|
Milang Language
Milang is a Siangic languages, Siangic or Tani languages, Tani language of Upper Siang district, Arunachal Pradesh, India. It is spoken in the 3 villages of Milang (Milang: ''Holon''), Dalbing, and Pekimodi (Milang: ''Moobuk Ade''), located in Mariyang Subdivision, Upper Siang District, Arunachal Pradesh (Tayeng 1976). Classification Milang has traditionally been classified as the most divergent of the Tani languages, hence ultimately Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan. Post & Blench (2011) reclassified it as Siangic languages, Siangic, on the basis of clear correspondences with the Koro language (India), Koro language in vocabulary that may not ultimately be of Sino-Tibetan origin. The implication is that Milang may, like other Siangic languages, harbour a non-Sino-Tibetan Substratum (linguistics), substrate, or may be a non-Sino-Tibetan language with Sino-Tibetan features acquired through prolonged contact, perhaps with the neighbouring and much larger Padam (tribe), Padam trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and largest town. It borders the Indian states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares Borders of India, international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region in the north at the McMahon Line. Arunachal Pradesh is claimed in its entirety by China as South Tibet as part of the Tibet Autonomous Region; China Sino-Indian War, occupied some regions of Arunachal Pradesh in 1962 but later withdrew its forces. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,383,727 and an area of . With only 17 inhabitants per square kilometre, it is the least densely populated state of India. It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koro Language (India)
Koro is a language spoken in Arunachal Pradesh, India. It is typically classified as a Sino-Tibetan language, and has some resemblances to Tani farther to the east. It has been argued that Koro is actually part of the Greater Siangic family, independent from but influenced by the Sino-Tibetan family. Koro is spoken by about 1,500 people in the Koro-Aka tribe who are found in East Kameng District, Arunachal Pradesh, northeast India. Few speakers are under 20 years old. The majority of Koro speakers live in bilingual households in which one or more members speak Ako or another indigenous language rather than Koro. The Koro-Aka tribe lives among the Aka (Hruso) tribe. However, the Koro-Aka people speak a very distantly related language from the remaining Aka tribe who speak Hruso-Aka. Researchers hypothesize Koro may have originated from a group of people enslaved and brought to the area. Classification Recognition in the academic literature of Koro as a distinct language goes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Languages Of India
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, invasive species, and climate change. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration. Human activity is a significant cause in causing some species to become endangered. Conservation status The conservation status of a species indicates the likelihood that it will become extinct. Multiple factors are considered whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeast India. It was formed from the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and India declared it as a state on 20 February 1987. Itanagar is its capital and largest town. It borders the Indian states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares Borders of India, international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region in the north at the McMahon Line. Arunachal Pradesh is claimed in its entirety by China as South Tibet as part of the Tibet Autonomous Region; China Sino-Indian War, occupied some regions of Arunachal Pradesh in 1962 but later withdrew its forces. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,383,727 and an area of . With only 17 inhabitants per square kilometre, it is the least densely populated state of India. It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bern
The University of Bern (, , ) is a public university, public research university in the Switzerland, Swiss capital of Bern. It was founded in 1834. It is regulated and financed by the canton of Bern. It is a comprehensive university offering a broad choice of courses and programs in eight faculty (division), faculties and some 150 institutes. With around 19,000 students, the University of Bern is the third largest university in Switzerland. Organization The University of Bern operates at three levels: university, faculties and institutes. Other organizational units include interfaculty and general university units. The university's highest governing body is the Senate, which is responsible for issuing statutes, rules and regulations. Directly answerable to the Senate is the University Board of Directors, the governing body for university management and coordination. The board comprises the rector, the vice-rectors and the administrative director. The structures and functions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padam Language
Padam, also known as Bor-abor, is a dialect of the Mishing language. Phonology The Padam dialect consists of the following phonemes: Consonants * /s/ can also be heard as a palatal fricative � Vowels References * {{Languages of Northeast India Tani languages Languages of Arunachal Pradesh Languages of Assam Endangered languages of India Vulnerable languages Endangered Sino-Tibetan languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padam (tribe)
Padam is a sub-tribe of Adi. Which speaks one of the Sino-Tibetan languages. They were a nomadic warrior race and used to had a reputation as fierce warrior among all the clans in Arunachal Pradesh , they are believed to have migrated to present Arunachal Pradesh from Tibet. Distribution They inhabits in the region of upper siang, east siang, lower Dibang valley and parts of Lohit and Namsai district of Arunachal Pradesh Geography Although it is almost from Pasighat, their land resides in the Upper Siang district, throughout the Lower Dibang Valley, and makes up about 50 percent of the Lohit district. Their indigenous land is watered by the Yamne River flowing through the valley. Culture They were originally nomadic people but usually grow their food, mainly rice. The Padam people eat birds and animals, such as pigs, cows, and mithun. They are great hunters and usually have licensed guns and (long metal swords). Padam men wear different varieties of clothes and costu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substratum (linguistics)
In linguistics, a stratum (Latin for 'layer') or strate is a historical layer of language that influences or is influenced by another language through contact. The notion of "strata" was first developed by the Italian linguist Graziadio Isaia Ascoli, and became known in the English-speaking world through the work of two different authors in 1932. Both concepts apply to a situation where an intrusive language establishes itself in the territory of another, typically as the result of migration. Whether the superstratum case (the local language persists and the intrusive language disappears) or the substratum one (the local language disappears and the intrusive language persists) applies will normally only be evident after several generations, during which the intrusive language exists within a diaspora culture. In order for the intrusive language to persist, the ''substratum'' case, the immigrant population will either need to take the position of a political elite or immigrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
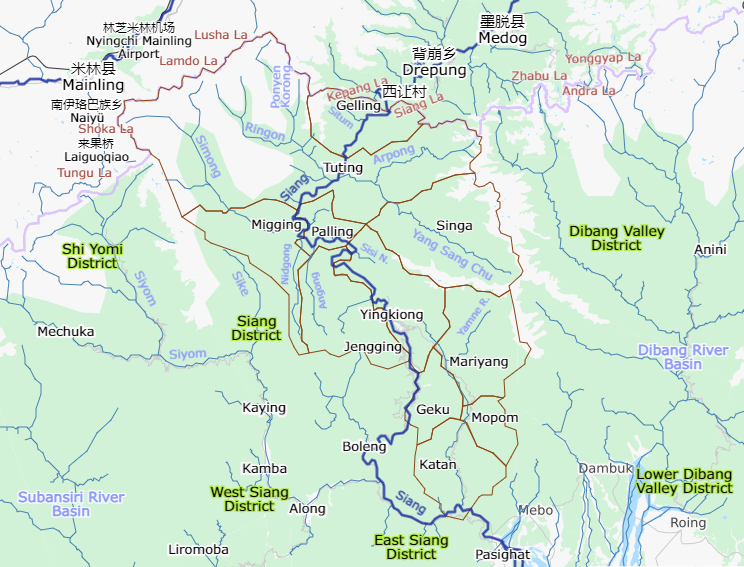
Upper Siang District
Upper Siang (Pron:/ˈsjæŋ or ˈsɪæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. It is the fourth least populous district in the country (out of 640). History The majority of the people are of the Adi tribe while the Memba, Khamba tribe also exists there. Part of the area was controlled by the Tibetan Kingdom of Powo when streams of Tibetan pilgrims searching for one of the 'hidden lands' or beyul () referred to in the prophecies of Guru Rinpoche in the East Himalayas from the mid-seventeenth century came south over the Doshong La pass, to seek the particular location of one of these earthly paradises called Padma bkod (written variously Pema köd, Pemakö and Pemako), literally 'Lotus Array' in the region. The region became administered by British India with the Simla Accord of 1914 and the demarcation of the McMahon Line, though China considers it part of South Tibet. The district was formed in 1999 when it was split from East Siang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Tibetan Languages
Sino-Tibetan (also referred to as Trans-Himalayan) is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan language. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Sinitic languages. Other Sino-Tibetan languages with large numbers of speakers include Burmese (33 million) and the Tibetic languages (6 million). Four United Nations member states (China, Singapore, Myanmar, and Bhutan) have a Sino-Tibetan language as a main native language. Other languages of the family are spoken in the Himalayas, the Southeast Asian Massif, and the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Most of these have small speech communities in remote mountain areas, and as such are poorly documented. Several low-level subgroups have been securely reconstructed, but reconstruction of a proto-language for the family as a whole is still at an early stage, so the higher-level structure of Sino-Tibetan re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Siang District
Upper Siang (Pron:/ˈsjæŋ or ˈsɪæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. It is the fourth least populous district in the country (out of 640). History The majority of the people are of the Adi tribe while the Memba, Khamba tribe also exists there. Part of the area was controlled by the Tibetan Kingdom of Powo when streams of Tibetan pilgrims searching for one of the 'hidden lands' or beyul () referred to in the prophecies of Guru Rinpoche in the East Himalayas from the mid-seventeenth century came south over the Doshong La pass, to seek the particular location of one of these earthly paradises called Padma bkod (written variously Pema köd, Pemakö and Pemako), literally 'Lotus Array' in the region. The region became administered by British India with the Simla Accord of 1914 and the demarcation of the McMahon Line, though China considers it part of South Tibet. The district was formed in 1999 when it was split from East Siang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tani Languages
The Tani language, often referred to as Tani languages, encompasses a group of closely related languages spoken by the Tani people in the northeastern region of India, primarily in the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam. These languages belong to the Sino-Tibetan family and include several major dialects such as in Mising people, Mising, Galo people, Galo, Apatani people, Apatani, Adi people, Adi, Tagin people, Tagin, and Nyishi people, Nyishi. Background The Tani languages are spoken by about 2,170,500 people of Arunachal Pradesh, including the Adi people, Adi, Apatani people, Apatani, Galo people, Galo, Mising people, Mising, Nishi people, Nyishi, Tagin people, Tagin, and of the East Kameng, West Kameng, Papumpare, Lower Subansiri, Upper Subansiri, West Siang, East Siang, Upper Siang, Lower Dibang Valley and Lohit districts of Arunachal Pradesh and Dhemaji district, Dhemaji, Lakhimpur district, North Lakhimpur, Sonitpur district, Sonitpur, Majuli etc. districts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |