|
Microvessel
The microcirculation is the circulatory system, circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ (anatomy), organ Tissue (biology), tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion, thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pericytes
Pericytes (formerly called Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane of blood capillaries, where they communicate with endothelial cells by means of both direct physical contact and paracrine signaling. The morphology, distribution, density and molecular fingerprints of pericytes vary between organs and vascular beds. Pericytes help in the maintainenance of homeostatic and hemostatic functions in the brain, where one of the organs is characterized with a higher pericyte coverage, and also sustain the blood–brain barrier. These cells are also a key component of the neurovascular unit, which includes endothelial cells, astrocytes, and neurons. Pericytes have been postulated to regulate capillary blood flow and the clearance and phagocytosis of cellular debris ''in vitro.'' Pericytes stabilize and monitor the maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
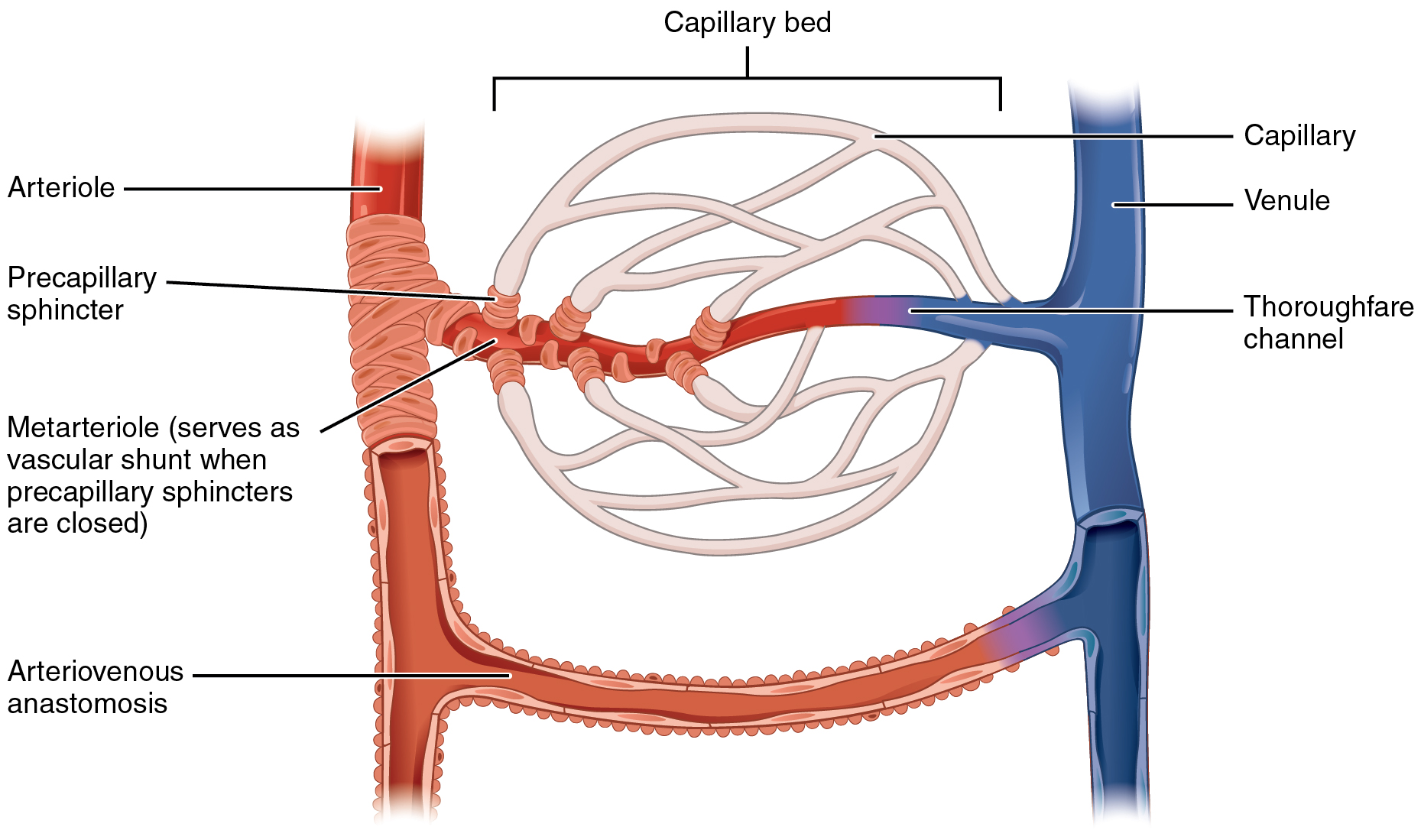
Metarteriole
A metarteriole is a short microvessel in the microcirculation that links arterioles and capillaries. Instead of a continuous tunica media The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. Artery The ..., they have individual smooth muscle cells placed a short distance apart, each forming a precapillary sphincter that encircles the entrance to that capillary bed. Constriction of these sphincters reduces or shuts off blood flow through their respective capillary beds. This allows the blood to be diverted to elsewhere in the body. Metarterioles exist in the '' mesenteric microcirculation'', and the name was originally conceived only to define the "''thoroughfare channels''" between arterioles and venules. In recent times the term has often been used instead to describe the smallest arterioles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lymphatic Capillaries
Lymph capillaries or lymphatic capillaries are tiny, thin-walled microvessels located in the spaces between cells (except in the central nervous system and non-vascular tissues) which serve to drain and process extracellular fluid. Upon entering the lumen of a lymphatic capillary, the collected fluid is known as lymph. Each lymphatic capillary carries lymph into a lymphatic vessel, which in turn connects to a lymph node, a small bean-shaped gland that filters and monitors the lymphatic fluid for infections. Lymph is ultimately returned to the venous circulation. Lymphatic capillaries are slightly larger in diameter than blood capillaries, and have closed ends (unlike the loop structure of blood capillaries). Lymph capillaries are strategically placed among the blood-related capillaries in order to have efficient and effective uptake from the interstitial fluid during capillary exchange. This intentional formation allows for a more rapid and continuous collection. Their unique s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
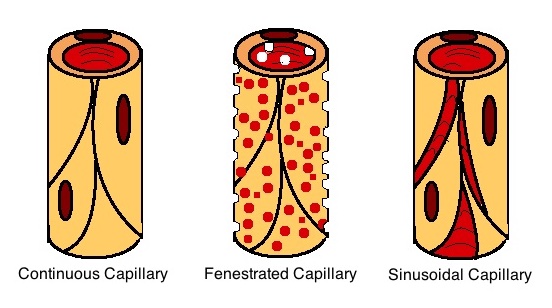
Capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metarteriole
A metarteriole is a short microvessel in the microcirculation that links arterioles and capillaries. Instead of a continuous tunica media The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside. Artery The ..., they have individual smooth muscle cells placed a short distance apart, each forming a precapillary sphincter that encircles the entrance to that capillary bed. Constriction of these sphincters reduces or shuts off blood flow through their respective capillary beds. This allows the blood to be diverted to elsewhere in the body. Metarterioles exist in the '' mesenteric microcirculation'', and the name was originally conceived only to define the "''thoroughfare channels''" between arterioles and venules. In recent times the term has often been used instead to describe the smallest arterioles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Endothelium
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the innermost layer of an artery or vein), consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the site of the exchange of many substances from the surrounding interstitial fluid, and they convey blood from the smallest branches of the arteries (arterioles) to those of the veins (venules). Other substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in microcirculation. Etymology ''Capillary'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "of or resembling hair", with use in English beginning in the mid-17th century. The meaning stems from the tiny, hairlike diameter of a capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Precapillary Sphincter
A precapillary sphincter is a band of contractile mural cells either classified as smooth muscle or pericytes that adjusts blood flow into capillaries. They were originally described in the mesenteric microcirculation, and were thought to only reside there. At the point where each of the capillaries originates from an arteriole, contractile mural cells encircle the capillary. This is called the precapillary sphincter. The precapillary sphincter has now also been found in the brain, where it regulates blood flow to the capillary bed. The sphincter can open and close the entrance to the capillary, by which contraction causes blood flow in a capillary to change as vasomotion occurs. In some tissues, the entire capillary bed may be bypassed by blood flow through arteriovenous anastomoses or through preferential flow through metarterioles. If the sphincter is damaged or cannot contract, blood can flow into the capillary bed at high pressures. When capillary pressures are high (as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Endothelial Cells
The endothelium (: endothelia) is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. Endothelial cells in direct contact with blood are called vascular endothelial cells whereas those in direct contact with lymph are known as lymphatic endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart to the smallest capillaries. These cells have unique functions that include fluid filtration, such as in the glomerulus of the kidney, blood vessel tone, hemostasis, neutrophil recruitment, and hormone trafficking. Endothelium of the interior surfaces of the heart chambers is called endocardium. An impaired function can lead to serious health issues throughout the body. Structure The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat (squamous) cells that line the interior s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer to fixation via perfusion, used in histological studies. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is delivered to tissue, or volume of blood per unit time (blood volumetric flow rate, flow) per unit tissue mass. The SI unit is m3/(s·kg), although for human organs perfusion is typically reported in ml/min/g. The word is derived from the French verb ''perfuser'', meaning to "pour over or through". All animal tissues require an adequate blood supply for health and life. Poor perfusion (malperfusion), that is, ischemia, causes health problems, as seen in cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and many other conditions. Tests verifying that adequate perfusion exists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |