|
Milos
Milos or Melos (; , ; ) is a volcanic Greek island in the Aegean Sea, just north of the Sea of Crete. It is the southwestern-most island of the Cyclades group. The ''Venus de Milo'' (now in the Louvre), the ''Poseidon of Melos'' (now in the NAMA) and the '' Asclepius of Milos'' (now in the British Museum) were all found on the island, as was an archaic Apollo now in Athens. Milos is a popular tourist destination during the summer. The municipality of Milos also includes the uninhabited offshore islands of Antimilos and Akradies. The combined land area is and at the 2021 census the population was 5,193 inhabitants. History Obsidian (a glass-like volcanic rock) from Milos was a commodity as early as 15,000 years ago. Natural glass from Milos was transported over long distances and used for razor-sharp "stone tools" well before farming began and later: "There is no early farming village in the Near East that doesn't get obsidian". The mining of obsidian did not lead to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Museum Of Milos
The Archaeological Museum of Milos is a museum in Plaka on the island of Milos, in Greece. Its collections include exhibits dating from the late Neolithic to the Byzantine period. The unique is collection of ancient Cycladic art, especially numerous findings from Phylakopi on Milos, from early Bronze Age to the late Bronze Age. The best pieces from Phylakopi are in the Ashmolean Museum (Oxford), British Museum, National Museum of Athens, and elsewhere around the world. The museum is housed since 1985 in a neo-classical building dating from 1870 on the main square in Plaka. In the porch of the building and on the courtyard is lapidary with torsos from the late antiquity. Archaeological Museum of Milos, facade of the building, 152616.jpg Archaeological Museum of Milos, Lapidary, 152665.jpg AM Milos, Lapidary in porch of the building, 152611.jpg Room 1 The first room hosts large pottery vessels since the late Bronze Age to the Greek archaic period, a modern copy of the statue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plaka, Milos
Plaka (official name: Milos) is the chief town in Milos, a Greek island in the Cyclades group. EETAA local government changes It is perched on the top of large rock, overlooking the gulf of Milos. No cars can enter the village because of the narrow spaces between walls and buildings. Motorbikes, mopeds and the like are the only usable vehicles. Population 902 (2021). References External links Plaka at Milos Island website Milos Populated places in Milos (regional unit) {{SouthAegean-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asclepius Of Milos
The Asclepius of Milos or Asklepios of Melos is a marble head from what was once a colossal ancient Greek statue of Asclepius found on the island of Milos in Greece. It was acquired by the British Museum along with the rest of the Blacas collection in 1867. Discovery The head was found in the mid nineteenth century at the shrine of Asclepius on the island of Milos in the Cyclades, Greece. It was later acquired by the French diplomat and collector Louis, Duke of Blacas. The Blacas collection was purchased in its entirety by the British Museum in 1867. Description The head is made from Parian marble and was once part of a twice life-size cult statue of the ancient Greek god of medicine and healing Asclepius (or Asklepios). It was made from three pieces, only two of which are extant. Around the head are drill holes and lead pegs for a now missing gold wreath that once crowned the statue. The serene expression on the deity's face is typical of Hellenistic sculpture from this peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milos (regional Unit)
Milos () is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of South Aegean. The regional unit covers the islands of Kimolos, Milos, Serifos, Sifnos and several smaller islands in the Aegean Sea. Administration As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the Milos regional unit was created out of part of the former Cyclades Prefecture. It is subdivided into 4 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox): * Kimolos (9) * Milos (11) * Serifos (15) * Sifnos (17) Province The province of Milos () was one of the provinces A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ... of the Cyclades Prefecture. It had the same territory as the present regional unit. It was abolished in 2006. References Regional units of the South Ae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klima, Milos
Klima is a seaside village of Milos, Cyclades, Greece. According to the 2021 Greek census it had 8 residents. The village is known for its traditional fishermen houses called ''syrmata'' (wires). They are two-store houses with the first floor being used by the fisherman's family to live and the ground floor being used to store the boat during winter. These houses usually have colorfully painted doors and windows. Nowadays some are used as tourist accommodations. Klima is near the location of ancient Milos and its theater el">:el:Αρχαίο_θέατρο_Μήλου">el and near the location where Venus de Milo The ''Venus de Milo'' or ''Aphrodite of Melos'' is an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek marble sculpture that was created during the Hellenistic art, Hellenistic period. Its exact dating is uncertain, but the modern consensus places it in the 2nd ... was found. References {{reflist Milos Populated places in Milos (regional unit) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimilos
Antimilos (; ) is a Greek island in the Cyclades group, northwest of Milos. Administratively, it is part of the municipality of Milos. Antimilos is an uninhabited mass of trachyte (671 m height), often called Erimomilos (Desert Milos). It is a volcanic island and the crater is still obvious. Ancient inhabitants transformed the crater to an open rain tank. On the island lives a rare variation of the common goat called ''Capra aegagrus pictus''. It is similar but not the same as the Cretan goat known as " kri-kri" (''Capra aegagrus creticus''). History According to an interpretation of Homer's ''Odyssey'', it is the island of the sun god Helios In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; ; Homeric Greek: ) is the god who personification, personifies the Sun. His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") an ..., where Odysseus's companions slaughtered the sacred cattle of the sun god. Previously, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Aegean
The South Aegean (, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It consists of the Cyclades and Dodecanese island groups in the central and southeastern Aegean Sea. Administration The South Aegean region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with the North Aegean region, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of the Aegean based at Piraeus. The capital of the region is situated in Ermoupoli on the island of Syros. The administrative region includes 50 inhabited islands, including the popular tourism destinations of Mykonos, Santorini and Rhodes. Until the Kallikratis reform, the region consisted of the two prefectures of the Cyclades (capital: Ermoupoli) and the Dodecanese (capital: Rhodes). Since 1 January 2011 it is divided into 13 regional units, formed around major islands: * Andros * Kalymnos * Karpathos-Kasos * Kea-Kyth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylakopi
Phylakopi (), located at the northern coast of the island of Milos, is one of the most important Bronze Age settlements in the Aegean and especially in the Cyclades. The importance of Phylakopi is in its continuity throughout the Bronze Age (i.e. from mid-3rd millennium BC until the 12th century BC) and because of this, it is the type-site for the investigation of several chronological periods of the Aegean Bronze Age. Excavations Phylakopi was first excavated between 1896 and 1899 under the British School at Athens (as well as all subsequent projects). The excavation was remarkably ahead of its time, with Duncan MacKenzie (the later foreman to Sir Arthur Evans at Knossos) recording detailed stratigraphic information. The excavation revealed a hitherto unknown Bronze Age Cycladic settlement with continuity throughout the Early Bronze Age to the very end of the Late Bronze Age. It was from this excavation that the three phase stratigraphy was suggested, the second and third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus De Milo
The ''Venus de Milo'' or ''Aphrodite of Melos'' is an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek marble sculpture that was created during the Hellenistic art, Hellenistic period. Its exact dating is uncertain, but the modern consensus places it in the 2nd century BC, perhaps between 160 and 110 BC. It was discovered in 1820 on the island of Milos, Greece, and has been displayed at the Musée du Louvre, Louvre Museum since 1821. Since the statue's discovery, it has become one of the most famous works of ancient Greek sculpture in the world. The ''Venus de Milo'' is believed to depict Aphrodite, the Greek goddess of love, whose Roman mythology, Roman Interpretatio graeca, counterpart was Venus (mythology), Venus. Made of Parian marble, the statue is larger than life size, standing over high. The statue is missing both arms. The original position of these missing arms is uncertain. The sculpture was originally identified as depicting Aphrodite holding the apple of discord as a marble hand h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter elements such as silicon, oxygen, aluminium, sodium, and potassium. It is commonly found within the margins of rhyolite, rhyolitic lava flows known as obsidian flows. These flows have a high content of silicon dioxide, silica, giving them a high viscosity. The high viscosity inhibits the atomic diffusion, diffusion of atoms through the lava, which inhibits the first step (nucleation) in the formation of mineral crystals. Together with rapid cooling, this results in a natural glass forming from the lava. Obsidian is hard, Brittleness, brittle, and amorphous; it therefore Fracture (mineralogy)#Conchoidal fracture, fractures with sharp edges. In the past, it was used to manufacture cutting and piercing tools, and it has been used experimentally as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
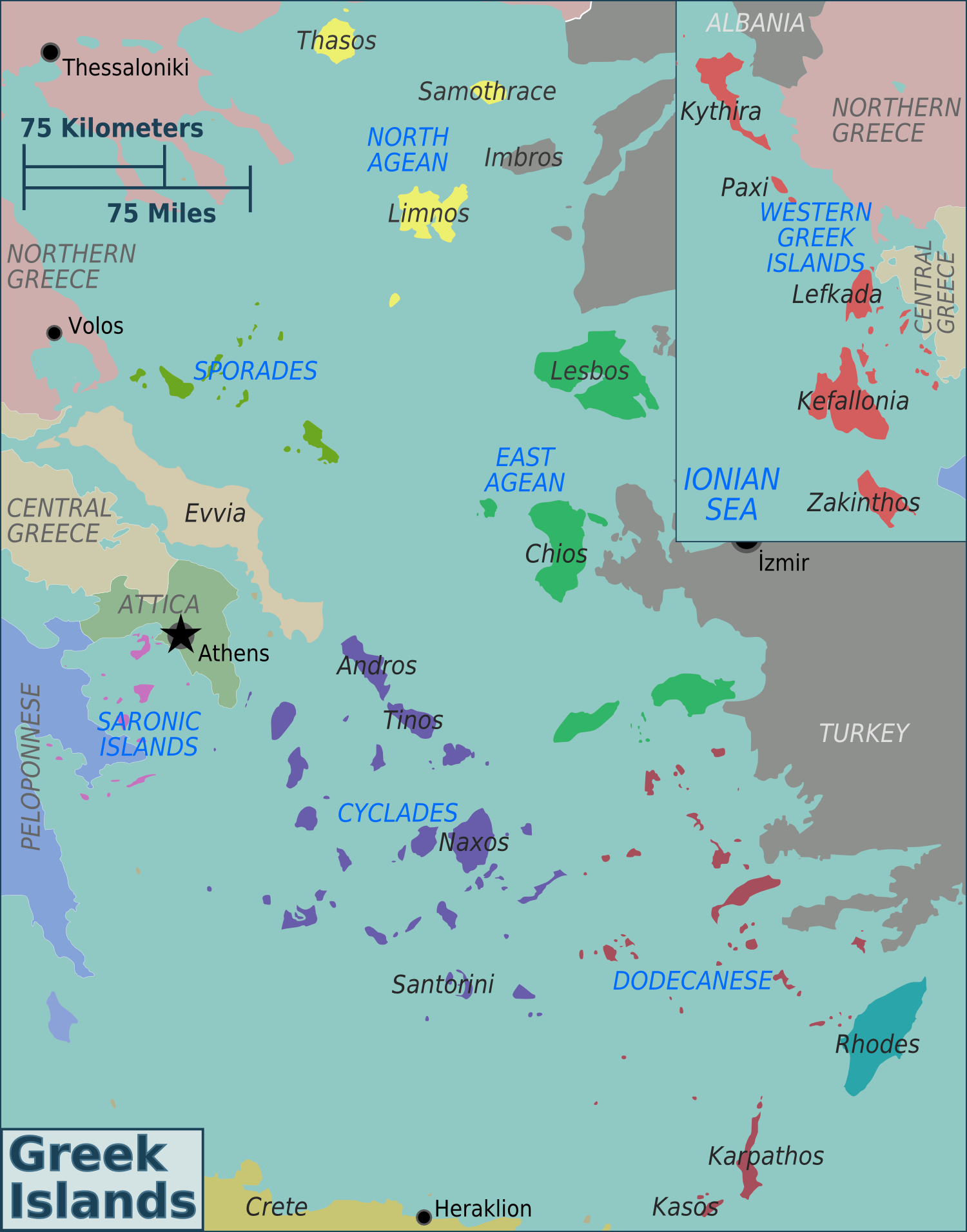
Greek Island
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by both area and population is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island in area is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn connects to the Black Sea, by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus, respectively. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639 m (8,658 ft) to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The Dodecanese, located to the southeast, includes the islands of Rhodes, Kos, and Patmos; the islands of Delos and Naxos are wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |