains There are some important trains at Jagadhri railway station * 18237/38 Chhattisgarh Express * 22687/88 Madurai–Dehradun Express * 12207/08 Kathgodam–Jammu Tawi Garib Rath Express * 12903/04 Golden Temple Mail * 12231/32 Lucknow–Chandigarh Express * 13005/06 Amritsar Mail * 14609/10 Hemkunt Express * 12053/54 Haridwar–Amritsar Jan Shatabdi Express * 14523/24 Harihar Express Carriage & Wagon Workshop, Jagadhri Carriage & Wagon Workshop, Jagadhari is in Yamunanagar district of Haryana. It is among the eight workshops operated by Northern Railways. References Jagadhri Jagadhri is a city and a municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Uttarakhand
Rail or rails may refer to: Rail transport *Rail transport and related matters *Railway track or railway lines, the running surface of a railway Arts and media Film * ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini * ''Rail'' (1967 film), a film by Geoffrey Jones for British Transport Films * ''Rail'' (2024 film), a Tamil-language film Magazines * ''Rail'' (magazine), a British rail transport periodical * ''Rails'' (magazine), a former New Zealand based rail transport periodical Other arts *The Rails, a British folk-rock band * Rail (theater) or batten, a pipe from which lighting, scenery, or curtains are hung Technology *Rails framework or Ruby on Rails, a web application framework *Rail system (firearms), a mounting system for firearm attachments *Front engine dragster *Runway alignment indicator lights, a configuration of an approach lighting system *Rule Augmented Interconnect Layout, a specification for expressing guidelines for printed circuit boards; companion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Haryana
Rail transport in the state of Haryana, India, is conducted by five rail divisions in three zones: the North Western Railway zone (the Bikaner railway division, Bikaner and Jaipur railway divisions), Northern Railway zone (the Delhi railway division, Delhi and Ambala railway divisions), and North Central Railway zone (the Agra railway division). The Diamond Quadrilateral High-speed rail in India, high-speed rail network, Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor, and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor pass through Haryana. History 19th century On 3 March 3 1859, the Allahabad-Kanpur line (North India's first passenger railway line) opened; it is now part of the Northern Railway zone. Tracks passing through Haryana were completed in 1864, when a broad gauge track from Kolkata, Calcutta to Delhi was laid. In 1866, trains started running on the East Indian Railway Company's Howrah-Delhi line. In 1870, the Scinde, Punjab & Delhi Railway completed its long Amritsar railway station, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines In Uttar Pradesh
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5 Ft 6 In Gauge Railways In India
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. Humans, and many other animals, have 5 digits on their limbs. Mathematics 5 is a Fermat prime, a Mersenne prime exponent, as well as a Fibonacci number. 5 is the first congruent number, as well as the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle, making part of the smallest Pythagorean triple ( 3, 4, 5). 5 is the first safe prime and the first good prime. 11 forms the first pair of sexy primes with 5. 5 is the second Fermat prime, of a total of five known Fermat primes. 5 is also the first of three known Wilson primes (5, 13, 563). Geometry A shape with five sides is called a pentagon. The pentagon is the first regular polygon that does not tile the plane with copies of itself. It is the largest face any of the five regular three-dimensional regular Platonic solid can have. A conic is determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay, Baroda And Central India Railway
The Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway (reporting mark BB&CI) was a company incorporated in 1855 to undertake the task of constructing railway lines between Bombay to the erstwhile Baroda State, that became the present-day Baroda (Vadodara) city in western India. BB&CI completed the work in 1864. The first suburban railway in India was started by BB&CI, operating between Virar and Bombay Backbay railway station, Bombay Backbay station (later extended to Colaba), a railway station in Bombay Backbay in April 1867. The railway was divided into two main systems, broad (5 ft. 6 in.) and Metre gauge railway, metre gauge. There was also a comparatively small mileage of gauge line worked by the BB&CI on behalf of the Indian States. In 1947 the mileage of the respective portions was stated to be: broad gauge, 1,198 miles, with a further 69 miles worked for Indian States; metre gauge, 1,879 miles, with a further 106 miles worked for Indian States; narrow-gauge, 152 miles, wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Nagpur Railway
The Bengal Nagpur Railway was one of the companies which pioneered development of the railways in eastern and central India. It was succeeded first by Eastern Railway and subsequently by South Eastern Railway. History The opening of the Mumbai–Thane line in 1853 marked the beginning of railways in India. Extension of the railways was set off throughout the country. On the north-eastern side of Mumbai, the Great Indian Peninsular Railway line was extended up to Bhusawal and then split in two. While one track led to Nagpur, the other to Jabalpur to connect with the East Indian Railway line from Allahabad to Jabalpur, thereby connecting Mumbai and Kolkata. The great famine of 1878 provided an opportunity for the construction of 150 km long meter gauge link called the Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway in 1882 connecting Nagpur with Rajnandgaon. The Bengal Nagpur Railway was formed in 1887 for the purpose of upgrading the Nagpur Chhattisgarh Line and then extending it via B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Railway Zone
The Eastern Railway (abbreviated ER) is among the 19 Indian Railways Zones and Divisions, zones of the Indian Railways. Its headquarters is at Fairley Place (Kolkata) and comprises four divisions: , , , and . Each division is headed by a Divisional Railway Manager (DRM). The name of the division denotes the name of the city where the divisional headquarters is located. Eastern Railway oversees the largest and second largest rail complexes in the country, Howrah Junction and Sealdah railway station, and also contains the highest number of A1 and A Category Stations like , , , , Kolkata railway station, Kolkata, , Barddhaman Junction railway station, Barddhaman, Rampurhat Junction, , , Jasidih Junction railway station, Jasidih, Bandel Junction railway station, Bandel and Naihati Junction railway station, Naihati. Eastern Railways operates India's oldest train, Kalka Mail. History The East Indian Railway (EIR) Company was incorporated in 1845 to connect eastern India with Delhi. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oudh And Tirhut Railway
The Oudh and Tirhut Railway was a Railway company operated in India. History On 1 January 1943, the Bengal and North Western Railway and the Rohilkund and Kumaon Railway (R&K worked) were acquired by the Government of India and they were amalgamated with the Tirhut Railway, the Mashrak-Thawe Extension Railway (BNW worked) and the Lucknow-Bareilly Railway (R&K worked) to form the Oudh and Tirhut Railway. Its headquarters was at Gorakhpur. Train no. 301UP – 302DOWN Kanpur Anwarganj-Siliguri Avadh (then Oudh)-Tirhut Mail (popularly known as A.T. Mail) was most legendary train of this zone. The Oudh and Tirhut Railway was later renamed the Oudh Tirhut Railway. On 14 April 1952, the Oudh Tirhut Railway was amalgamated with the Assam Railway and the Kanpur-Achnera section of the Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway to form North Eastern Railway, one of the 16 zones of the current Indian Railways Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise that is organised as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
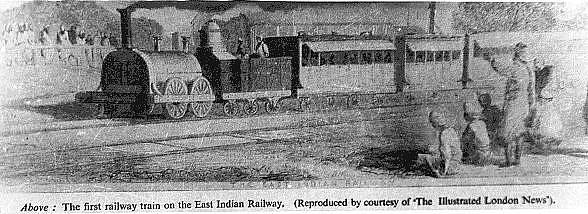
East Indian Railway Company
The East Indian Railway Company, operating as the East Indian Railway (reporting mark EIR), introduced railways to East India and North India, while the Companies such as the Great Indian Peninsula Railway, South Indian Railway, Bombay, Baroda and Central India Railway and the North-Western Railway operated in other parts of India. The company was established on 1 June 1845 in London by a deed of settlement with a capital of £4,000,000, largely raised in London. 1845–1849 The first board of directors formed in 1845 comprised thirteen members and Rowland Macdonald Stephenson became the first managing director of the company. Rowland Macdonald Stephenson (later Sir Rowland, but familiarly known as Macdonald StephensonDiaries of George Turnbull (Chief Engineer, East Indian Railway Company) held at the Centre of South Asian Studies at Cambridge University, England) and three assistants travelled from England in 1845 and ''"with diligence and discretion"'' surveyed, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |