|
Micronize
Micronization is the process of reducing the average diameter of a solid material's particles. Traditional techniques for micronization focus on mechanical means, such as milling and grinding. Modern techniques make use of the properties of supercritical fluids and manipulate the principles of solubility. The term micronization usually refers to the reduction of average particle diameters to the micrometer range, but can also describe further reduction to the nanometer scale. Common applications include the production of active chemical ingredients, foodstuff ingredients, and pharmaceuticals. These chemicals need to be micronized to increase efficacy. Traditional techniques Traditional micronization techniques are based on friction to reduce particle size. Such methods include milling, bashing and grinding. A typical industrial mill is composed of a cylindrical metallic drum that usually contains steel spheres. As the drum rotates the spheres inside collide with the particles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone (medication)
Progesterone (P4), sold under the brand name Prometrium among others, is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is a progestogen (medication), progestogen and is used in combination with estrogen (medication), estrogens mainly in hormone replacement therapy, hormone therapy for menopause, menopausal symptoms and hypogonadism, low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in women to support pregnancy and fertility and to treat gynecological disorders. Progesterone can be taken oral administration, by mouth, intravaginal administration, vaginally, and by injection (medicine), injection into muscle or fat, among other route of administration, routes. A progesterone vaginal ring and progesterone intrauterine device used for hormonal contraception, birth control also exist in some areas of the world. Progesterone is tolerability, well tolerated and often produces few or no side effects. However, a number of side effects are possible, for instance mood (psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
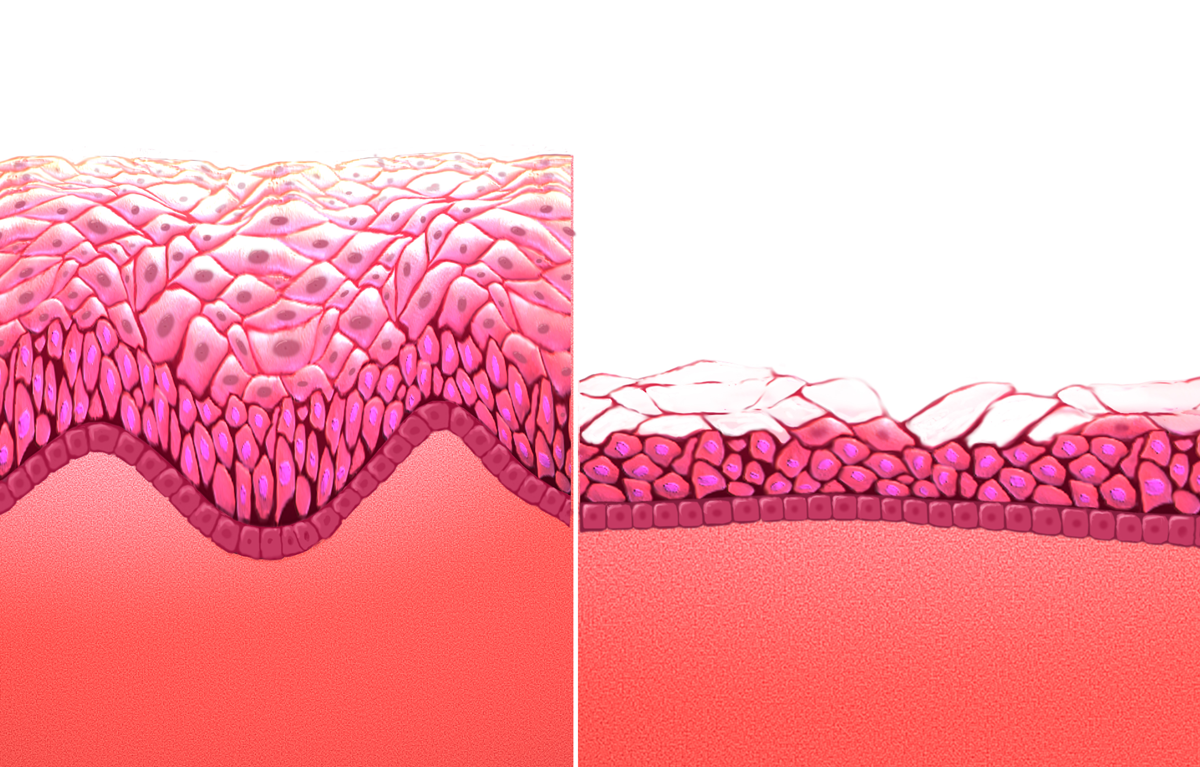
Hormone Replacement Therapy (menopause)
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such as hot flashes, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, and complications such as osteoporosis (bone loss), sexual dysfunction, and vaginal atrophy. They are mostly caused by low levels of female sex hormones (e.g. estrogens) that occur during menopause. Estrogens and progestogens are the main hormone drugs used in HRT. Progesterone is the main female sex hormone that occurs naturally and is also manufactured into a drug that is used in menopausal hormone therapy. Although both classes of hormones can have symptomatic benefit, progestogen is specifically added to estrogen regimens, unless the uterus has been removed, to avoid the increased risk of endometrial cancer. Unopposed estrogen therapy promotes e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (engineering)
In engineering, a process is a series of interrelated tasks that, together, transform inputs into a given output.ANSI/EIA-632-1998 Processes for Engineering a System, Appendix A These tasks may be carried out by people, nature or machines using various resources; an engineering process must be considered in the context of the agents carrying out the tasks and the resource attributes involved. Systems engineering normative documents and those related to Maturity Models are typically based on processes, for example, systems engineering processes of the EIA-632 and processes involved in the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) institutionalization and improvement approach. Constraints imposed on the tasks and resources required to implement them are essential for executing the tasks mentioned. Semiconductor industry Semiconductor process engineers face the unique challenge of transforming raw materials into high-tech devices. Common semiconductor devices include Integrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersaturation
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution (chemistry), solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at Solubility equilibrium, equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a liquid, but it can also be applied to liquids and gases dissolved in a liquid. A supersaturated solution is in a metastable state; it may return to equilibrium by separation process, separation of the excess of solute from the solution, by dilution of the solution by adding solvent, or by increasing the solubility of the solute in the solvent. History Early studies of the phenomenon were conducted with sodium sulfate, also known as Glauber's Salt because, unusually, the solubility of this salt in water may decrease with increasing temperature. Early studies have been summarised by Tomlinson. It was shown that the crystallization of a supersaturated solution does not simply come from its agitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creatine
Creatine ( or ) is an organic compound with the nominal formula . It exists in various tautomers in solutions (among which are neutral form and various zwitterionic forms). Creatine is found in vertebrates, where it facilitates recycling of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), primarily in muscle and brain tissue. Recycling is achieved by converting adenosine diphosphate (ADP) back to ATP via donation of phosphate groups. Creatine also acts as a Buffer solution, buffer. History Creatine was first identified in 1832 when Michel Eugène Chevreul isolated it from the basified water-extract of skeletal muscle. He later named the crystallized precipitate after the Ancient Greek, Greek word for meat, ('). In 1928, creatine was shown to exist in Tautomer, equilibrium with creatinine. Studies in the 1920s showed that consumption of large amounts of creatine did not result in its excretion. This result pointed to the ability of the body to store creatine, which in turn suggested its use as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Regular monthly vaginal bleeding during the reproductive years, menstruation, is a normal physiologic process. During the reproductive years, bleeding that is excessively heavy (menorrhagia or heavy menstrual bleeding), occurs between monthly menstrual periods (intermenstrual bleeding), occurs more frequently than every 21 days (abnormal uterine bleeding), occurs too infrequently (oligomenorrhea), or occurs after vaginal intercourse (postcoital bleeding) should be evaluated. The causes of abnormal vaginal bleeding vary by age, and such bleeding can be a sign of specific medical conditions ranging from hormone imbalances or anovulation to malignancy (cervical cancer, vaginal cancer or uterine ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 μm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the Brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloid, colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nanoparticles cannot be seen with ordinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material made up of two or more different chemical substances which can be separated by physical method. It is an impure substance made up of 2 or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proportion. A mixture is the physical combination of two or more substances in which the identities are retained and are mixed in the form of solutions, suspensions or colloids. Mixtures are one product of mechanically blending or mixing chemical substances such as elements and compounds, without chemical bonding or other chemical change, so that each ingredient substance retains its own chemical properties and makeup. Despite the fact that there are no chemical changes to its constituents, the physical properties of a mixture, such as its melting point, may differ from those of the components. Some mixtures can be separated into their components by using physical (mechanical or thermal) means. Azeotropes are one kind of mixture that usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (matter)
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of material that is chemically uniform, physically distinct, and (often) mechanically separable. In a system consisting of ice and water in a glass jar, the ice cubes are one phase, the water is a second phase, and the humid air is a third phase over the ice and water. The glass of the jar is a different material, in its own separate phase. (See .) More precisely, a phase is a region of space (a thermodynamic system), throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, magnetization and chemical composition. The term ''phase'' is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but there can be several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (as where oil and water separate into distinct phases, both in the liquid state). Types of phases Distinct phases may be described as different states of matter such as gas, liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity And Heterogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvation
Solvations describes the interaction of a solvent with dissolved molecules. Both ionized and uncharged molecules interact strongly with a solvent, and the strength and nature of this interaction influence many properties of the solute, including solubility, reactivity, and color, as well as influencing the properties of the solvent such as its viscosity and density. If the attractive forces between the solvent and solute particles are greater than the attractive forces holding the solute particles together, the solvent particles pull the solute particles apart and surround them. The surrounded solute particles then move away from the solid solute and out into the solution. Ions are surrounded by a concentric shell of solvent. Solvation is the process of reorganizing solvent and solute molecules into solvation complexes and involves bond formation, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. Solvation of a solute by water is called hydration. Solubility of solid compounds dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |