|
Metal Gate
A metal gate, in the context of a lateral metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) stack, is the gate electrode separated by an oxide from the transistor's channel – the gate material is made from a metal. In most MOS transistors since about the mid-1970s, the "M" for metal has been replaced by polysilicon, but the name remained. Aluminum gate The first MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) was made by Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in 1959, and demonstrated in 1960. They used silicon as channel material and a non-self-aligned aluminum gate. Aluminum gate metal (typically deposited in an evaporation vacuum chamber onto the wafer surface) was common through the early 1970s. Polysilicon By the late 1970s, the industry had moved away from aluminum as the gate material in the metal–oxide–semiconductor stack due to fabrication complications and performance issues. A material called polysilicon ( polycrystalline silicon, highly doped wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-1-1 Pits From Aluminum Alloying
111 (usually pronounced ''one-one-one'') is the emergency telephone number in New Zealand. It was first implemented in Masterton and Carterton on 29 September 1958, and was progressively rolled out nationwide with the last exchanges converting in 1988. About 870,000 111 calls are made every year, and the police introduced a new number (105) in 2019, to take non-urgent police calls away from the "111" service (see 105 (telephone number)). History Introduction Before the introduction of 111, access to emergency services was complicated. For the quarter of New Zealand’s then 414,000 telephone subscribers still on manual telephone exchange, one would simply pick up the telephone and ask the answering operator for the police, ambulance, or fire service by name. However, the problem on manual exchanges was that calls were answered first-come-first-served, which meant on busy exchanges, emergency calls could be delayed. For automatic exchanges, one would need to know the local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties that differ from those of the pure elements from which they are made. The vast majority of metals used for commercial purposes are alloyed to improve their properties or behavior, such as increased strength, hardness or corrosion resistance. Metals may also be alloyed to reduce their overall cost, for instance alloys of gold and Copper(II) sulfate, copper. A typical example of an alloy is SAE 304 stainless steel, 304 grade stainless steel which is commonly used for kitchen utensils, pans, knives and forks. Sometime also known as 18/8, it as an alloy consisting broadly of 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The chromium and nickel alloying elements add strength and hardness to the majority iron element, but their main function is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
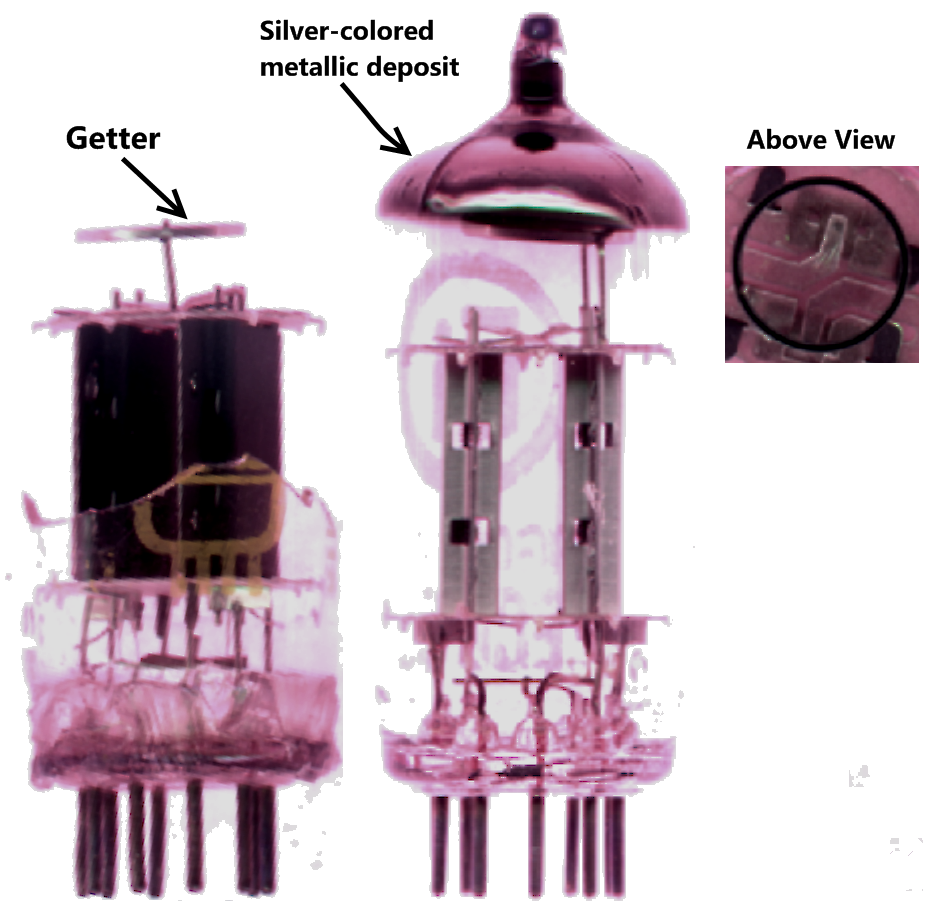
Gettering
A getter is a deposit of reactive material that is placed inside a vacuum system to complete and maintain the vacuum. When gas molecules strike the getter material, they combine with it chemically or by adsorption. Thus the getter removes small amounts of gas from the evacuated space. The getter is usually a coating applied to a surface within the evacuated chamber. A vacuum is initially created by connecting a container to a vacuum pump. After achieving a sufficient vacuum, the container can be sealed, or the vacuum pump can be left running. Getters are especially important in sealed systems, such as vacuum tubes, including cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), vacuum insulating glass (or vacuum glass) and vacuum insulated panels, which must maintain a vacuum for a long time. This is because the inner surfaces of the container release adsorbed gases for a long time after the vacuum is established. The getter continually removes residues of a reactive gas, such as oxygen, as long as it is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMOS Logic
PMOS or pMOS logic, from p-channel metal–oxide–semiconductor, is a family of digital circuits based on p-channel, enhancement mode metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In the late 1960s and early 1970s, PMOS logic was the dominant semiconductor technology for large-scale integrated circuits before being superseded by NMOS and CMOS devices. History and application Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng manufactured the first working MOSFET at Bell Labs in 1959. They fabricated both PMOS and NMOS devices but only the PMOS devices were working. It would be more than a decade before contaminants in the manufacturing process (particularly sodium) could be managed well enough to manufacture practical NMOS devices. Compared to the bipolar junction transistor, the only other device available at the time for use in an integrated circuit, the MOSFET offers a number of advantages: *Given semiconductor device fabrication processes of similar precision, a MOS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Voltage
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth or VGS(th), of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage (VGS) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important scaling factor to maintain power efficiency. When referring to a junction field-effect transistor (JFET), the threshold voltage is often called pinch-off voltage instead. This is somewhat confusing since ''pinch off'' applied to insulated-gate field-effect transistor (IGFET) refers to the channel pinching that leads to current saturation behavior under high source–drain bias, even though the current is never off. Unlike ''pinch off'', the term ''threshold voltage'' is unambiguous and refers to the same concept in any field-effect transistor. Basic principles In n-channel ''enhancement-mode'' devices, a conductive channel does not exist naturally within the transistor. With no VGS, dopant ions added to the body of the FET form a region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss ", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type semiconductor, p-type and n-type semiconductor, n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including Nonvolatile BIOS memory, CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data conversion, data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1948, Bardeen and Brattain patented an insulated-gate transistor (IGFET) with an inversion layer. Bardeen's concept forms the basis of CMOS technology today. The CMOS process was presented by Fairchild Semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMOS Logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. NMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type transistor body. This inversion layer, called the n-channel, can conduct electrons between n-type ''source'' and ''drain'' terminals. The n-channel is created by applying voltage to the third terminal, called the ''gate''. Like other MOSFETs, nMOS transistors have four modes of operation: cut-off (or subthreshold), triode, saturation (sometimes called active), and velocity saturation. NMOS AND-by-default logic can produce unusual glitches or buggy behavior in NMOS components, such as the 6502 "illegal opcodes" which are absent in CMOS 6502s. In some cases such as Commodore's VIC-II chip, the bugs present in the chip's logic were extensively exploited by programmers for graphics effects. For many years, NMOS ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithographic
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design''. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146, .Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. ''Typographic Design: Form and Communication'', Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 11. Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Traditionally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax onto the surface of a smooth and flat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-aligned Gate
In semiconductor electronics fabrication technology, a self-aligned gate is a transistor manufacturing approach whereby the gate electrode of a MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor) is used as a mask for the doping of the source and drain regions. This technique ensures that the gate is naturally and precisely aligned to the edges of the source and drain. The use of self-aligned gates in MOS transistors is one of the key innovations that led to the large increase in computing power in the 1970s. Self-aligned gates are still used in most modern integrated circuit processes. Introduction IC construction Integrated circuits (ICs, or "chips") are produced in a multi-step process that builds up multiple layers on the surface of a disk of silicon known as a " wafer". Each layer is patterned by coating the wafer in photoresist and then exposing it to ultraviolet light being shone through a stencil-like "mask". Depending on the process, the photoresist that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drain (transistor)
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by the Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |