|
Mini-STX
Mini-STX (mSTX, Mini Socket Technology EXtended, originally "Intel 5x5") is a computer motherboard form factor that was released by Intel in 2015 (as "Intel 5x5"). These motherboards measure 147mm by 140mm (5.8" x 5.5"), making them larger than "4x4" NUC (102x102mm / 4.01" x 4.01" inches) and Nano-ITX (120x120mm / 4.7" x 4.7") boards, but notably smaller than the more common Mini-ITX (170x170mm / 6.7" x 6.7") boards. Unlike these standards, which use a square shape, the Mini-STX form factor is 7mm longer from front-to-rear, making it slightly rectangular. Mini-STX design elements The Mini-STX design suggests (but does not require) support for: * Socketed processors (e.g. LGA or PGA CPUs) * Onboard power regulation circuitry, enabling direct DC power input * IO ports embedded on the front and rear of the motherboard (akin to NUC, but unlike typical motherboards which often use headers instead to connect built-in ports on enclosures) Adoption by manufacturers This motherbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
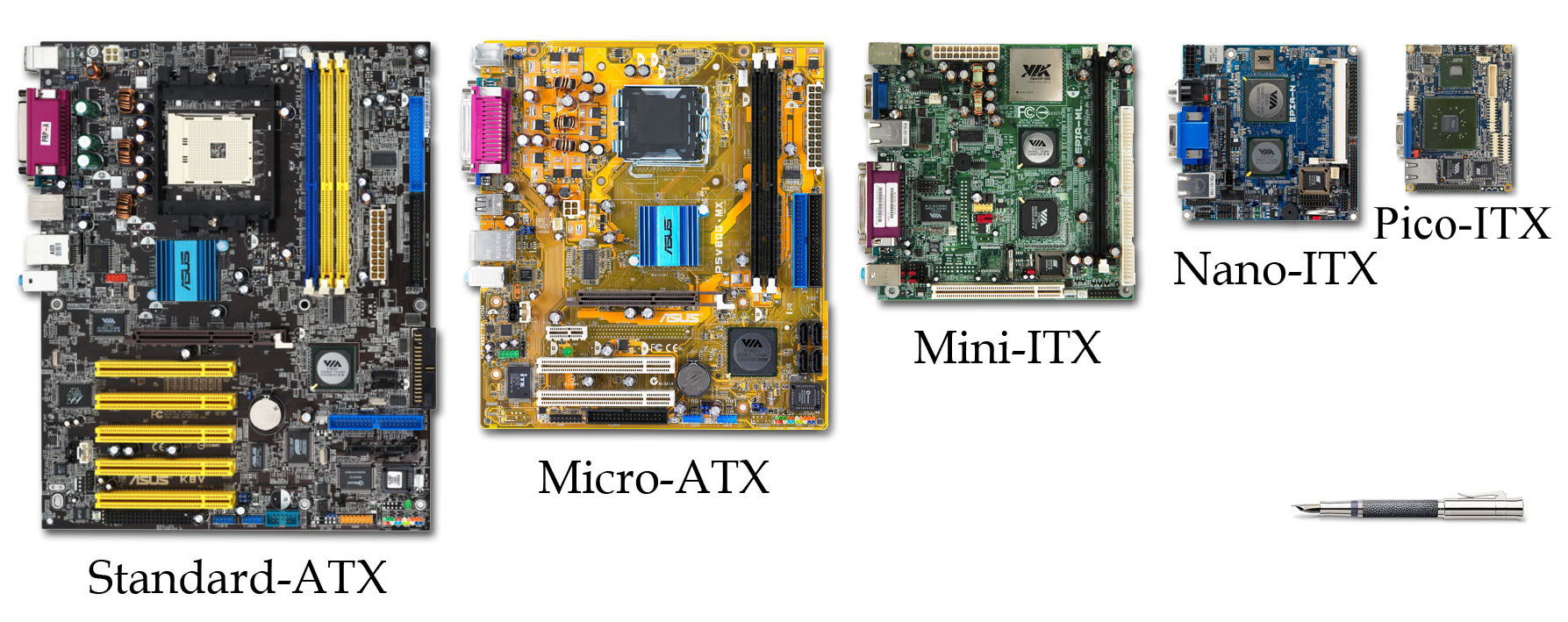
Motherboard Form Factor
In computing, the motherboard form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented. Overview of form factors A PC motherboard is the main circuit board within a typical desktop computer, laptop or server. Its main functions are as follows: * To serve as a central backbone to which all other modular parts such as CPU, RAM, and hard drives can be attached as required to create a computer * To be interchangeable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Next Unit Of Computing
Next Unit of Computing (NUC) is a line of Small form factor (desktop and motherboard), small-form-factor Barebone computer, barebone computer kits designed by Intel. It was previewed in 2012 and launched in early 2013. The NUC has developed over ten generations, spanning from Sandy Bridge-based Celeron CPUs in the first generation through Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge-based Intel Core, Core i3 and i5 CPUs in the second generation to Gemini Lake-based Pentium and Celeron CPUs and Kaby Lake-based Core i3, i5, and i7 CPUs in the seventh and eighth generations. The NUC motherboard usually measures approximately , although some models have had different dimensions. The Barebone computer, barebone kits consist of the board, in a plastic case with a fan, an external power supply, and a Flat Display Mounting Interface, VESA mounting plate. Intel does sell just the NUC motherboards, which have a built-in CPU, although () the price of a NUC motherboard is very close to the cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nano-ITX
Nano-ITX is a computer motherboard form factor first proposed by VIA Technologies at CeBIT in March 2003, and implemented in late 2005. Nano-ITX boards measure , and are fully integrated, very low power consumption motherboards with many uses, but targeted at smart digital entertainment devices such as Digital video recorder, DVRs, set-top boxes, Home theater PC, media centers, car PCs, and thin devices. Nano-ITX motherboards have slots for SO-DIMM. There are four Nano-ITX motherboard product lines so far, VIA's EPIA N, EPIA NL, EPIA NX, and the VIA EPIA NR. These boards are available from a wide variety of manufacturers supporting numerous different CPU platforms. Udoo has now released at least 1 nano-ITX board: the Udoo Bolt. See also *Mini-ITX *Pico-ITX *Mobile-ITX *EPIA, mini-ITX and nano-ITX motherboards from VIA *Ultra-Mobile PC *Minimig, is an open source re-implementation of an Amiga 500 in Nano-ITX format References External links Jetway Computer Corp. J8F9 AMD Nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini-ITX
Mini-ITX is a motherboard form-factor, developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. They are commonly used in small-configured computer systems. Originally, they were a niche product, designed for fan-less cooling with a low Thermal design power, power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience. The four mounting holes in a Mini-ITX board line up with four of the holes in ATX-specification motherboards, and the locations of the backplate and expansion slot are the same (though one of the holes used was optional in earlier versions of the ATX spec). Mini-ITX boards can therefore often be used in cases designed for ATX, micro-ATX and other ATX variants if desired. The design provides one expansion slot. Earlier motherboards conventionally have a standard 33 MHz 5V 32-bit Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI slot. Many older case designs use riser cards and some even have two-slot riser card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
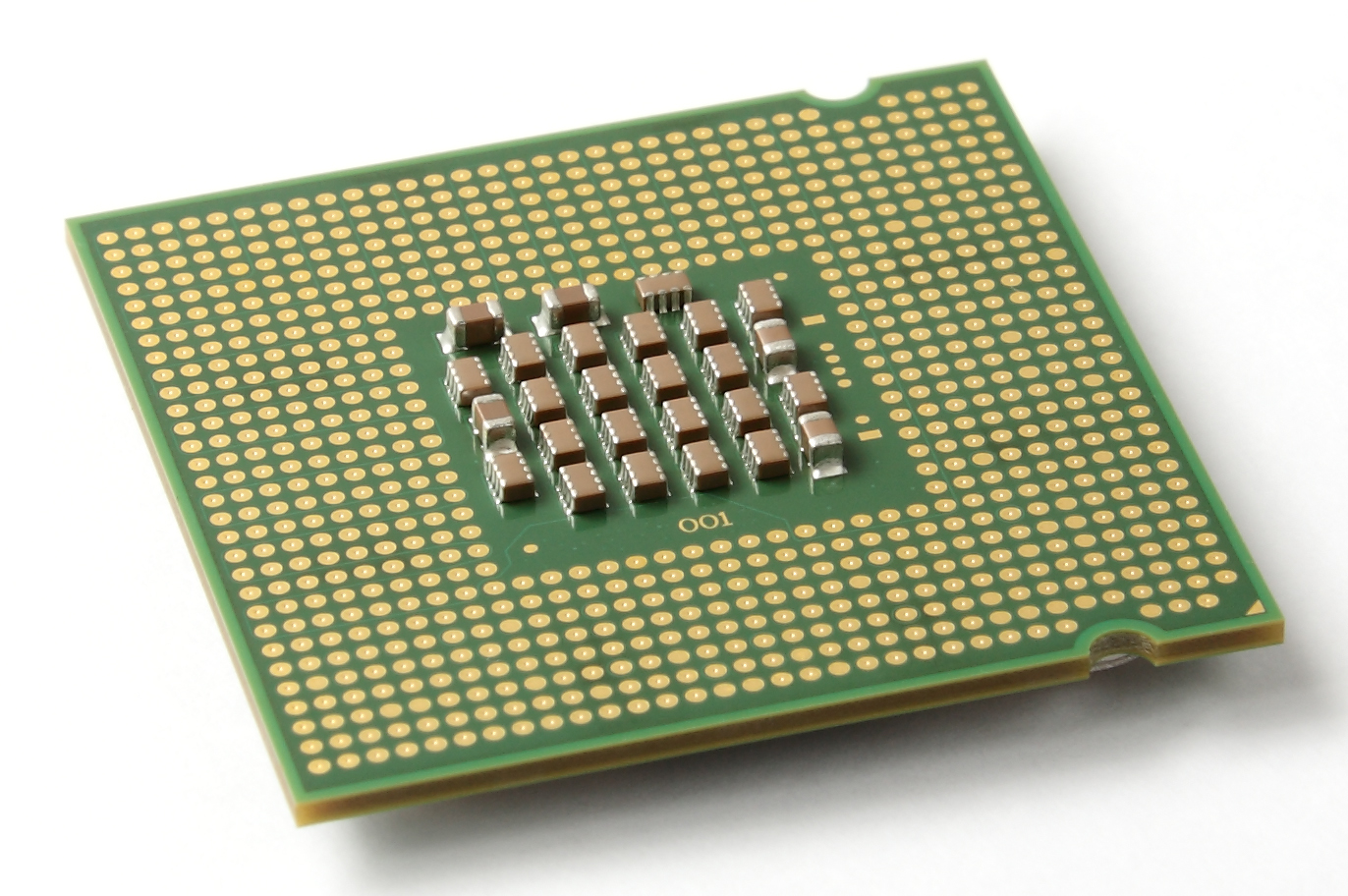
Land Grid Array
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket (when a socket is used) rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board. Description The ''land grid array'' is a packaging technology with a grid of contacts, 'lands', on the underside of a package. The contacts are to be connected to a grid of contacts on the PCB. Not all rows and columns of the grid need to be used. The contacts can either be made by using an LGA socket, or by using solder paste. The grid elements found in use can be e.g. circular, triangular or other polygonal shapes and might have even different sizes. Grids might sometimes appear like honey comb patterns. Designs are often optimized for factors like contact likeliness despite tolerances, electrical gap to neighboring contacts and for allowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pin Grid Array
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package. PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit boards using the through hole method or inserted into a socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package (DIP). PGA variants Plastic Plastic pin grid array (PPGA) packaging was used by Intel for late-model Mendocino core Celeron processors based on Socket 370. Some pre-Socket 8 processors also used a similar form factor, although they were not officially referred to as PPGA. Flip chip A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-PGA or FCPGA) is a form of pin grid array in which the die faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASRock
ASRock Inc. is a Taiwanese manufacturer of motherboards, industrial PCs and home theater PCs (HTPC). Founded by Ted Hsu, it was founded in 2002 and is currently owned by Taiwanese electronics company Pegatron. History ASRock was originally spun off from Asus in 2002 in order to compete with companies like Foxconn for the commodity OEM market. Since then, ASRock has also gained momentum in the DIY sector and plans for moving the company upstream began in 2007 following a successful IPO on the Taiwan Stock Exchange. It was acquired by Pegatron in 2010. As of 2011, ASRock is the world's third largest motherboard manufacturer, having cooperated with professional esports player Johnathan Wendel in the development of a gaming-oriented enthusiast motherboard in 2011. ASRock established itself as a server motherboard affiliate in April 2013, having received orders from 10 mid-size clients for server and industrial PC motherboards and forming partnerships with system integrators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabyte Technology
Gigabyte Technology (branded as GIGABYTE or sometimes GIGA-BYTE; formally GIGA-BYTE Technology Co., Ltd.) is a Taiwanese manufacturer and distributor of computer hardware. Gigabyte's principal business is motherboards. It shipped 4.8 million motherboards in the first quarter of 2015, which allowed it to become the leading motherboard vendor. Gigabyte also manufactures custom graphics cards and laptop computers (including thin and light laptops under its ''Aero'' sub-brand). In 2010, Gigabyte was ranked 17th in "Taiwan's Top 20 Global Brands" by the Taiwan External Trade Development Council. The company is publicly held and traded on the Taiwan Stock Exchange, stock ID number . History Gigabyte Technology was established in 1986 by Pei-Cheng Yeh. One of Gigabyte's key advertised features on its motherboards is its "Ultra Durable" construction, advertised with "all solid capacitors". On 8 August 2006 Gigabyte announced a joint venture with Asus. Gigabyte developed the world's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile PCI Express Module
A Mobile PCI Express Module (MXM) is an interconnect standard for GPUs (MXM Graphics Modules) in laptops using PCI Express created by MXM-SIG. The goal was to create a non-proprietary, industry standard socket, so one could easily upgrade the graphics processor in a laptop, without having to buy a whole new system or relying on proprietary vendor upgrades. 1st generation configurations Smaller graphics modules can be inserted into larger slots, but type I and II heatsinks will not fit type III and above or vice versa. The Alienware m5700 platform uses a heatsink that will fit Type I, II, & III cards without modification. 2nd generation configurations (MXM 3) Smaller graphics modules can be inserted into larger slots. Heatsink mounting remains the same for type A and B modules. MXM 3.1 was released in March 2012 and added PCIe 3.0 support. Module compatibility First generation modules are ''not'' compatible with second generation modules and vice versa. First generation m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
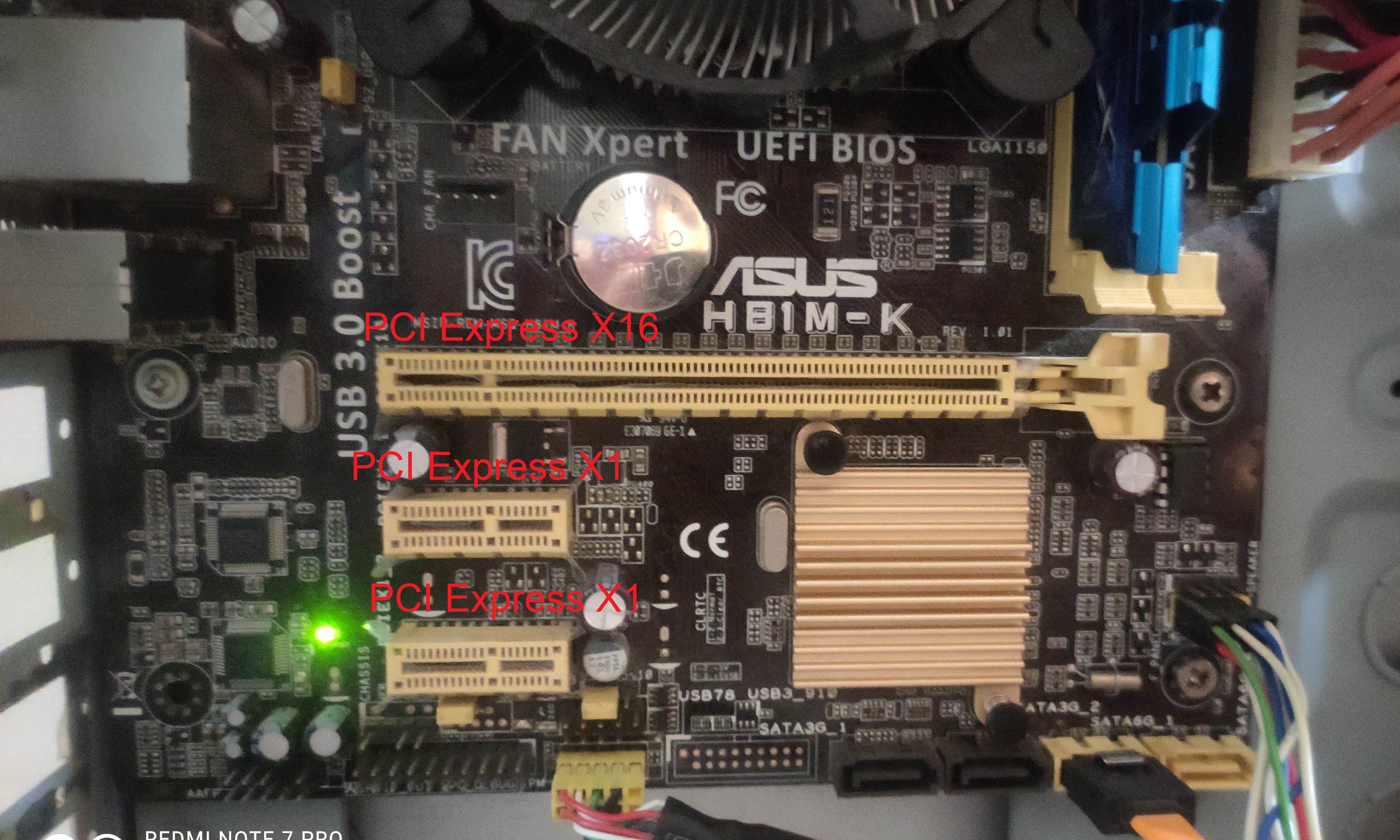
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the case, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, speakers and motherboard. By contrast, software is the set of instructions that can be stored and run by hardware. Hardware is so-termed because it is " hard" or rigid with respect to changes, whereas software is "soft" because it is easy to change. Hardware is typically directed by the software to execute any command or instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system, although other systems exist with only hardware. Von Neumann architecture The template for all modern computers is the Von Neumann architecture, detailed in a 1945 paper by Hungarian mathematician John von Neumann. This describes a design architecture for an electronic digital computer with subdivisions of a processing unit consisting of an arithmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_CPU-pins_PNr°0295.jpg)


.jpg)

