|
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, color, magnetism and biological activity. The angles between bonds that an atom forms depend only weakly on the rest of a molecule, i.e. they can be understood as approximately local and hence transferable properties. Determination The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. IR, microwave and Raman spectroscopy can give information about the molecule geometry from the details of the vibrational and rotational absorbance detected by these techniques. X-ray crystallography, neutron diffraction and electron diffraction can g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Molecule Dimensions
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible spectrum, visible, near infrared, or ultraviolet, near ultraviolet range is used, although X-ray Raman scattering, X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Time-resolved spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a path graph (or linear graph) is a graph whose vertices can be listed in the order such that the edges are where . Equivalently, a path with at least two vertices is connected and has two terminal vertices (vertices of degree 1), while all others (if any) have degree 2. Paths are often important in their role as subgraphs of other graphs, in which case they are called paths in that graph. A path is a particularly simple example of a tree, and in fact the paths are exactly the trees in which no vertex has degree 3 or more. A disjoint union of paths is called a linear forest. Paths are fundamental concepts of graph theory, described in the introductory sections of most graph theory texts. See, for example, Bondy and Murty (1976), Gibbons (1985), or Diestel (2005). As Dynkin diagrams In algebra, path graphs appear as the Dynkin diagrams of type A. As such, they classify the root system of type A and the Weyl group of type A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
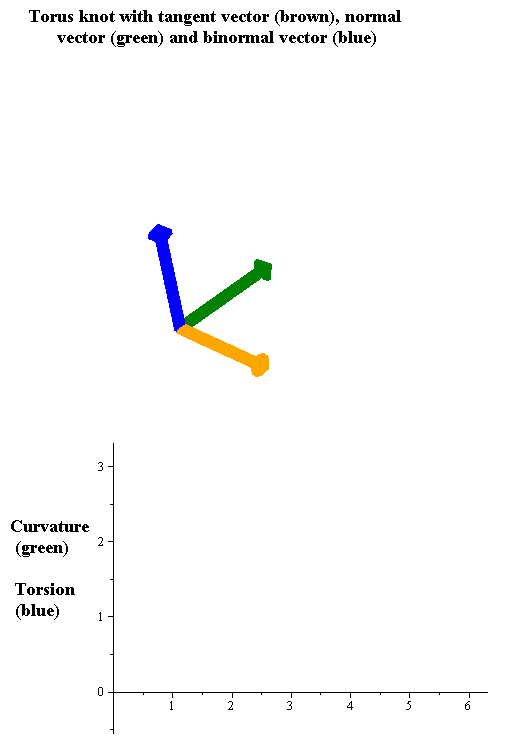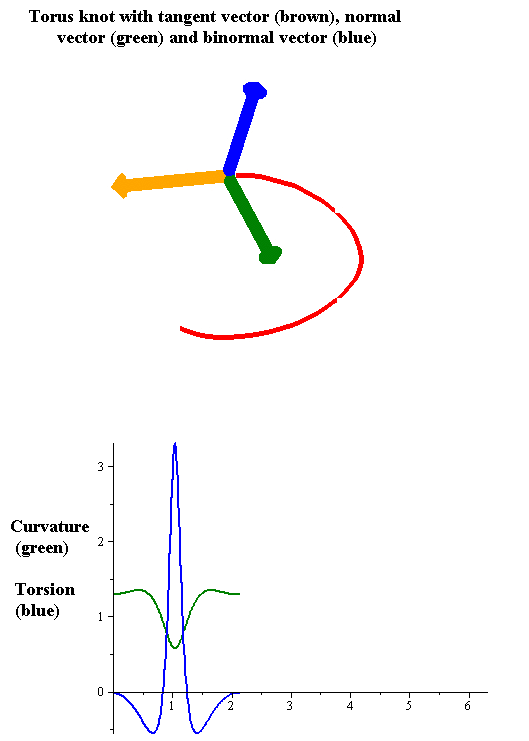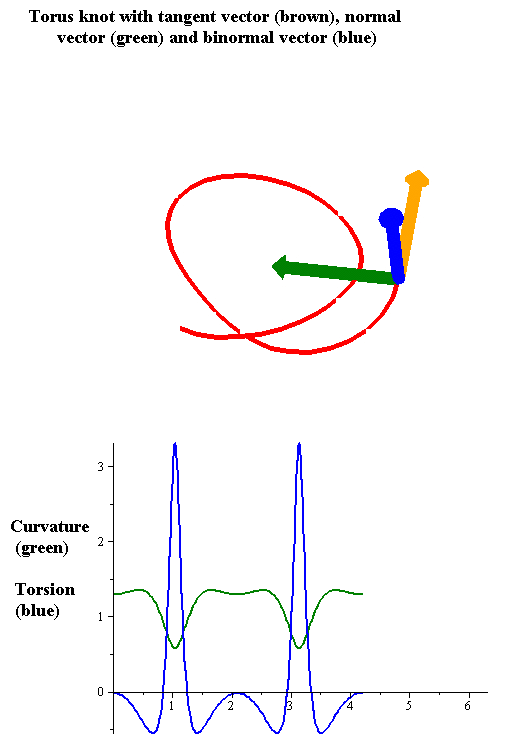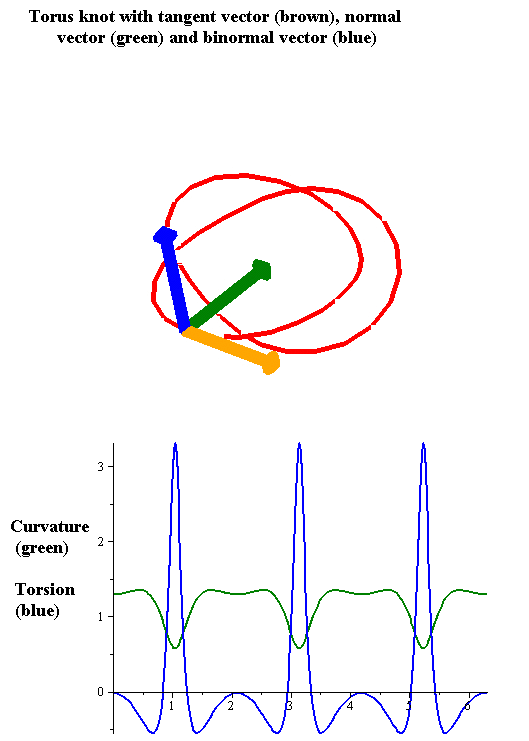
Torsion Of A Curve
In the differential geometry of curves in three dimensions, the torsion of a curve measures how sharply it is twisting out of the osculating plane. Taken together, the curvature and the torsion of a space curve are analogous to the curvature of a plane curve. For example, they are coefficients in the system of differential equations for the Frenet frame given by the Frenet–Serret formulas. Definition Let be a space curve parametrized by arc length and with the unit tangent vector . If the curvature of at a certain point is not zero then the principal normal vector and the binormal vector at that point are the unit vectors : \mathbf=\frac, \quad \mathbf=\mathbf\times\mathbf respectively, where the prime denotes the derivative of the vector with respect to the parameter . The torsion measures the speed of rotation of the binormal vector at the given point. It is found from the equation : \mathbf' = -\tau\mathbf. which means : \tau = -\mathbf\cdot\math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds, or some combination of these effects. Chemical bonds are described as having different strengths: there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding. Since opposite electric charges attract, the negatively charged electrons surrounding the nucleus and the positively charged protons within a nucleus attract each other. Electrons shared between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them. "Constructive quantum mechanical wavefunction interference" stabilizes the paired nuclei (see Theories of chemical bonding). Bonded nuclei maintain an optima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ab Initio Quantum Chemistry Methods
''Ab initio'' quantum chemistry methods are a class of computational chemistry techniques based on quantum chemistry that aim to solve the electronic Schrödinger equation. ''Ab initio'' means "from first principles" or "from the beginning", meaning using only physical constants and the positions and number of electrons in the system as input. This ''ab initio'' approach contrasts with other computational methods that rely on empirical parameters or approximations. By solving this fundamental equation, ''ab initio'' methods seek to accurately predict various chemical properties, including electron densities, energies, and molecular structures. The ability to run these calculations has enabled theoretical chemists to solve a range of problems and their importance is highlighted by the awarding of the 1998 Nobel prize to John Pople and Walter Kohn. The term was first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
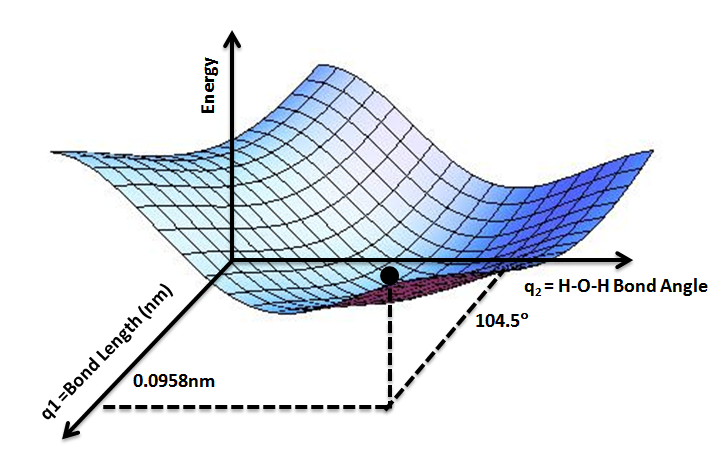
Potential Energy Surface
A potential energy surface (PES) or energy landscape describes the energy of a Physical system, system, especially a collection of atoms, in terms of certain Parameter, parameters, normally the positions of the atoms. The Surface (mathematics), surface might define the energy as a Function (mathematics), function of one or more coordinates; if there is only one coordinate, the surface is called a ''potential energy curve'' or energy profile. An example is the Morse/Long-range potential. It is helpful to use the analogy of a landscape: for a system with two Degrees of freedom (physics and chemistry), degrees of freedom (e.g. two bond lengths), the value of the energy (analogy: the height of the land) is a function of two bond lengths (analogy: the coordinates of the position on the ground). The PES concept finds application in fields such as physics, chemistry and biochemistry, especially in the theoretical sub-branches of these subjects. It can be used to theoretically explore p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformational Isomerism
In chemistry, rotamers are chemical species that differ from one another primarily due to rotations about one or more single bonds. Various arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can also be referred to as conformations. Conformers/rotamers differ little in their energies, so they are almost never separable in a practical sense. Rotations about single bonds are subject to small energy barriers. When the time scale for interconversion is long enough for isolation of individual rotamers (usually arbitrarily defined as a half-life of interconversion of 1000 seconds or longer), the species are termed atropisomers (''see:'' atropisomerism). The Ring flip, ring-flip of substituted cyclohexanes constitutes a common form of conformers. The study of the energetics of bond rotation is referred to as conformational analysis. In some cases, conformational analysis can be used to predict and explain product selectivity, mechanisms, and rates of reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Förster Resonance Energy Transfer
Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), fluorescence resonance energy transfer, resonance energy transfer (RET) or electronic energy transfer (EET) is a mechanism describing energy transfer between two light-sensitive molecules (chromophores). A donor chromophore, initially in its electronic excited state, may transfer energy to an acceptor chromophore through nonradiative dipole–dipole coupling. The efficiency of this energy transfer is inversely proportional to the sixth power of the distance between donor and acceptor, making FRET extremely sensitive to small changes in distance. Measurements of FRET efficiency can be used to determine if two fluorophores are within a certain distance of each other. Such measurements are used as a research tool in fields including biology and chemistry. FRET is analogous to Near and far field, near-field communication, in that the radius of interaction is much smaller than the Light, wavelength of light emitted. In the near-field region, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crysta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Electron Diffraction
Gas electron diffraction (GED) is one of the applications of electron diffraction techniques. The target of this method is the determination of the structure of gaseous molecules, i.e., the geometrical arrangement of the atoms from which a molecule is built up. GED is one of two experimental methods (besides microwave spectroscopy) to determine the structure of free molecules, undistorted by intermolecular forces, which are omnipresent in the solid and liquid state. The determination of accurate molecular structures by GED studies is fundamental for an understanding of structural chemistry. Introduction Diffraction occurs because the wavelength of electrons accelerated by a potential of a few thousand volts is of the same order of magnitude as internuclear distances in molecules. The principle is the same as that of other electron diffraction methods such as LEED and RHEED, but the obtainable diffraction pattern is considerably weaker than those of LEED and RHEED because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |