|
Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The Mobile River and Tensaw River empty into the northern end of the bay, making it an estuary. Several smaller rivers also empty into the bay: Dog River, Deer River, and Fowl River on the western side of the bay, and Fish River on the eastern side. Mobile Bay is the fourth-largest estuary in the United States with a discharge of of water per second. Annually, and often several times during the summer months, the fish and crustaceans will swarm the shallow coastline and shore of the bay. This event, appropriately named a jubilee, draws a large crowd because of the abundance of fresh, easily caught seafood. Mobile Bay is in area. It is long by a maximum width of . The deepest areas of the bay are located within the shipping channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alonso Álvarez De Pineda
Alonso Álvarez de Pineda (; 1494–1520) was a Spanish conquistador and cartography, cartographer who was the first to prove the insularity of the Gulf of Mexico by sailing around its coast. In doing so he created the first map to depict what is now Texas and parts of the Gulf Coast of the United States. Life Born in Aldeacentenera, Spain, i1494 he led several expeditions in 1519 to map the westernmost coastlines of the Gulf of Mexico, from the Yucatán Peninsula to the Pánuco River, and also explored parts of Florida, which at the time was believed to be an island. Antón de Alaminos' explorations had eliminated the western areas as being the site of the passage, leaving the land between the Pánuco River and Florida to be mapped.Weber (1992), p. 34. An expedition was organized to chart the remainder of the Gulf. Francisco de Garay, Governor of the Colony of Santiago, outfitted three ships with two hundred and seventy soldiers and placed them under the command of Álvarez de P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut (; also spelled Glascoe; July 5, 1801 – August 14, 1870) was a flag officer of the United States Navy during the American Civil War. He was the first Rear admiral (United States), rear admiral, Vice admiral (United States), vice admiral, and Admiral (United States), admiral in the United States Navy.#Farragut79, Farragut, 1879, p. 3#Hickman, Hickman, 2010, p. 216 He is remembered in U.S. Navy tradition for his bold order at the Battle of Mobile Bay, usually abbreviated to "Damn the torpedoes ... full speed ahead."#Stein, Stein, 2005, p. 5#Spears, Spears, 1905, p. 328 Born near Knoxville, Tennessee, Farragut was fostered by naval officer David Porter (naval officer), David Porter after the death of his mother. When he was 11 years old, Farragut served in the War of 1812 under the command of his adoptive father. He received his first command in 1823, at the age of 22, and went on to participate in West Indies anti-piracy operations of the United States, ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
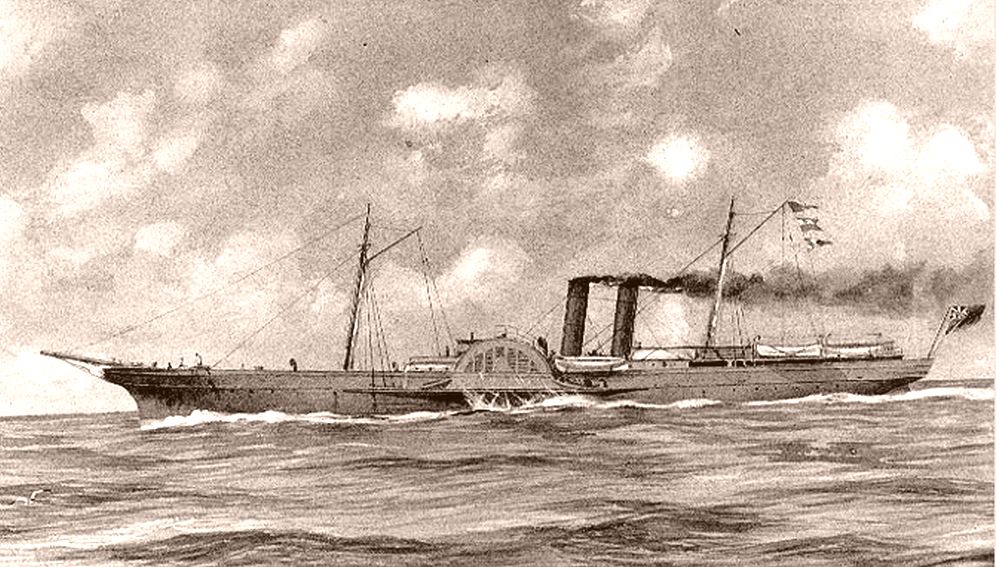
Blockade Runners Of The American Civil War
During the American Civil War, blockade runners were used to get supplies through the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America that extended some along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coastlines and the lower Mississippi River. The Confederacy had little industrial capability and could not produce the quantity of arms and other supplies needed to fight against the Union (American Civil War), Union. To meet this need, British investors financed numerous blockade runners that were constructed in the British Isles and were used to import the guns, ordnance and other supplies, in exchange for cotton that the Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution, British textile industry needed greatly. To penetrate the blockade, these relatively lightweight shallow draft ships, mostly built in British shipyards and specially designed for speed, but not suited for transporting large quantities of cotton, had to cruise undetected, usually at night, through the Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile ( , ) is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population was 187,041 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. After a successful vote to annex areas west of the city limits in July 2023, Mobile's population increased to 204,689 residents, making it the List of municipalities in Alabama, second-most populous city in Alabama. Mobile is the principal municipality of the Mobile metropolitan area. Alabama's only saltwater port, Mobile is located on the Mobile River at the head of Mobile Bay on the north-central Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast. The Port of Mobile has always played a key role in the economic health of the city, beginning with the settlement as an important trading center between the French colonization of the Americas, French colonists and Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans, down to its current role as the 12th-largest port in the United States.Drechsel, Emanuel. ''Mobilian Jargon: Lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana (New France)
Louisiana or French Louisiana was a administrative divisions of France, district of New France. In 1682 the French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle erected a cross near the mouth of the Mississippi River and claimed the whole of the drainage basin of the Mississippi River in the name of King Louis XIV, naming it "Louisiana". This land area stretched from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico and from the Appalachian Mountains to the Rocky Mountains. The area was under French control France in the early modern period, from 1682 to 1762 and in part French First Republic, from 1801 (nominally) to 1803. Louisiana included two regions, now known as Illinois Country, Upper Louisiana (), which began north of the Arkansas River, and ''Lower Louisiana'' (). The U.S. state of Louisiana is named for the historical region, although it is only a small part of the vast lands claimed by France. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
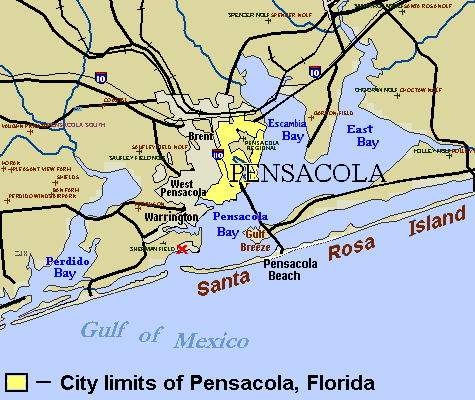
Pensacola
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only city in Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which had 509,905 residents in the 2020 census. Pensacola was first settled by the Spanish Empire in 1559, antedating the establishment of St. Augustine by six years, but was abandoned due to a significant hurricane and not resettled until 1698. Pensacola is a seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located in Pensacola. It is the base of the Blue Angels flight-demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The University of West Florida is situated north of the city center. The area was originally inhabited by Muskogean-speaking peoples. The Pensacola people lived there at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tristán De Luna Y Arellano
Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510 – September 16, 1573) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador of the 16th century.Herbert Ingram Priestley, Tristan de Luna: Conquistador of the Old South: A Study of Spanish Imperial Strategy (1936). http://palmm.digital.flvc.org/islandora/object/uwf%3A14851#page/191/mode/1up Biography Born in Borobia, Spain, to a noble family, he came to New Spain, and was sent on an expedition to colonize Florida in 1559. He was the cousin of the viceroy of New Spain, Antonio de Mendoza, and of Juana de Zúñiga, wife of Hernán Cortés. In August of that year, he established an ephemeral colony at modern-day Pensacola, the earliest multi-year European settlement in the continental United States. Pinson, Stev"The Tristan de Luna Expedition" From de-luna.com. Retrieved January 9, 2007. During his years in Mexico, Luna had served with Francisco Vásquez de Coronado on his expedition to the Seven Cities of Cíbola and crushed an Indian rebellion in O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Tuscaloosa
Tuskaloosa (less commonly spelled as ''Tuskalusa'', ''Tastaluca'', ''Tuskaluza'') (birthdate unknown, - 1540) was a paramount chief of a Mississippian chiefdom in what is now the U.S. state of Alabama. His people were ancestors to the several southern Native American confederacies (the Choctaw and Creek peoples) who later emerged in the region. The modern city of Tuscaloosa, Alabama is named in his honor. Tuskaloosa is notable for leading the Battle of Mabila at his fortified village against the Spanish conquistador Hernando de Soto. After being taken hostage by the Spanish as they passed through his territory, Tuskaloosa organized a surprise attack on his captors at Mabila, but was ultimately defeated. Contemporary records describe the paramount chief as being very tall and well built, with some of the chroniclers saying Tuaskaloosa stood a foot and a half taller than the Spaniards. His name, derived from the western Muskogean language elements ''tashka'' and ''losa'', mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mabila
Mabila (also spelled Mavila, Mavilla, Maubila, or Mauvilla, as influenced by Spanish or French transliterations) was a small fortress town known to the paramount chief Tuskaloosa in 1540, in a region of present-day central Alabama. The exact location has been debated for centuries, but southwest of present-day Selma, Alabama, is one possibility. In late 2021, archaeologists announced the excavation of Spanish artifacts at several Native American settlement sites in Marengo County, Alabama, Marengo County that indicate that they have found the historical province of Mabila, although not the town itself. They theorize that the town site is within a few miles of their excavations. In 1540 Chief Tuskaloosa arranged for more than 2,500 native warriors to be concealed at Mabila, prepared to attack a large party of foreign invaders in the Mississippian culture territory: Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto and his expedition.Sylvia Flowers, "DeSoto's Expedition", U.S. National Park Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |