|
Mesonet
In meteorology and climatology, a mesonet, portmanteau of mesoscale network, is a network of automated weather and, often also including environmental monitoring stations, designed to observe mesoscale meteorological phenomena and/or microclimates. Dry lines, squall lines, and sea breezes are examples of phenomena observed by mesonets. Due to the space and time scales associated with mesoscale phenomena and microclimates, weather stations comprising a mesonet are spaced closer together and report more frequently than synoptic scale observing networks, such as the WMO Global Observing System (GOS) and US ASOS. The term mesonet refers to the collective group of these weather stations, which are usually owned and operated by a common entity. Mesonets generally record in situ surface weather observations but some involve other observation platforms, particularly vertical profiles of the planetary boundary layer (PBL). Other environmental parameters may include insolation and vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Weather Stations
A weather station is a facility, either on land or sea, with instruments and equipment for measuring atmospheric conditions to provide information for weather forecasts and to study the weather and climate. The measurements taken include temperature, atmospheric pressure, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, and precipitation amounts. Wind measurements are taken with as few other obstructions as possible, while temperature and humidity measurements are kept free from direct solar radiation, or insolation. Manual observations are taken at least once daily, while automated measurements are taken at least once an hour. Weather conditions out at sea are taken by ships and buoys, which measure slightly different meteorological quantities such as sea surface temperature (SST), wave height, and wave period. Drifting weather buoys outnumber their moored versions by a significant amount. Weather instruments A weather instrument is any device that measures weather related conditions. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automatic Weather Station
An automatic weather station (AWS) is an automated version of the traditional weather station, either to save human labor or to enable measurements from remote areas. An AWS will typically consist of a weather-proof enclosure containing the data logger, rechargeable battery, telemetry (optional) and the meteorological sensors with an attached solar panel or wind turbine and mounted upon a mast. The specific configuration may vary due to the purpose of the system. The system may report in near real time via the Argos System, LoRa and the Global Telecommunications System, or save the data for later recovery. In the past, automatic weather stations were often placed where electricity and communication lines were available. Nowadays, the solar panel, wind turbine and mobile phone technology have made it possible to have wireless stations that are not connected to the electrical grid or hardline telecommunications network. One of the main advantages of an automatic weather station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
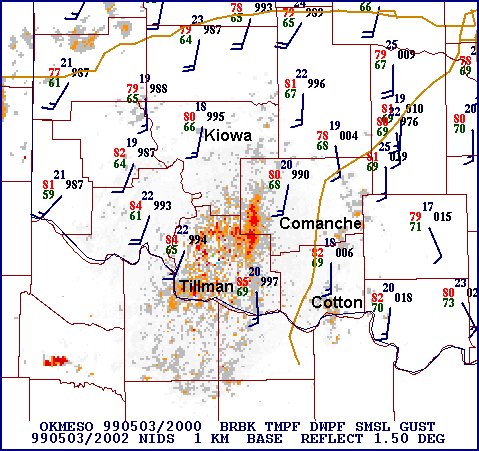
Wake Low
A wake low, or wake depression, is a mesoscale low-pressure area which trails the mesoscale high following a squall line. Due to the subsiding warm air associated with the system's formation, clearing skies are associated with the wake low. Once difficult to detect in surface weather observations due to their broad spacing, the formation of mesoscale weather station networks, or mesonets, has increased their detection.Mark R. Conder, Steven R. Cobb, and Gary D. Skwira (2006)West Texas Mesonet Observations of Wake Lows and Heat Bursts Across Northwest Texas.American Meteorological Society. Retrieved on 2009-04-24. Severe weather, in the form of high winds, can be generated by the wake low when the pressure difference between the mesohigh preceding it and the wake low is intense enough.. When the squall line is in the process of decay, heat bursts can be generated near the wake low. Once new thunderstorm activity along the squall line concludes, the wake low associated with it weak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often slightly but sometimes substantially. The term may refer to areas as small as a few square meters or smaller (for example a raised-bed gardening, garden bed, underneath a rock, or a cave) or as large as many square kilometers. Because climate is statistics, statistical, which implies Spatial analysis, spatial and temporal variation of the mean values of the describing parameters, microclimates are identified as statistically distinct conditions which occur and/or persist within a region. Microclimates can be found in most places but are most pronounced in topographically dynamic zones such as mountainous areas, islands, and coastal areas. Microclimates exist, for example, near bodies of water which may cool the local atmosphere, or in heavy urban areas where brick, concrete, and Asphalt concrete, asphalt absorb the sun's energy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automated Airport Weather Station
Airport weather stations are automated sensor suites which are designed to serve aviation and meteorological operations, weather forecasting and climatology. Automated airport weather stations have become part of the backbone of weather observing in the United States and Canada and are becoming increasingly more prevalent worldwide due to their efficiency and cost-savings. System types within the United States In the United States, there are several varieties of automated weather stations that have somewhat subtle but important differences. These include the automated weather observing system (AWOS) and the automated surface observing system (ASOS). Automated weather observing system (AWOS) The automated weather observing system (AWOS) units are mostly operated, maintained and controlled by state or local governments and other non-federal entities and are certified under the FAA non-federal AWOS Program. The FAA completed an upgrade of the 230 FAA owned AWOS and former autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mountain Breeze And Valley Breeze
In meteorology, a mountain breeze and a valley breeze are two related, localized winds that occur one after the other on a daily cycle. They are an example of anabatic and katabatic winds occurring at local scales. These winds are opposite from each other. Mountain winds blow from mountain towards valley after sunset, when mountain cools down and valley zone is comparatively warmer. While valley breezes occur when the warm air rises up the sides of the valley, warm air in a mountain breeze will rise up the middle. Cause Mountain and valley breezes form through a process similar to sea and land breezes. During the day, the sun heats up mountain air rapidly while the valley remains relatively cooler. Convection Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ... causes it to rise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Meteorological Applications
''Meteorological Applications'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of meteorology published four times per year since 1994. It is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of the Royal Meteorological Society. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in Current Contents (under Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences) and in the Science Citation Index, among other places. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.119, ranking it 64th out of 94 journals in the category "Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences". References External links * {{Official website, http://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/hub/journal/10.1002/(ISSN)1469-8080 Wiley-Blackwell academic journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in cumulonimbus clouds. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce Heavy rain (meteorology), heavy rain and sometimes Thundersnow, snow, Ice pellets, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms can produce little or Dry thunderstorm, no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may thunderstorm training, line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or #Severe thunderstorms, severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere. It occurs when warmer, less dense air rises, while cooler, denser air sinks. This process is driven by parcel-environment instability, meaning that a "parcel" of air is warmer and less dense than the surrounding environment at the same altitude. This difference in temperature and density (and sometimes humidity) causes the parcel to rise, a process known as buoyancy. This rising air, along with the compensating sinking air, leads to mixing, which in turn expands the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL), the lowest part of the atmosphere directly influenced by the Earth's surface. This expansion contributes to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points (the temperature below which condensation occurs). Convection plays a crucial role in weather patterns, influencing cloud formation, wind, and the development of thunderstorms, which can be associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mesohigh
A mesohigh (sometimes called a "bubble high") is a mesoscale meteorology, mesoscale high-pressure area that forms beneath thunderstorms. While not always the case, it is usually associated with a mesoscale convective system. In the early stages of research on the subject, the mesohigh was often referred to as a "thunderstorm high". Formation A mesohigh forms underneath the downdraft in a squall line and is associated with the cold pool of a thunderstorm. It is largely formed by hydrostatic phenomenon, specifically the evaporation of falling precipitation (meteorology), precipitation. As precipitation, primarily rain, falls in the downdraft, it evaporates in the Dew point, unsaturated air, leading to cooling in the downdraft due to an absorption of latent heat. The cooling of the air leads to an increase in the pressure as the air becomes denser. While not the primary mechanism behind the mesohigh, melting or Sensible heat, sensible cooling of hail can also lead to increased pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mountain Wave
In meteorology, lee waves are atmospheric stationary waves. The most common form is mountain waves, which are atmospheric internal gravity waves. These were discovered in 1933 by two German glider pilots, Hans Deutschmann and Wolf Hirth, above the Giant Mountains. They are periodic changes of atmospheric pressure, temperature and orthometric height in a current of air caused by vertical displacement, for example orographic lift when the wind blows over a mountain or mountain range. They can also be caused by the surface wind blowing over an escarpment or plateau, or even by upper winds deflected over a thermal updraft or cloud street. The vertical motion forces periodic changes in speed and direction of the air within this air current. They always occur in groups on the lee side of the terrain that triggers them. Sometimes, mountain waves can help to enhance precipitation amounts downwind of mountain ranges. Usually a turbulent vortex, with its axis of rotation parallel to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |