|
Mirko Kovač (writer)
Mirko Kovač (26 December 1938 – 19 August 2013) was a Yugoslav writer. In his rich career he wrote novels, short stories, essays, film scripts, TV and radio plays. Among his best known works are the novels ''Gubilište'', ''Životopis Malvine Trifković'', ''Vrata od utrobe'', ''Grad u zrcalu'', the short story collection ''Ruže za Nives Koen'', the book of essays ''Europska trulež'' and the scripts for some of the most successful films of Yugoslav cinema like '' Handcuffs'', '' Playing Soldiers'' and ''Occupation in 26 Pictures'' among others. He was one quarter of the infamous Belgrade quartet, the other three being Danilo Kiš, Borislav Pekić and Filip David. Biography Kovač was born to a Croat father and a Serb mother in the village of Petrovići in Banjani region near Nikšić, Montenegro. He went to elementary school in Trebinje but after leaving his family at the age of 16 he went to Vojvodina where he finished high school in Novi Sad. During that time he discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
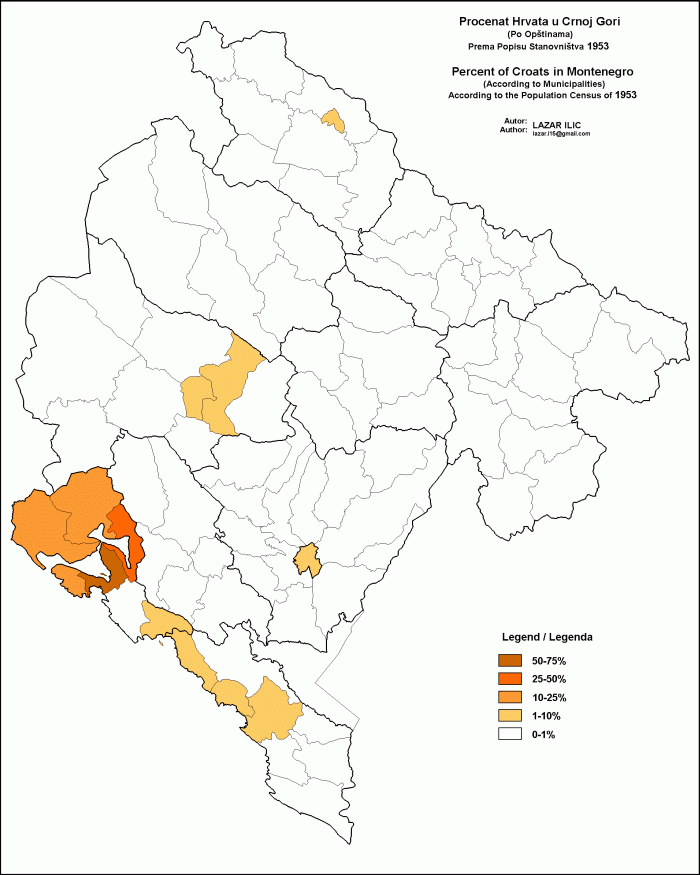
Croats Of Montenegro
The Croats have a minority in Boka Kotorska (''Bay of Kotor''), a coastal region in Montenegro, the largest of their kind in Tivat. The three municipalities making up the Bay of Kotor ( Tivat, Kotor and Herceg-Novi) include 4,519 Croats or 6.70%. They are also known as Bokelji, a common name for all inhabitants for of Boka Kotorska. Tivat is home to the minority political party Croatian Civic Initiative, and to the ''National Council of Croats in Montenegro''. Kotor is home to Croatian Civic Society of Montenegro. Religion Many Croats in this region are followers of the Roman Catholic Church. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Kotor in Kotor is part of the Archdiocese of Split-Makarska in Croatia and its faithful are mostly the Croats in Boka. ;Places of worship * Our Lady of the Rocks * Cathedral of Saint Tryphon Demographics Settlements in Montenegro with significant Croatian minority (10 percent or more) include (2011): *Bogdašići (27 or 47,37%) * Donja Lastva (3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predrag Matvejević
Predrag Matvejević (7 October 1932 – 2 February 2017) was a Bosnian and Croatian writer and scholar. A literature scholar who taught at universities in Zagreb, Paris and Rome, he is best known for his 1987 non-fiction book ''Mediterranean: A Cultural Landscape'', a seminal work of cultural history of the Mediterranean region which has been translated into more than 20 languages. Biography Predrag Matvejević was born in Mostar in 1932, at the time part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, modern Bosnia and Herzegovina, into a family of mixed ethnicity, to an ethnic Russian father, who had previously emigrated from Odessa, or in Matvejević's own words, father of Ukrainian ethnicity and Russian language and a native Herzegovinian Croat mother. During World War II in Yugoslavia he briefly worked as a military messenger for the Partisans, and after the war he graduated from the Mostar Gymnasium and then went on to study French language and literature, first at the University of Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Davičo
Oskar Davičo ( sr-cyr, Оскар Давичо; 18 January 1909 — 30 September 1989) was a Serbian and Yugoslavian novelist and poet. A leading literary figure of his generation, he was one of the most acclaimed Serbian surrealist writers, but also a revolutionary socialist activist and a politician. Davičo was awarded prestigious literary NIN Award a record three times. Biography Early life Oskar Davičo was born on 18 January 1909 in Šabac to a Jewish family. His father was an atheist Jewish accountant and a socialist. During World War I in Serbia, Šabac was the scene of heavy fighting, so the whole family moved temporarily to Negotin. Interwar period Davičo finished the elementary school and lower gymnasium Šabac, and then continued his education at the First Belgrade Gymnasium in Belgrade. Davičo started to write poetry while in gymnasium. He was expelled from the gymnasium in 6th grade for criticizing religion in a self-published magazine. He later graduated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branko Miljković
Branko Miljković (Serbian Cyrillic: Бранко Миљковић; 29 January 1934 – 12 February 1961) was a Serbian poet. Biography Miljković was born in Niš to a Serb father Gligorije Miljković, who hails from Gadžin Han, and a Croat mother Marija Brailo, who hails from Trbounje near Drniš. He was best known throughout Yugoslavia, the Soviet Union and other countries of the Eastern Bloc for his influential writings. At a time when no one could have foreseen anything but a bright future for the poet, he died prematurely in 1961 at the age of 27. He was found hanging from a tree in Zagreb, today's Croatia. This controversial incident was officially recorded as a suicide. In his one-line poem "Epitaph", he writes "''Ubi me prejaka reč''" ("''I was killed by a word too strong''") almost sensing his premature end of life. During the last years of his life, he published five books of poetry (''I Wake Her in Vain'', ''Death against Death'', ''The Origin of Hope'', ''Fire an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vjekoslav Kaleb
Vjekoslav Kaleb (27 September 1905 – 13 April 1996) was a Croatian short story writer and novelist. Biography Kaleb was born in Tisno and educated in Zadar, Belgrade, Šibenik and Zagreb, where he attended Teacher’s Academy (today: Faculty of Teacher Education, University of Zagreb, Faculty of Teacher Education of the University of Zagreb). He later worked as a teacher in villages of the Zagora (Croatia), Zagora region in Croatia before joining the Yugoslav Partisans, Partisans in 1943. After the World War II, Kaleb served as editor of many literary magazines (''Književnik'', ''Naprijed'', ''Republika'', ''Kolo (magazine), Kolo'') and secretary of the Croatian Writers’ Association and Matica hrvatska. He has published 57 short stories and three novels, most of which deal with existential struggles of people in the remote hamlets of the rural Zagora during wartimes. The short story ''Gost'' (The Guest) is one of his first works (published in 1940), but also his best and most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antun Branko Šimić
Antun Branko Šimić (18 November 1898 – 2 May 1925) was a Croatian expressionist poet, considered to be one of the most important poets of Croatian literature of the 20th century. Life He was born to a Croat family from Drinovci near Grude on 18 November 1898, in the family of Vida and Martin Šimić. He attended primary school in his native village, and then the first three forms of the Franciscan classical grammar school in Široki Brijeg. He decided to change school in the fourth form and went to Mostar and afterwards to Vinkovci (Gymnasium Vinkovci). His unruly spirit made him change his surroundings again and so he continued his education in Zagreb, in the upper town grammar school. In 1917, he started the journal for art and culture, '' Vijavica'' (Whirlwind), which forced him to leave school. This is when he lost his parents' support and it also meant a hard life overpowered by many illnesses. After four issues of ''Vijavica'', taking the example of German j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladan Desnica
Vladan Desnica ( sr-cyr, Владан Десница; 17 September 1905 – 4 March 1967) was a Yugoslav writer and translator. Life He was born in Zadar, Austria-Hungary to Uroš Desnica (von Desnica), a politician from the noble Orthodox Serbian family from Obrovac and Islam Grčki, descendant of Stojan Janković, and his mother Fani Desnica was from a Catholic Croatian family Luković from Prčanj near Kotor in what is today Montenegro. He wrote poems, short stories, science fiction and novels, usually dealing with life in cities and villages of Northern Dalmatia. His best work is the novel ''Proljeća Ivana Galeba'' (''The Springs of Ivan Galeb''), published in 1957, in which he gives a first-person account of an intellectual lying in a hospital bed and meditating about illness and mortality. He died in Zagreb. Like many writers who used to work in Yugoslavia, he is claimed both by Croatian and Serbian literature. His talents were also used for the medium of film. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranko Marinković
Ranko Marinković (22 February 1913 – 28 January 2001) was a Croatian novelist and dramatist. Born in Komiža on the island of Vis (then a part of Austria-Hungary), Marinković's childhood was marked by World War I. He later earned a degree in philosophy at the University of Zagreb. In the 1930s, he began to make his name in Zagreb literary circles with his plays and stories. His career was interrupted briefly during World War II. When his native island was occupied by Fascist Italy, he was arrested in Split and interned in the Ferramonti camp. After the capitulation of Italy, Marinković went to Bari, and then to the El Shatt refugee camp where he made contacts with Tito's Partisans. After the war, he spent time working in theatre. His best known works are ''Glorija'' (1955), a play in which he criticised the Catholic Church, and ''Kiklop'' (1965), a semi-autobiographical novel in which he described the gloomy atmosphere among Zagreb intellectuals before the Axis invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Ujević
Augustin Josip "Tin" Ujević (; 5 July 1891 – 12 November 1955) was a Croatian poet, considered by many to be the greatest poet in 20th century Croatian literature. From 1921, he ceased to sign his name as Augustin, thereafter using the signature Tin Ujević. Biography Ujević was born in Vrgorac, a small town in the Dalmatian hinterland, and attended school in Imotski, Makarska, Split and Zagreb. He completed Classical Gymnasium in Split, and in Zagreb he studied Croatian language and literature, classical Philology, Philosophy, and Aesthetics. In 1909, while studying literature, his first sonnet "''Za novim vidicima''" (Towards New Horizons) appeared in the journal ''Mlada Hrvatska'' (Young Croatia). After the assassination attempts on the ban Slavko Cuvaj in 1912, Ujević became active in the Nationalist youth movement and was repeatedly imprisoned. On the eve of the First World War, he lived briefly in Dubrovnik, Šibenik, Zadar, Rijeka and for a longer time in Split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; hu, Újvidék, ; german: Neusatz; see below for other names) is the second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pannonian Plain on the border of the Bačka and Syrmia geographical regions. Lying on the banks of the Danube river, the city faces the northern slopes of Fruška Gora. , Novi Sad proper has a population of 231,798 while its urban area (including the adjacent settlements of Petrovaradin and Sremska Kamenica) comprises 277,522 inhabitants. The population of the administrative area of the city totals 341,625 people. Novi Sad was founded in 1694 when Serb merchants formed a colony across the Danube from the Petrovaradin Fortress, a strategic Habsburg military post. In subsequent centuries, it became an important trading, manufacturing and cultural centre, and has historically been dubbed ''the Serbian Athens''. The city was heavily dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative center, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia. The historic regions of Banat, Bačka, and Syrmia overlap the province. Modern Vojvodina is multi-ethnic and multi-cultural, with some 26 ethnic groups and six official languages. About two million people, nearly 27% of Serbia's population, live in the province. Naming ''Vojvodina'' is also the Serbian word for voivodeship, a type of duchy overseen by a voivode. The Serbian Voivodeship, a precursor to modern Vojvodina, was an Austrian province from 1849 to 1860. Its official name is the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Its name in the province's six official languages is: * Croatian: ''Autonomna Pokrajina Vojvodina'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
