|
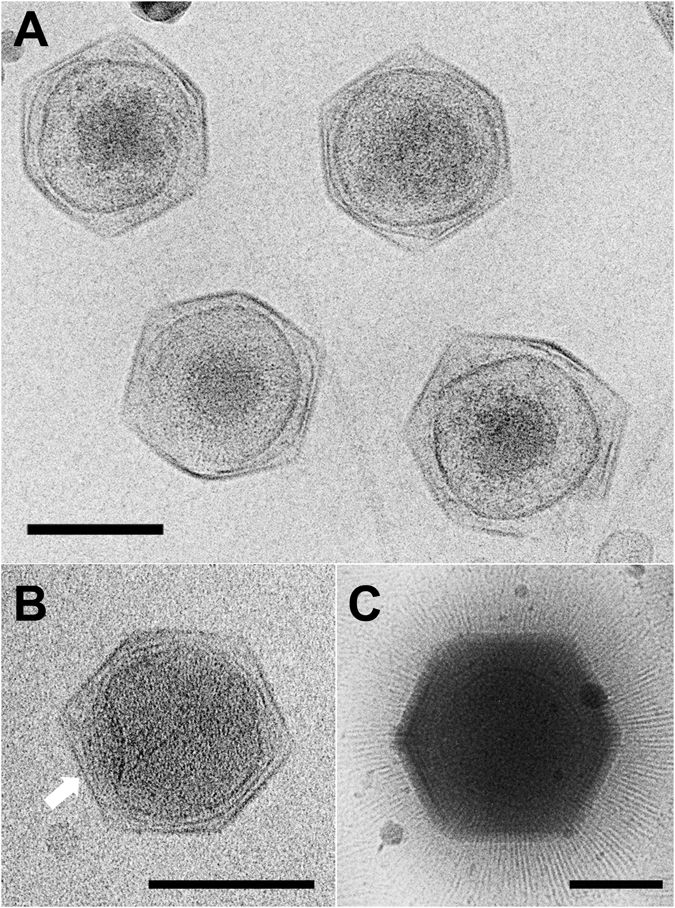
Mimivirus
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant viruses, in the family ''Mimiviridae''. It is believed that Amoeba serve as their natural hosts. It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses. In colloquial speech, APMV is more commonly referred to as just "mimivirus". Mimivirus, short for "mimicking microbe", is so called to reflect its large size and apparent Gram-staining properties. Mimivirus has a large and complex genome compared with most other viruses. Until 2013, when a larger virus ''Pandoravirus'' was described, it had the largest capsid diameter of all known viruses. History APMV was discovered accidentally in 1992 within the amoeba ''Acanthamoeba, Acanthamoeba polyphaga'', after which it is named, during research into legionellosis by researchers from Marseille and Leeds. The virus was observed in a Gram stain and mistakenly thought to be a Gram-positive bacterium. As a consequence it was named ''Bradfordcoccus'', after Bradford, England, where the amoeba h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sputnik Virophage
Sputnik virophage (from Russian "satellite") is a subviral agent that reproduces in amoeba cells that are already infected by a certain helper virus; Sputnik uses the helper virus's machinery for reproduction and inhibits replication of the helper virus. It is known as a virophage, in analogy to the term ''bacteriophage''. Viruses like Sputnik that depend on co-infection of the host cell by helper viruses are known as satellite viruses. At its discovery in a Paris water-cooling tower in 2008, Sputnik was the first known satellite virus that inhibited replication of its helper virus and thus acted as a parasite of that virus. In analogy, it was called a '' virophage''. Sputnik virophages were found infecting giant viruses of '' Mimiviridae'' group A. However, they are able to grow in amoebae infected by ''Mimiviridae'' of any of the groups A, B, and C. Virology Sputnik was first isolated in 2008 from a sample obtained from humans; it was harvested from the contact lens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamavirus
Mamavirus is a large and complex virus in the Group I family ''Mimiviridae''. The virus is exceptionally large, and larger than many bacteria. Mamavirus and other mimiviridae belong to nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus (NCLDVs) family. Mamavirus can be compared to the similar complex virus mimivirus; mamavirus was so named because it is similar to but larger than mimivirus. Discovery Mamavirus was first reported in September 2008. Like mimivirus, mamavirus was isolated from an amoeba in a cooling tower. The mimiviridae were not discovered until recently because of their size; when filtered the mimiviridae stay with the bacteria which led scientists to believe they were also bacteria. Mimivirus was first isolated in 1992 when scientists were looking for the cause of a pneumonia outbreak in Bradford, UK. Due to its size it was named ''Bradfordcoccus'' and put in a freezer with scientists thinking it was a bacterium. A decade later, Jean-Michel Claverie and Didier Raoult discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Virus
A giant virus, sometimes referred to as a girus, is a very large virus, some of which are larger than typical bacteria. All known giant viruses belong to the phylum ''Nucleocytoviricota''. Description While the exact criteria as defined in the scientific literature vary, giant viruses are generally described as viruses having large, pseudo-Capsid#Icosahedral, icosahedral capsids (200 to 400 nanometers in diameter) that may be surrounded by a thick (approximately 100 nm) layer of filamentous protein fibers. The viruses have large, double-stranded DNA genomes (300 to >1000 kilobasepairs) that encode a large contingent of genes (of the order of 1000 genes). The best characterized giant viruses are the phylogenetically related mimivirus and megavirus, which belong to the family ''Mimiviridae'' (aka ''Megaviridae''), and are distinguished by their large capsid diameters. Giant viruses from the deep ocean, terrestrial sources, and human patients contain genes encoding Cytochrome P4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimiviridae
''Mimiviridae'' is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family contains three subfamilies that contain nine genera., UCPMS ID: 1889607PDF/ref> Fig. 4 and §Discussion: "Considering that tupanviruses comprise a sister group to amoebal mimiviruses..." Viruses in this family belong to the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA virus clade (NCLDV), also referred to as giant viruses. History The first member of this family, Mimivirus, was discovered in 2003, and the first complete genome sequence was published in 2004. However, the mimivirus Cafeteria roenbergensis virus was isolated and partially characterized in 1995, although the host was misidentified at the time, and the virus was designated BV-PW1. Taxonomy The family contains the following subfamilies and genera (-''virinae'' denotes subfamily and -''virus'' denotes genus): * '' Aliimimivirinae'' ** '' Rheavirus'' * '' Klosneuvirinae'' ** '' Fadolivirus'' ** '' Theiavirus'' ** '' Yasminev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megavirus
''Megavirus'' is a viral genus, phylogenetically related to '' Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). In colloquial speech, ''Megavirus chilense'' is more commonly referred to as just "Megavirus". Until the discovery of pandoraviruses in 2013, it had the largest capsid diameter of all known viruses, as well as the largest and most complex genome among all known viruses. Discovery ''Megavirus'' was isolated from a water sample collected in April 2010 off the coast of Chile, near the marine station in Las Cruces, by Jean-Michel Claverie and Chantal Abergel from the Structural & Genomic Information laboratory (IGS, CNRS and Aix-Marseille University). Megavirus was isolated by co-cultivation with a variety of ''Acanthamoeba'' laboratory strains ('' Acanthamoeba polyphaga'', '' Acanthamoeba castellanii'', '' Acanthamoeba griffini'') following a protocol pioneered by Timothy Rowbotham for isolating intracellular parasitic bacteria. Megavirus infects amoebas. Structure The Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee On Taxonomy Of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families. History The International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses (ICNV) was established in 1966, at the International Congress for Microbiology in Moscow, to standardize the naming of virus taxa. The ICVN published its first report in 1971. For viruses infecting vertebrates, the first report i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram Staining
Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884. Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Gram-positive cells have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the cell wall that retains the primary stain, crystal violet. Gram-negative cells have a thinner peptidoglycan layer that allows the crystal violet to wash out on addition of ethanol. They are stained pink or red by the counterstain, commonly safranin or fuchsine. Lugol's iodine solution is always added after addition of crystal violet to form a stable complex with crystal violet that strengthens the bonds of the stain with the cell wall. Gram staining is almost always the first step in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |