|
Mingo Oak
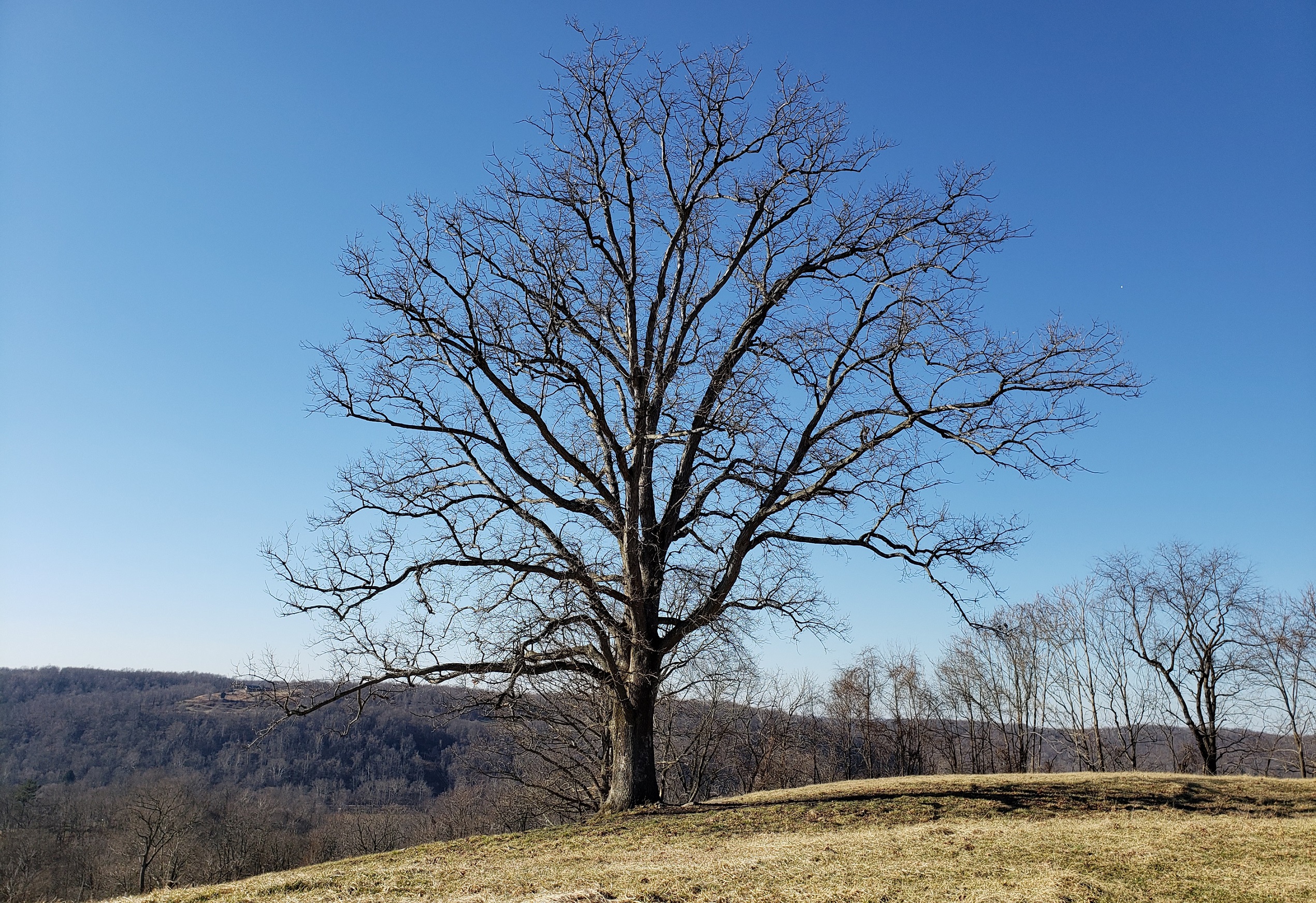
The Mingo Oak (also known as the Mingo White Oak) was a white oak (''Quercus alba'') in the U.S. state of West Virginia. First recognized for its age and size in 1931, the Mingo Oak was the oldest and largest living white oak tree in the world until its death in 1938. The Mingo Oak stood in Mingo County, West Virginia, in a cove at the base of Trace Mountain near the headwaters of the Trace Fork of Pigeon Creek, a tributary stream of Tug Fork. The tree reached a height of over , and its trunk was in height. Its crown measured in diameter and in height. The tree's trunk measured in diameter and the circumference of its base measured . Assessments of its potential board lumber ranged from to . Following the tree's felling in 1938, it was estimated to weigh approximately . While the tree had long been known about for its size, the unique status of the Mingo Oak was not recognized until 1931, when John Keadle and Leonard Bradshaw of Williamson took measurements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercus Alba
''Quercus alba'', the white oak, is one of the preeminent hardwoods of eastern and central North America. It is a long-lived oak, native to eastern and central North America and found from Minnesota, Ontario, Quebec, and southern Maine south as far as northern Florida and eastern Texas. Specimens have been documented to be over 450 years old. Although called a white oak, it is very unusual to find an individual specimen with white bark; the usual colour is a light gray. The name comes from the colour of the finished wood. In the forest it can reach a magnificent height and in the open it develops into a massive broad-topped tree with large branches striking out at wide angles. Description ''Quercus alba'' typically reaches heights of at maturity, and its canopy can become quite massive as its lower branches are apt to extend far out laterally, parallel to the ground. Trees growing in a forest will become much taller than ones in an open area which develop to be short and mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoil Tip
A spoil tip (also called a boney pile, culm bank, gob pile, waste tip or bing) is a pile built of accumulated ''spoil'' – waste material removed during mining. Spoil tips are not formed of slag, but in some areas, such as England and Wales, they are referred to as slag heaps. In Scotland the word ''bing'' is used. In North American English the term is mine dump or mine waste dump. The term "spoil" is also used to refer to material removed when digging a foundation, tunnel, or other large excavation. Such material may be ordinary soil and rocks (after Coal preparation plant, separation of coal from waste), or may be heavily contaminated with chemical waste, determining how it may be disposed of. Clean spoil may be used for land reclamation. Spoil is distinct from tailings, which is the processed material that remains after the valuable components have been extracted from ore. Etymology The phrase originates from the French word ''espoilelier'', a verb conveying the meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
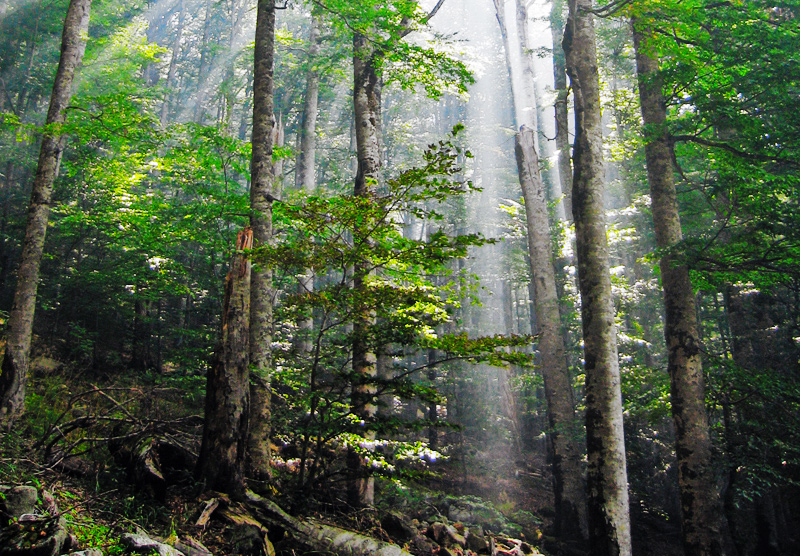
Temperate Broadleaf And Mixed Forest
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions. These forests are richest and most distinctive in central China and eastern North America, with some other globally distinctive ecoregions in the Himalayas, Western and Central Europe, the southern coast of the Black Sea, Australasia, Southwestern South America and the Russian Far East. Ecology The typical structure of these forests includes four layers. * The uppermost layer is the canopy composed of tall mature trees ranging from high. Below the canopy is the three-layered, shade-tolerant understory that is roughly shorter than the canopy. * The top layer of the understory is the sub-canopy composed of smaller mature trees, saplings, and suppressed juvenile canopy layer trees awaiting an opening in the canopy. * Below the sub-canop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chestnut
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Description Chestnut trees are of moderate growth rate (for the Chinese chestnut tree) to fast-growing for American and European species. Their mature heights vary from the smallest species of chinkapins, often shrubby,''Chestnuts, Horse-Chestnuts, and Ohio Buckeyes'' . In Yard and Garden Brief, Horticulture department at University of Minnesota. to the giant of past American forests, '' C. dentata'' that could reach . Between these extremes ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit. The antonym of deciduous in the botanical sense is evergreen. Generally, the term "deciduous" means "the dropping of a part that is no longer needed or useful" and the "falling away after its purpose is finished". In plants, it is the result of natural processes. "Deciduous" has a similar meaning when referring to animal parts, such as deciduous antlers in deer, deciduous teeth (baby teeth) in some mammals (including humans); or decidua, the uterine lining that sheds off after birth. Botany In botany and horticulture, deciduous plants, including trees, shrubs and herbaceous perennials, are those that lose all of their Leaf, leaves for part of the year. This process is called abscission. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old-growth Forest
An old-growth forest or primary forest is a forest that has developed over a long period of time without disturbance. Due to this, old-growth forests exhibit unique ecological features. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines primary forests as naturally regenerated forests of native tree species where there are no clearly visible indications of human activity and the ecological processes are not significantly disturbed. One-third (34 percent) of the world's forests are primary forests. Old-growth features include diverse tree-related structures that provide diverse wildlife habitats that increases the biodiversity of the forested ecosystem. Virgin or first-growth forests are old-growth forests that have never been logged. The concept of diverse tree structure includes multi-layered canopies and canopy gaps, greatly varying tree heights and diameters, and diverse tree species and classes and sizes of woody debris., the world has of primary forest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain. The general definition used is one followed by the United States Geological Survey and the Geological Survey of Canada to describe the respective countries' Physiographic region, physiographic regions. The U.S. uses the term Appalachian Highlands and Canada uses the term Appalachian Uplands; the Appalachian Mountains are not synonymous with the Appalachian Plateau, which is one of the provinces of the Appalachian Highlands. The Appalachian range runs from the Newfoundland (island), Island of Newfoundland in Canada, southwestward to Central Alabama in the United States; south of Newfoundland, it crosses the 96-square-mile (248.6 km2) archipelago of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, an overseas collectivity of France, meaning it is technica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
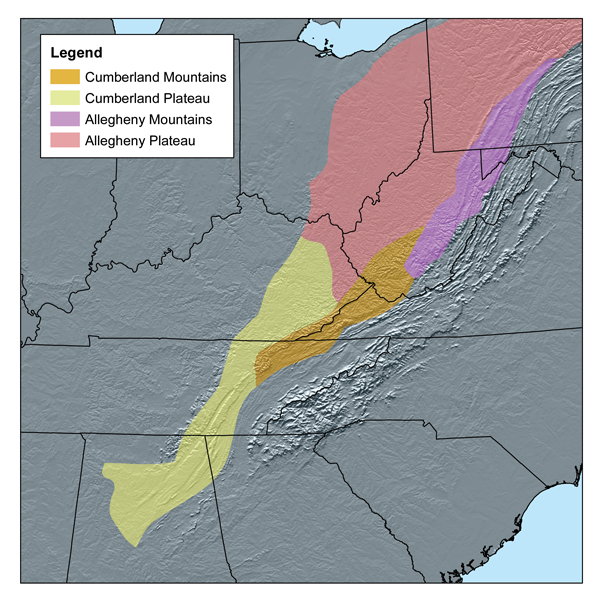
Cumberland Mountains
The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the Crab Orchard Mountains. Their highest peak, with an elevation of above mean sea level, is High Knob, which is located near Norton, Virginia. According to the USGS, the Cumberland Mountain range is long and wide, bounded by the Russell Fork on the northeast, the Pound River and Powell River on the southeast, Cove Creek on the southwest, and Tackett Creek, the Cumberland River, Poor Fork Cumberland River, and Elkhorn Creek on the northwest. The crest of the range forms the Kentucky and Virginia boundary from the Tennessee border to the Russell Fork River. Variant names of the Cumberland Mountains include Cumberland Mountain, Cumberland Range, Ouasioto Mountains, Ouasiota Mountains, Laurel Mountain, and Pine Mountain. They are nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range ( ) — also spelled Alleghany or Allegany, less formally the Alleghenies — is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada. Historically it represented a significant barrier to westward land travel and development. The Alleghenies have a northeast–southwest orientation, running for about from north-central Pennsylvania southward, through western Maryland and eastern West Virginia. The Alleghenies comprise the rugged western-central portion of the Appalachians. They rise to in northeastern West Virginia. In the east, they are dominated by a high, steep escarpment known as the Allegheny Front. In the west, they slope down into the closely associated Allegheny Plateau, which extends into Ohio and Kentucky. The principal settlements of the Alleghenies are Altoona, State College, and Johnstown, Pennsylvania; and Cumberland, Maryland. Using the USGS classification of physical geography (physiography) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau ( ) is a large dissected plateau area of the Appalachian Mountains in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio. It is divided into the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau and the glaciated Allegheny Plateau. The plateau extends southward into western West Virginia, eastern Kentucky, and Tennessee, where it is instead called the Cumberland Plateau. The plateau terminates in the east at the Allegheny Mountains, which are the highest ridges just west of the Allegheny Front. The Front extends from central Pennsylvania through Maryland and into eastern West Virginia. The plateau is bordered on the west by glacial till plains in the north, generally north of the Ohio River, and the Bluegrass Region south of the Ohio River. Elevations vary greatly. In the glaciated Allegheny Plateau, relief may only reach one hundred feet or less. In the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau in southeastern Ohio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration
Exploration is the process of exploring, an activity which has some Expectation (epistemic), expectation of Discovery (observation), discovery. Organised exploration is largely a human activity, but exploratory activity is common to most organisms capable of directed Animal locomotion, locomotion and the ability to learn, and has been described in, amongst others, social insects foraging behaviour, where feedback from returning individuals affects the activity of other members of the group. Types Geographical Geographical exploration, sometimes considered the default meaning for the more general term exploration, is the practice of discovering lands and regions of the planet Earth remote or relatively inaccessible from the origin of the explorer. The surface of the Earth not covered by water has been relatively comprehensively explored, as access is generally relatively straightforward, but underwater and subterranean areas are far less known, and even at the surface, much is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settler
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a Human settlement, settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among the first settling at a place that is new to the settler community. The process of settling land can be, and has often been, controversial: while human migration is a normal phenomenon by itself, it has not been uncommon throughout human history for settlers to have arrived in already-inhabited lands Settler colonialism, without the intention of living alongside the native population. In these cases, the conflict that arises between the settlers and the natives (or Indigenous peoples) may result in the dispossession of the latter within the contested territory, usually violently. While settlers can act independently, they may receive support from the government of their country or colonial empire or from a non-governmental organization as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |