|
Meiler Fitzhenry
Meiler FitzHenry (sometimes spelled Meilyr; died 1220) was a Cambro-Norman nobleman and Lord Chief Justice of Ireland during the Lordship of Ireland. Background and early life Meilyr FitzHenry was the son of Henry FitzHenry, an illegitimate son of King Henry I, by Nest, daughter of Rhys ap Tewdwr, the last king of Deheubarth (South Wales). He was thus related to the noblest Norman and native families of South Wales. Robert Fitz-Stephen, Maurice FitzGerald, David FitzGerald, bishop of St. David's, and William FitzGerald of Carew were his uncles. Meilyr's cousins included Raymond le Gros, Gerald of Wales, prince Rhys ap Gruffydd, the famous Lord Rhys, as well as Henry II. In 1158 his father, Henry FitzHenry, was killed in battle during Henry II's campaign in Wales. Meilyr, Henry's oldest son, succeeded to his father's possessions of Narberth and Pebidiog, the central and north-eastern parts of the modern Pembrokeshire. In Ireland In 1169 he accompanied his uncle Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cambro-Norman
Cambro-Normans (; "Wales", ; ) were Normans who settled in southern Wales and the Welsh Marches after the Norman invasion of Wales. Cambro-Norman knights were also the leading force in the Cambro-Norman invasion of Ireland, led by Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke in 1170. In Wales Following the Norman conquest of England, Norman forces would invade South Wales, where William FitzOsbern, 1st Earl of Hereford overran the Kingdom of Gwent and the Earl of Shrewsbury invaded the Kingdom of Deheubarth. Despite a number of Welsh revolts against Norman rule, these areas (along with the Gower), would become the main focus of Norman settlement in Wales. Although Welsh forces would retake much of the Norman territories following their crushing victory at the Battle of Crug Mawr in 1136, the Norman King of England would control much of the Welsh borders and southern agricultural land by the 12th century. This led to Wales being split in two, with one area becoming the Marcher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Robert De Barry
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
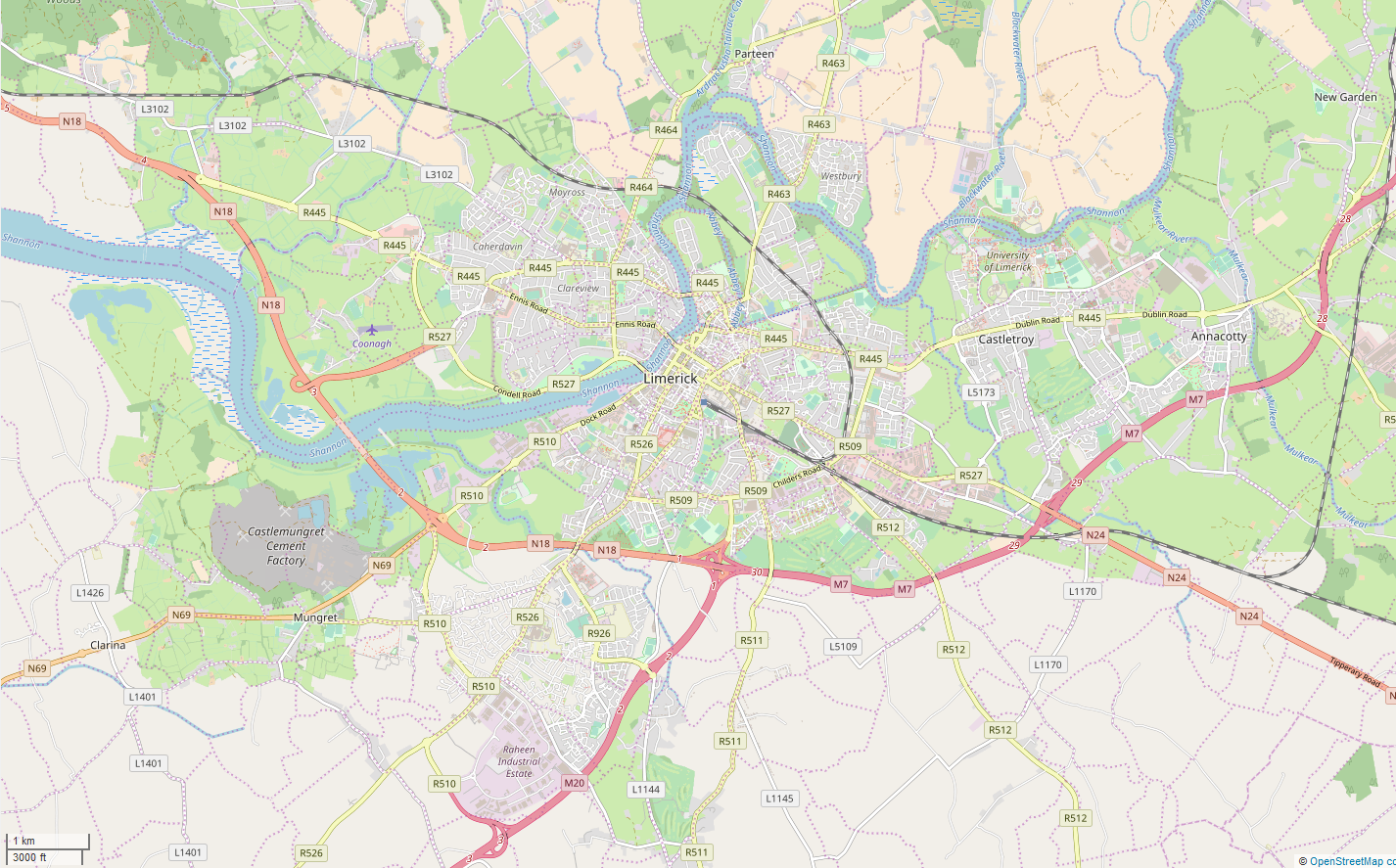
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( or archaic ') is the major river on the island of Ireland, and at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of Ireland. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying into the Atlantic Ocean through the long Shannon Estuary. Limerick city stands at the point where the river water meets the sea water of the estuary. The Shannon is tidal east of Limerick as far as the base of the Ardnacrusha dam. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south (Leinster and most of Munster; County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. With a population of 102,287 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, Limerick is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, third-most populous urban area in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland. It was founded by Scandinavian settlers in 812, during the Viking Age. The city straddles the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, Limerick, King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey River, Limerick, Abbey Rivers. Limerick is at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the Local gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carbury, County Kildare
Carbury (), also formerly spelt "Carbery", is a rural community and a village in north-west County Kildare, Ireland. It is situated on the R402 road (Ireland), R402 Regional road (Ireland), regional road between Enfield, County Meath, Enfield and Edenderry, near the border with County Offaly, and includes the smaller hamlets of Derrinturn, Ticknevin and Killina along the Grand Canal (Ireland). The source of the River Boyne is located just north of the village. The village is in a townland and Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name. Places of interest Carbury Hill This prominent hill just north of the village of Carbury has been inhabited since the Bronze Age. Although partly silted up, at least two barrows from that time can still be found on top of the hill. The site was anciently known as Sídhe Neachtain or “The Mansion of Neachtain”, from Nuadha Neacht, a leader of the mythological Tuatha de Danann who became King of Leinster for a year In 45 AD accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cantred
A cantred was a subdivision of a county in the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Ireland between the thirteenth and fifteenth centuries, analogous to the cantref of Wales or the hundred of England. In County Dublin the equivalent unit was termed a serjeanty, while in County Meath and environs it was a barony. The area of a cantred usually corresponded to that of an earlier ("thirty hundreds") of Gaelic Ireland, and sometimes to that of a rural deanery in the medieval Irish church. Paul Mac Cotter has "demonstrated the existence of 151 certain cantreds and indicated the probable existence of a further 34." Cantreds were replaced by baronies from the sixteenth century. Functions In the Anglo-Norman shires and liberties, the cantred was originally a unit of subinfeudation; a magnate or tenant-in-chief who received a grant from the King of England as Lord of Ireland would typically grant a cantred or half-cantred to a baron as mesne lord, who would hold the chief manor and grant sub-manors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Waterford
Waterford ( ) is a City status in Ireland, city in County Waterford in the South-East Region, Ireland, south-east of Ireland. It is located within the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster. The city is situated at the head of Waterford Harbour. It is the oldestWaterford City Council : About Our City . Waterfordcity.ie. Retrieved on 23 July 2013. and the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, fifth most populous city in the Republic of Ireland. It is the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, ninth most populous settlement on the island of Ireland. As of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, 60,079 people lived in the city and its suburbs. Historically the site of a Viking settlement, Waterford's medieval defensive walls and fortifications include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Richard De Clare, 2nd Earl Of Pembroke
Richard de Clare (c. 1130 – 20 April 1176), the second Earl of Pembroke, also Lord of Leinster and Lord Chief Justice of Ireland, Justiciar of Ireland (sometimes known as Richard FitzGilbert), was an Anglo-Norman nobleman notable for his leading role in the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. Like Gilbert de Clare, 1st Earl of Pembroke, his father, Richard is commonly known by his nickname, Strongbow (). After his son and heir, Gilbert, died childless before 1189, the earldom passed through Richard's daughter Isabel de Clare, 4th Countess of Pembroke, Isabel de Clare and to her husband, William Marshal, 1st Earl of Pembroke, William Marshal. Nickname During the Middle Ages, official documents, with few exceptions, were written in Latin; in the Domesday Exchequer annals, written between 1300 and 1304 (that means, over 120 years after Richard's death), he was referred to as "''Ricardus cognomento Stranghose Comes Strugulliae"'', which translates to "Richard, known as Stranghose, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hugh De Lacy, Lord Of Meath
Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, 4th Baron Lacy (; before 1135 – 25 July 1186), was an Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman landowner and royal office-holder. He had substantial land holdings in Herefordshire and Shropshire. Following his participation in the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland, he was granted, in 1172, the lands of the Kingdom of Meath by the Anglo-Norman Henry II of England, King Henry II, but he had to gain control of them. The Lordship of Meath was then the most extensive Liberty (division), liberty in Lordship of Ireland, Ireland. Early life Hugh de Lacy was the son of Gilbert de Lacy (died after 1163) of Ewyas Lacy, Weobley, and Ludlow. He is said to have had a dispute with Josce de Dinan as to certain lands in Herefordshire in 1154. He was in possession of his father's lands before 1163, and in 1165–66 held fifty-eight and three-quarters knight's fees, and had nine tenants without knight service. Career in Ireland In October 1171 Lacy went over with Henry II as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair
Ruaidrí mac Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (Modern Irish: Ruairí Ó Conchúir; anglicised as Rory O'Conor) ( – 2 December 1198) was King of Connacht from 1156 to 1186, and High King of Ireland from 1166 to 1198. He was the last High King of Ireland before the Anglo-Norman invasion. Ruaidrí was one of over twenty sons of King Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156). He and his sister Mór were Tairrdelbach's only children from his third wife, Cailech Dé Ní Eidin of Aidhne. ''Rigdamna Connachta'' Ruaidrí was not a favourite of his father, his brother Conchobar Ua Conchobair being Tairrdelbach's ''tánaiste'' and designated heir. In 1136, he and his brother Aedh (died 1195) took advantage of a low in Tairrdelbach's fortunes to stage a rebellion. Aedh was blinded by Conchobar on Tairrdelbach's orders but Ruaidrí was protected by the Archbishop of Connacht, Muireadhach Ua Dubhthaigh. In 1143, he staged another rebellion. He was arrested by Conchobar and Tighearnán Ua R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Dublin (1171)
The siege of Dublin was an unsuccessful attempt of the last high king of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair, to capture the City of Dublin from the Anglo-Normans in 1171. Ua Conchobair was allegedly able to gather sixty-thousand men for his cause, meanwhile, the city was held by Strongbow; who had proven his martial prowess just a few months prior, when another Irish army had attempted to seize the city, but Strongbow had been able to drive the besiegers off with a sally. Ua Conchobair divided his forces into four camps and during the night Strongbow led a surprise attack Military deception (MILDEC) is an attempt by a military unit to gain an advantage during warfare by misleading adversary decision makers into taking action or inaction that creates favorable conditions for the deceiving force. This is usually ... on Ua Conchobair's camp, killing a thousand and a half, causing the rest of Irish forces to rout. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Dublin, Siege of 1171 in Irel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Domnall Mór Ua Briain
Domnall Mór Ua Briain, or Domnall Mór mac Toirrdelbaig Uí Briain, was King of Thomond in History of Ireland, Ireland from 1168 in Ireland, 1168 to 1194 in Ireland, 1194 and a claimant to the title King of Munster. He was also styled History of Limerick, King of Limerick, a title belonging to the O'Brien dynasty since Brian Boru's Burning of Luimneach, sacking of the Hiberno-Norse city state after the Battle of Sulcoit in the 10th century. History Domnall Mór ("Donall the Great") was the third son of Toirdhealbhach mac Diarmada Ua Briain, King of Munster, who reigned from 1142 to 1167. He ascended to the throne in 1168 after the death of his eldest brother, Muirchertach, who had succeeded their father as king. Muirchertach was killed at the instigation of his cousin Conchobar mac Muirchertach Ua Briain. His other brother Brian of Slieve Bloom was blinded in 1169. The same year, Domnall entered into conflict with the High King of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair and was forced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |