|
Mono Lake
Mono Lake ( ) is a saline soda lake in Mono County, California, formed at least 760,000 years ago as a terminal lake in an endorheic basin. The lack of an outlet causes high levels of salts to accumulate in the lake which make its water alkaline. The desert lake has an unusually productive ecosystem based on brine shrimp, which thrive in its waters, and provides critical habitat for two million annual migratory birds that feed on the shrimp and alkali flies (''Ephydra hians''). Historically, the native Kutzadika'a people ate the alkali flies' pupae, which live in the shallow waters around the edge of the lake. When the city of Los Angeles diverted water from the freshwater streams flowing into the lake, it lowered the lake level, which imperiled the migratory birds. The Mono Lake Committee formed in response and won a legal battle that forced Los Angeles to partially replenish the lake level. Geology Mono Lake occupies part of the Mono Basin, an endorheic basin that has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mono County, California
Mono County ( ) is a county located in the east central portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,195, making it the fourth-least populous county in California. The county seat is Bridgeport. The county is located east of the Sierra Nevada between Yosemite National Park and Nevada. The only incorporated town in the county is Mammoth Lakes, which is located at the foot of Mammoth Mountain. Other locations, such as June Lake, are also famous as skiing and fishing resorts. Located in the middle of the county is Mono Lake, a vital habitat for millions of migratory and nesting birds. The lake is located in a wild natural setting, with pinnacles of tufa arising out of the salty and alkaline lake. Also located in Mono County is Bodie, the official state gold rush ghost town, which is now a California State Historic Park. History Mono County was formed in 1861 from parts of Calaveras, Fresno and Mariposa counties. A portion of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brine Shrimp
''Artemia'' is a genus of aquatic crustaceans also known as brine shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Artemiidae. The first historical record of the existence of ''Artemia'' dates back to the first half of the 10th century AD from Urmia Lake, Iran, with an example called by an Iranian geographer an "aquatic dog," although the first unambiguous record is the report and drawings made by Schlösser in 1757 of animals from Lymington, England. ''Artemia'' populations are found worldwide in inland saltwater lakes, but not in oceans. ''Artemia'' are able to avoid cohabiting with most types of predators, such as fish, by their ability to live in waters of very high salinity (up to 25%). The ability of the ''Artemia'' to produce dormant eggs, known as cysts, has led to extensive use of ''Artemia'' in aquaculture. The cysts may be stored indefinitely and hatched on demand to provide a convenient form of live feed for larval fish and crustaceans. Nauplii of the brine shrimp ''Arte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Valley Caldera
Long Valley Caldera is a depression in eastern California that is adjacent to Mammoth Mountain. The valley is one of the Earth's largest calderas, measuring about long (east-west), wide (north-south), and up to deep. Long Valley was formed 760,000 years ago when a very large eruption released hot ash that later cooled to form the Bishop tuff that is common to the area. The eruption emptied the magma chamber under the area to the point of collapse. The second phase of the eruption released pyroclastic flows that burned and buried thousands of square miles. Ash from this eruption blanketed much of the western part of what is now the United States. Geography The caldera is a giant bowl-shaped depression, approximately wide, surrounded by mountains except to the southeast. The elevation of the bottom of the bowl ranges from , being higher in the west. Near the center of the bowl, there is a resurgent dome formed by magmatic uplift. The southeastern slope from the caldera do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flows that can spread over great areas before cooling and solidifying. Flood basalts are thick sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Nevada (U
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily in Nevada. The Sierra Nevada is part of the American Cordillera, an almost continuous chain of mountain ranges that forms the western "backbone" of the Americas. The Sierra runs north-south and its width ranges from to across east–west. Notable features include General Sherman, the largest tree in the world by volume; Lake Tahoe, the largest alpine lake in North America; Mount Whitney at , the highest point in the contiguous United States; and Yosemite Valley sculpted by glaciers from one-hundred-million-year-old granite, containing high waterfalls. The Sierra is home to three national parks, twenty wilderness areas, and two national monuments. These areas include Yosemite, Sequoia, and Kings Canyon National Parks; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the Earth#Surface, surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust (geology), crust or Mantle (geology), mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock (geology), rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basin And Range
Basin and range topography is characterized by alternating parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is a result of crustal extension due to mantle upwelling, gravitational collapse, crustal thickening, or relaxation of confining stresses. The extension results in the thinning and deformation of the upper crust, causing it to fracture and create a series of long parallel normal faults. This results in block faulting, where the blocks of rock between the normal faults either subside, uplift, or tilt. The movement of these blocks results in the alternating valleys and mountains. As the crust thins, it also allows heat from the mantle to more easily melt rock and form magma, resulting in increased volcanic activity. Types of faulting Symmetrical faulting: horst and graben With crustal extension, a series of normal faults which occur in groups, form in close proximity and dipping in opposite directions. As the crust extends it fractures in series of fault planes, some block ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
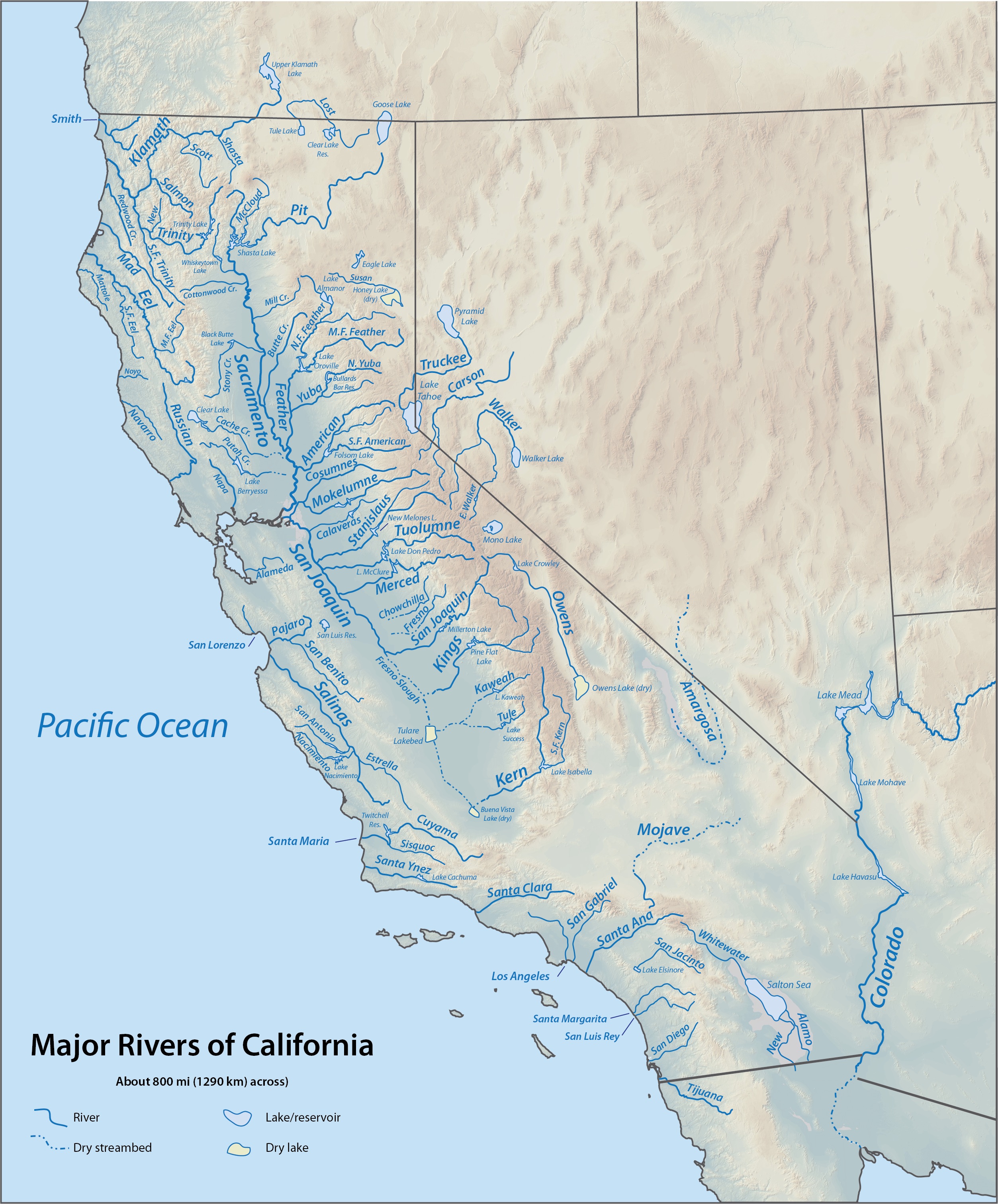
List Of Rivers Of California
This is a list of rivers in the U.S. state of California, grouped by region. Major lakes and reservoirs, if applicable, are indicated in italics. North Coast (north of Humboldt Bay) Rivers and streams between the Oregon border and Humboldt Bay that empty into the Pacific Ocean (arranged north to south; tributaries with those entering nearest the sea first). Bold indicates rivers with more detailed lists in following sections. * Smith River ( jump to tributaries) *Elk Creek *Wilson Creek *Klamath River ( jump to tributaries) * Redwood Creek ( jump to tributaries) *Little River * Mad River ( jump to tributaries) Smith River * Smith River **Rowdy Creek **Mill Creek **Myrtle Creek **South Fork Smith River ***Craigs Creek ***Coon Creek ***Rock Creek ***Gordon Creek ***Goose Creek ***Hurdygurdy Creek ***Jones Creek ***Buck Creek ***Quartz Creek ***Eightmile Creek ***Harrington Creek ***Prescott Fork Smith River ** Middle Fork Smith River ***Patrick Creek ***Little Jones Creek ***Monke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
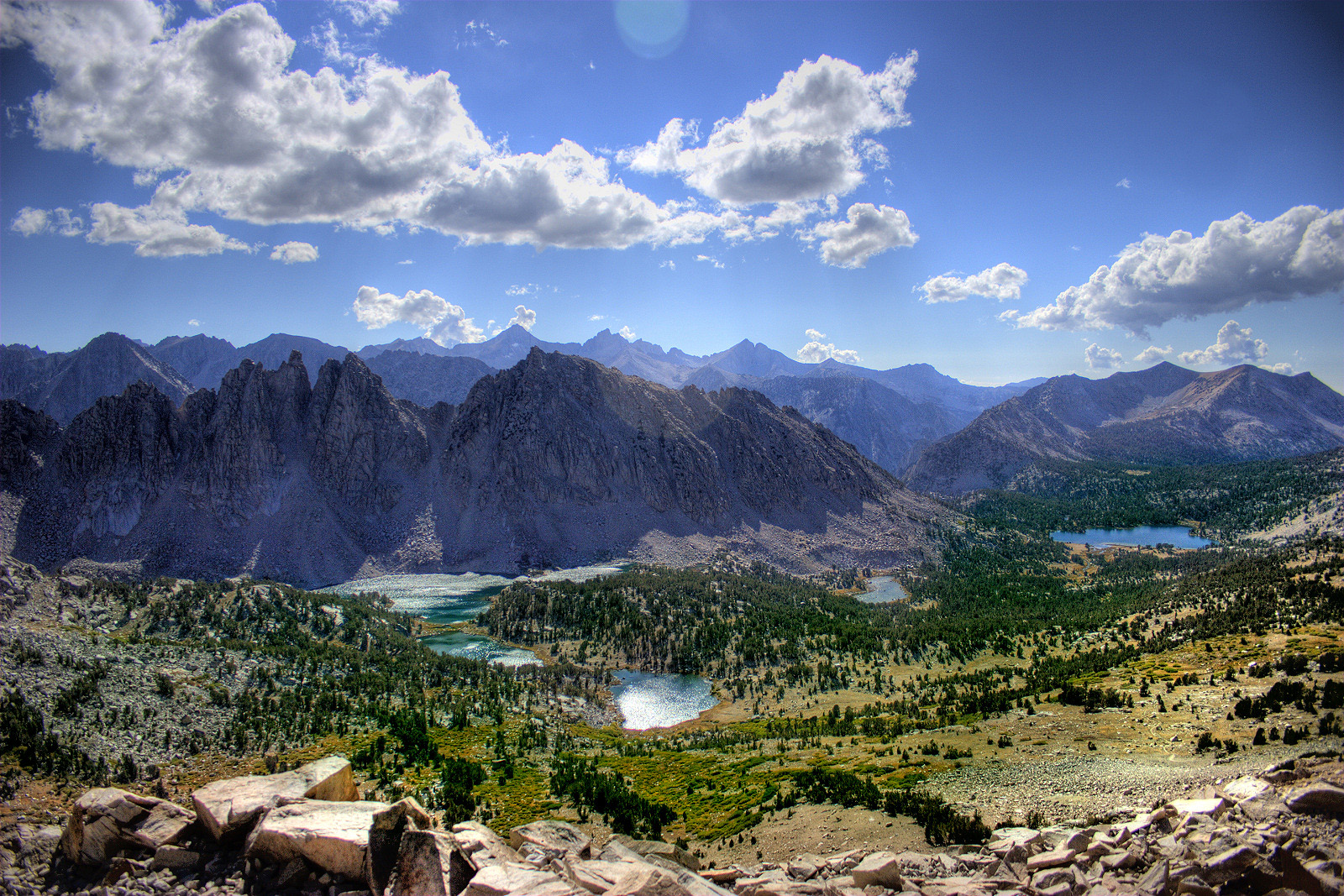
Mono Basin
The Mono Basin is an endorheic drainage basin located east of Yosemite National Park in California and Nevada. It is bordered to the west by the Sierra Nevada, to the east by the Cowtrack Mountains, to the north by the Bodie Hills, and to the south by the north ridge of the Long Valley Caldera. Estimates of the size of the basin range from 634 to 801 square miles, and the basin's elevation ranges from around 6,380 feet (level of Mono Lake as of 1986) to 13,061 feet atop Mount Dana near the Sierra Crest. Notable features in the basin include Mono Lake and the Mono-Inyo Craters, as well as the town of Lee Vining. Geology Geologically the basin is a structural basin that is bordered to the west by the frontal fault of the Sierra Nevada. The basin is part of the Walker Lane, an area where much of the deformation between the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate occurs. The basin was created by geological forces over the last five million years by crustal stretching of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mono Lake Committee
The Mono Lake Committee (MLC) is an environmental organization based in Lee Vining, California in the United States. Its mission is to preserve Mono Lake, by reducing diversions of water from the Eastern Sierra watersheds by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP). Mono Lake Mono Lake is an alkaline lake east of Yosemite National Park, largely fed by streams from the Sierra Nevada; it has no natural outlet. In 1919 the level of the lake peaked at 6427' above sea level. Birds bred and nested on a few volcanic islands in the lake, sustained by the extensive brine shrimp and alkali flies, which also attracted large numbers of migratory birds. In 1941, the LADWP began redirecting water from the streams feeding Mono Lake into the Los Angeles Aqueduct. As time passed, this both reduced the level of the lake and dried out the lower sections of the source streams. By 1981 the level of the lake had been reduced to 6372' above sea level, with the lake's volume cut in half, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by humans, and is driven primarily by the availability of food. It occurs mainly in the northern hemisphere, where birds are funneled onto specific routes by natural barriers such as the Mediterranean Sea or the Caribbean Sea. Migration of species such as storks, turtle doves, and swallows was recorded as many as 3,000 years ago by Ancient Greek authors, including Homer and Aristotle, and in the Book of Job. More recently, Johannes Leche began recording dates of arrivals of spring migrants in Finland in 1749, and modern scientific studies have used techniques including bird ringing and satellite tracking to trace migrants. Threats to migratory birds have grown with habitat destruction, especially of stopover and wintering sites, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |