|
Milion
The Milion ( or , ''Mílion''; ) was a marker from which all distances across the Roman Empire were measured. Erected by Septimius Severus in the 3rd century AD in the city of Byzantium, it became the zero-mile marker for the empire upon the re-founding of the city as Constantinople in 330 AD. Thereafter, it would serve as the starting-place for the measurement of distances for all the roads leading to the cities of the Eastern Roman Empire. It thus served the same function as the Golden Milestone (') in Rome's forum, erected by Augustus. The domed building of the Milion rested on four large arches and, over the centuries, it was expanded and decorated with several statues and paintings. Though it had survived the sack of Constantinople in 1204 and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453, it disappeared by the start of the 16th century in the Ottoman era. During excavations in the 1960s, some partial fragments of the Milion were discovered under houses in the area. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Constantinople Imperial District
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
14 Regions Of Constantinople
The ancient city of Constantinople was divided into 14 administrative regions (, ). The system of fourteen ''regiones'' was modelled on the fourteen ''regiones'' of Rome, a system introduced by the first Roman emperor Augustus in the 1st century AD. After Emperor Constantine the Great re-founded Byzantium as Constantinople and ''Nova Roma'' ('New Rome') in the early 4th century, he or his immediate successors divided Constantinople into its own 14 ''regiones''. Each region () was numbered, and their boundaries and landmarks in the 5th century were enumerated by the '' Notitia Urbis Constantinopolitanae'', which also gives details of the city's '' Cura Annonae'', the public grain ration which was distributed by ''regio''. Two ''regiones,'' XIII and XIV, were outside the original city walls. The 14 regions ''Regio I'' The area of the Ist ''regio'' was defined by the Great Palace, which lay within it, the southeastern edge of Hippodrome, the Byzantine acropolis, and the sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Walls Of Constantinople
The Walls of Constantinople (; ) are a series of defensive wall, defensive stone walls that have surrounded and protected the city of Constantinople (modern Fatih district of Istanbul) since its founding as the new capital of the Roman Empire by Constantine the Great. With numerous additions and modifications during their history, they were the last great fortification system of ancient history, antiquity, and one of the most complex and elaborate systems ever built. They were also the largest and strongest fortification in both the ancient and medieval world. Initially built by Constantine the Great, the walls surrounded the new city on all sides, protecting it against attack from both sea and land. As the city grew, the famous double line of the Theodosian Walls was built in the 5th century. Although the other sections of the walls were less elaborate, they were, when well-manned, almost impregnable for any medieval besieger. They saved the city, and the Byzantine Empire with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia (; ; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque (; ), is a mosque and former Church (building), church serving as a major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The last of three church buildings to be successively erected on the site by the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire, it was completed in AD 537, becoming the world's largest interior space and among History of Roman and Byzantine domes, the first to employ a fully pendentive dome. It is considered the epitome of Byzantine architecture and is said to have "changed the history of architecture". From its dedication in 360 until 1453 Hagia Sophia served as the cathedral of Constantinople in the Divine Liturgy#Byzantine Rite, Byzantine liturgical tradition, except for the period 1204‑1261 when the Latin Empire, Latin Crusaders installed their own Hierarchy of the Catholic Church, hierarchy. After the fall of Constantinople in 1453, it served as a mosque, having its Minaret, minarets added ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
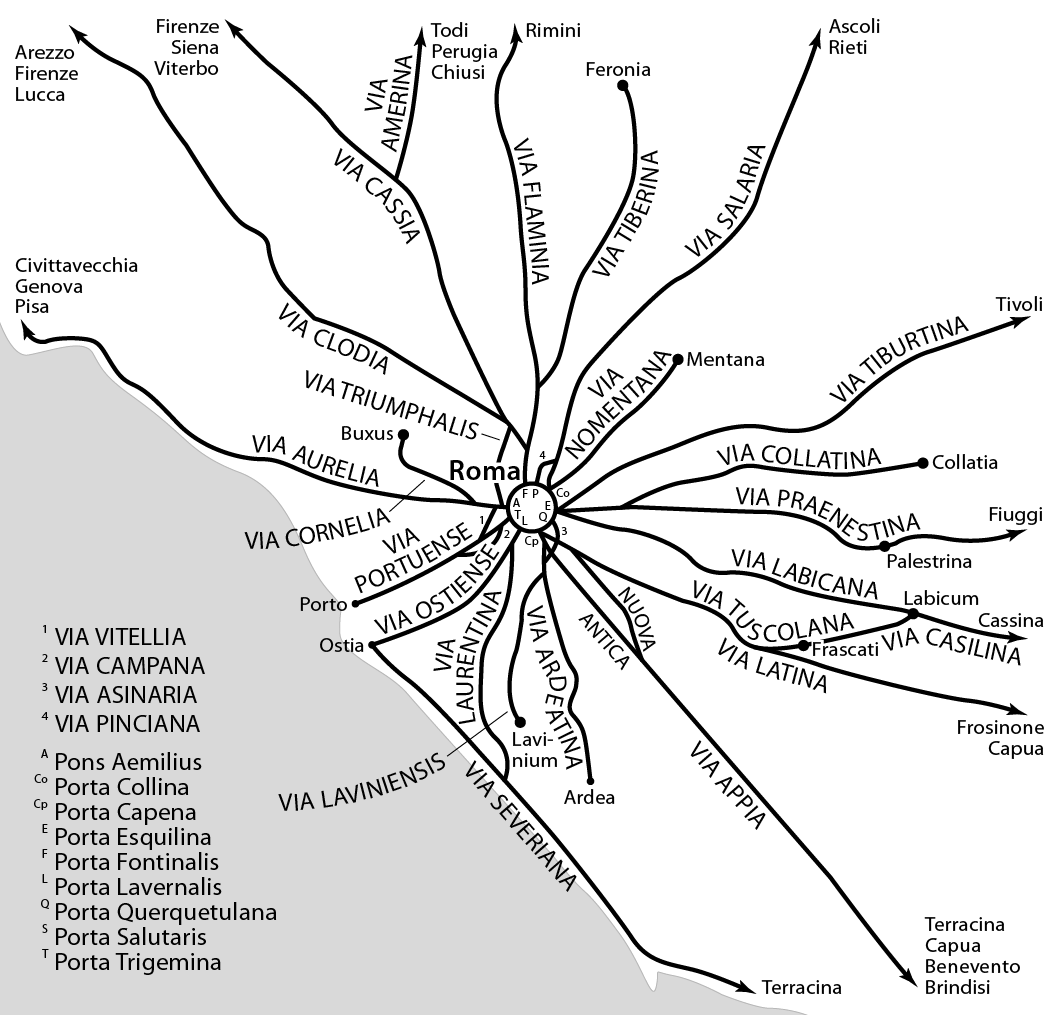
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Milliarium Aureum
The ''Milliarium Aureum'' (; ), or the "Golden Milestone," was a monument, probably of marble or gilded bronze, erected by the Emperor Augustus near the Temple of Saturn in the central Forum of Ancient Rome. All roads were considered to begin at this monument and all distances in the Roman Empire were measured relative to it. On it perhaps were listed all the major cities in the empire and distances to them, though the monument's precise location and inscription has remained a matter of debate among historians. According to the 19th century ecclesiastical historian Philip Schaff, the phrase "all roads lead to Rome" is a reference to the ''Milliarium Aureum''—the specific point to which all roads were said to lead. A marble structure speculated to be the base of the milestone is present in the Roman Forum. History According to Cassius Dio, Augustus, in his position as ''curator viarum'', erected the monument in 20 BCE. It probably received the name ''Milliarium Aureum'' soo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Augustaeum
The ''Augustaion'' () or, in Latin language, Latin, ''Augustaeum'', was an important ceremonial square in ancient and medieval Constantinople (modern Istanbul, Turkey), roughly corresponding to the modern ''Aya Sofya Meydanı'' (Turkish language, Turkish, "Hagia Sophia Square"). Originating as a public market, in the 6th century it was transformed into a closed courtyard surrounded by porticoes, and provided the linking space between some of the most important edifices in the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine capital. The square survived until the late Byzantine period, albeit in ruins, and traces were still visible in the early 16th century. History The square dates back to ancient Byzantium, before its conversion into an imperial capital by Constantine the Great. When Roman Emperor Septimius Severus (r. 193–211) rebuilt the city, he erected a large square surrounded by porticoes, hence named the ''Tetrastoon'' ("four stoas"). In the center of the square stood a column with a statue o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tetrapylon
A tetrapylon (plural tetrapyla; ; , also used in English) is a rectangular form of monument with arched passages in two directions, at right angles, generally built on a Crossroads (culture), crossroads. They appear in ancient Roman architecture, usually as a form of the Roman triumphal arch at significant crossroads or geographical "focal points". A tetrapylon was effectively a 'doubling' of the original triumphal arch form; with a total of four major arched openings, one on each side of the structure (one pair of openings opposite each other along one axis, and a second pair of openings of equal or lesser prominence perpendicular to the first pair; hence a structure with two barrel vaulted passageways, in the form of a cross). Roman examples are usually roughly square in floor plan, plan, with the crossing archways of the same size; in some later examples, the plan is oblong, with the longer sides having a larger archway as for example at the Arc de Triomphe in Paris. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mese (Constantinople)
The ''Mese'' ( ''i Mése dós', lit. "Middle treet) was the main thoroughfare of ancient Constantinople and the scene of many Byzantine imperial processions. Its ancient course is largely followed by the modern ''Divan Yolu'' ("Road to the Divan"). Route of the Mese The ''Mese'' started at the Milion monument, close to the Hagia Sophia, and led straight westwards. It passed the Hippodrome and the palaces of Lausos and Antiochus, and after ca. 600 meters reached the oval-shaped Forum of Constantine where one of the city's two Senate houses stood. This stretch of the street was also known as the ''Regia'' (, "Imperial Road"), as it formed the original ceremonial route from the Great Palace and the Augustaion square to the forum of the city's founder. From there, the street continued to the square Forum of Theodosius or Forum of the Bull (''Forum Tauri''), as it was also known. In about the middle of this stretch, the great mall known as ''Makros Embolos'' joined the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a Rotunda (architecture), rotunda wall, a Tholobate, drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an Oculus (architecture), oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian architecture, Persian, Ancient Greek architecture, Hellenistic, Ancient Roman architecture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |