|
Mehdya, Morocco
Mehdya (), also Mehdia or Mehedya, is a town in Kénitra Province, Rabat-Salé-Kénitra, in north-western Morocco. Previously called al-Ma'mura, it was known as São João da Mamora under 16th century Portuguese occupation, or as La Mamora under 17th century Spanish occupation. According to the 2004 census, the town has a population of 16,262. It is located on Sebou River (Oued Sebu). History Mehdya was previously called Al-Ma'mura ("the well-populated") or La Mamora in Europe, and was a harbour on the coast of Morocco. Per an ancient account, a colony was founded at the site in the 5th century BCE by the Carthaginians, who called it Thymiaterium. Portuguese occupation (1515) It was captured by the Portuguese in 1515, and renamed ''São João da Mamora''. Altogether, the Portuguese are documented to have seized 6 Moroccan towns, and built 6 stand-alone fortresses on the Moroccan Atlantic coast, between the river Loukos in the north and the river of Sous in the south. Four of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Morocco
Regions are currently the highest administrative divisions in Morocco. Since 2015, Morocco officially administers 12 regions, including one (Dakhla-Oued Ed-Dahab) that lies completely within the disputed territory of Western Sahara and two (Laâyoune-Sakia El Hamra and Guelmim-Oued Noun) that lie partially within it. The regions are subdivided into a total of 75 second-level administrative divisions, which are Prefectures and provinces of Morocco, prefectures and provinces. A region is governed by a directly elections in Morocco, elected regional council. The president of the council is responsible for carrying out the council's decisions. Prior to the 2011 Moroccan constitutional referendum, 2011 constitutional reforms, this was the responsibility of the Wali (administrative title), Wali, the representative of the central government appointed by the King, who now plays a supporting role in the administration of the region. Regions since 2015 On 3 January 2010, the Moroccan g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agadir
Agadir (, ; ) is a major List of cities in Morocco, city in Morocco, on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean near the foot of the Atlas Mountains, just north of the point where the Sous River, Souss River flows into the ocean, and south of Casablanca. Agadir is the capital of the Agadir-Ida Ou Tanane Prefecture, Agadir Ida-U-Tanan Prefecture and of the Souss-Massa economic region. Agadir is one of the major urban centres of Morocco. The municipality of Agadir recorded a population of 924,000 in the 2014 Moroccan census. According to the 2004 census, there were 346,106 inhabitants in that yearGeneral Census of the population and habitat 2004, Commisariat of Planning Website: www.lavieeco.com, consulted on 7 February 2012 ; and the population of the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Careening
Careening (also known as "heaving down") is a method of gaining access to the hull of a sailing vessel without the use of a dry dock. It is used for cleaning or repairing the hull. Before ship's hulls were protected from marine growth by fastening copper sheets over the surface of the hull, fouling by this growth would seriously affect the sailing qualities of a ship, causing a large amount of drag. As this growth was underwater, removing it was difficult. Beaching the vessel at high tide allowed the lower hull to be exposed for cleaning or repairs. Etymology The term, and similar terms in French, Spanish and Italian, derive from the term for a ship's keel—''carène'' (French), ''carena'' (Spanish), ''carena'' (Italian). These come from the Latin term for keel, ''carīna''. Practice The ship was grounded broadside on a steep beach at high tide or, in dockyards, moored at a permanent facility for careening known as a ''careening wharf''. A beach favoured for careening was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Mainwaring
Sir Henry Mainwaring (1587–1653), was an English lawyer, soldier, writer, seaman and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1621 to 1622. He was for a time a pirate based in Newfoundland and then a naval officer with the Royal Navy. He supported the Royalist cause in the English Civil War. Early life Mainwaring was born in Ightfield, Shropshire, second son of Sir George Mainwaring and his wife Ann, the daughter of Sir William More of Loseley Park in Surrey. His maternal grandfather was Sir William More, Vice-Admiral of Sussex. He graduated from Brasenose College at the University of Oxford, where he was awarded a B.A. in Law, at the age of 15, in 1602. He then served as trial lawyer (admitted in 1604 as a student at Inner Temple), soldier (possibly in the Low Countries), sailor, and author (pupil of John Davies of Hereford) before turning to piracy. From pirate-hunter to pirate In 1610, at the age of 24, Mainwaring was given a commission from Lord High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy In The Atlantic World
The Atlantic World refers to the period and interconnected history of the European colonization of the Americas from around 1492 to the early nineteenth century. This term refers to the expanded naval presence of European powers at the time (Spain, Portugal, Britain, and others) for exploration, trade, and migration. Piracy became increasingly prevalent during this era due to various natural factors that diminished the abilities of law enforcement across vast areas, further reducing state control over many coastal regions and increasing competition between European powers. Some of the best-known pirates of this era were the Golden Age Pirates (c. 1650–1730), who roamed the seas of North America, Africa, and the Caribbean coasts. Background In the mercantile economy of the Atlantic world, piracy emerged as a profitable venture, targeting the trade routes that made European colonization possible. Defying traditional alliances, pirates attacked and captured merchant vesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munster
Munster ( or ) is the largest of the four provinces of Ireland, located in the south west of the island. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" (). Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the ancient kingdoms were shired into Counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has seen further sub-division of the historic counties. Munster has no official function for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government purposes. For the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization, ISO, the province is listed as one of the provincial sub-divisions of the State (ISO 3166-2:IE) and coded as "IE-M". Geographically, Munster covers a total area of and has a population of 1,373,346, with the most populated city being Cork (city), Cork. Other significant urban centres in the provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
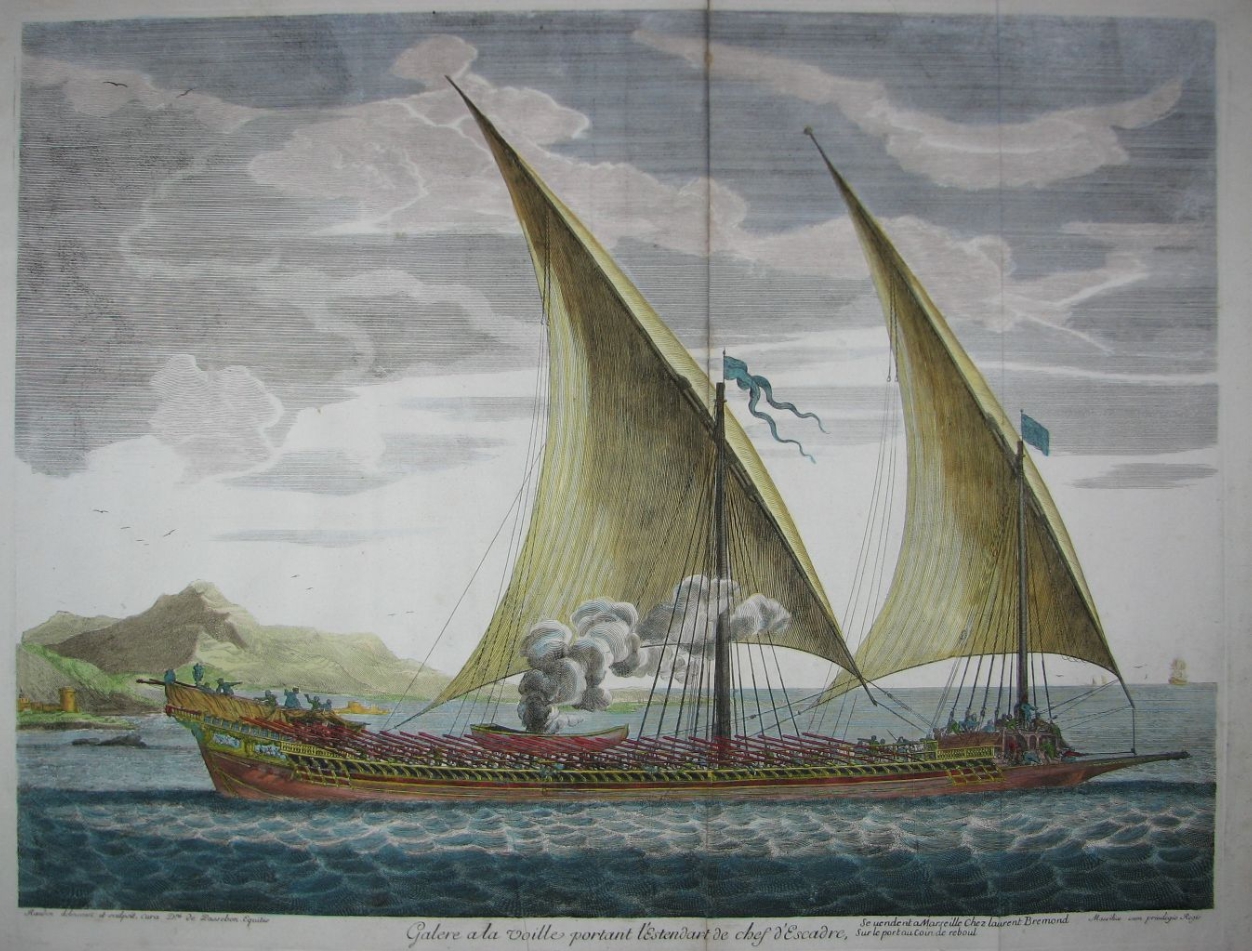
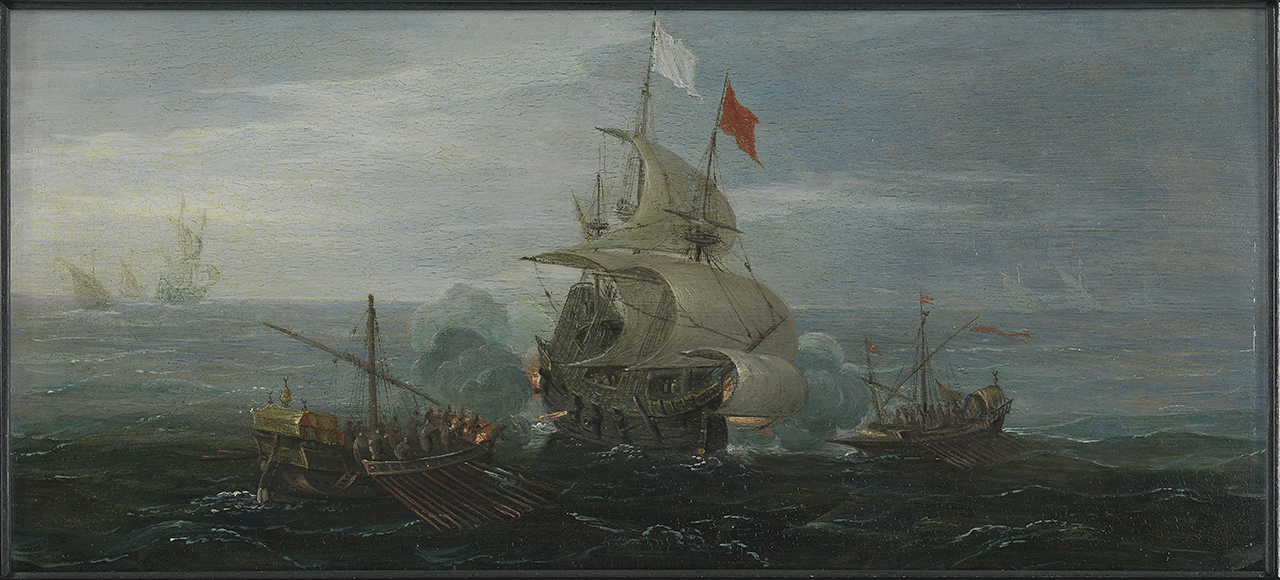
Galley
A galley is a type of ship optimised for propulsion by oars. Galleys were historically used for naval warfare, warfare, Maritime transport, trade, and piracy mostly in the seas surrounding Europe. It developed in the Mediterranean world during Classical antiquity, antiquity and continued to exist in various forms until the early 19th century. It typically had a long, slender hull, shallow draft (hull), draft, and often a low freeboard (nautical), freeboard. Most types of galleys also had sails that could be used in favourable winds, but they relied primarily on oars to move independently of winds and currents or in battle. The term "galley" originated from a Greek term for a small type of galley and came in use in English from about 1300. It has occasionally been used for unrelated vessels with similar military functions as galley but which were not Mediterranean in origin, such as medieval Scandinavian longships, 16th-century Ghali (ship), Acehnese ghalis and 18th-century North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Sultanate
The Saadi Sultanate (), also known as the Sharifian Sultanate (), was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of Northwest Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arab Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510, when Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in southern Morocco in their resistance against the Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez from the Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed a relatively peaceful reign. His successors, however, fought with each other, culminating in the 1578 Battle of Ksar el-Kebir (or "Battle of the Three Kings"), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirate Haven
Pirate havens or Pirate coves are ports or harbors that are a safe place for pirates to repair their vessels, resupply, recruit, spend their plunder, avoid capture, and/or lie in wait for merchant ships to pass by. The areas have governments that are unable or unwilling to enforce Admiralty law, maritime laws. This creates favorable conditions for piracy. Pirate havens were places where pirates could find shelter, protection, support, and trade. These havens were often near maritime shipping lanes. Although some havens were merely hidden coves, some were established by governments who employed privateers to disrupt the overseas trade of rival nations. Some of the most famous island strongholds included Tortuga (Haiti), Tortuga in the Caribbean, Madagascar in the Indian Ocean, and the Sulu Archipelago in the Sulu Sea. Some historic pirate havens included Barataria Bay, Port Royal, and Tortuga (Haiti), Tortuga. These provided some autonomy for privateers and buccaneers. Impact Pira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbary Coast
The Barbary Coast (also Barbary, Berbery, or Berber Coast) were the coastal regions of central and western North Africa, more specifically, the Maghreb and the Ottoman borderlands consisting of the regencies in Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli, as well as the Sultanate of Morocco from the 16th to 19th centuries. The term originates from an exonym for the Berbers. Political Diversity Barbary was not always a unified political entity. From the 16th century onward, it was divided into four political entities—from west to east—the Alawi Sultanate, the Regency of Algiers, the Regency of Tunis, and the Regency of Tripoli. Major rulers and petty monarchs during the times of the Barbary states' plundering parties included the sultan of Morocco, the dey of Algiers, bey of Tunis, and pasha of Tripoli, respectively. The slave trade The slave trade was not just an economic lifeline to the Barbary States, but was often justified as a form of jihad against Christian states. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
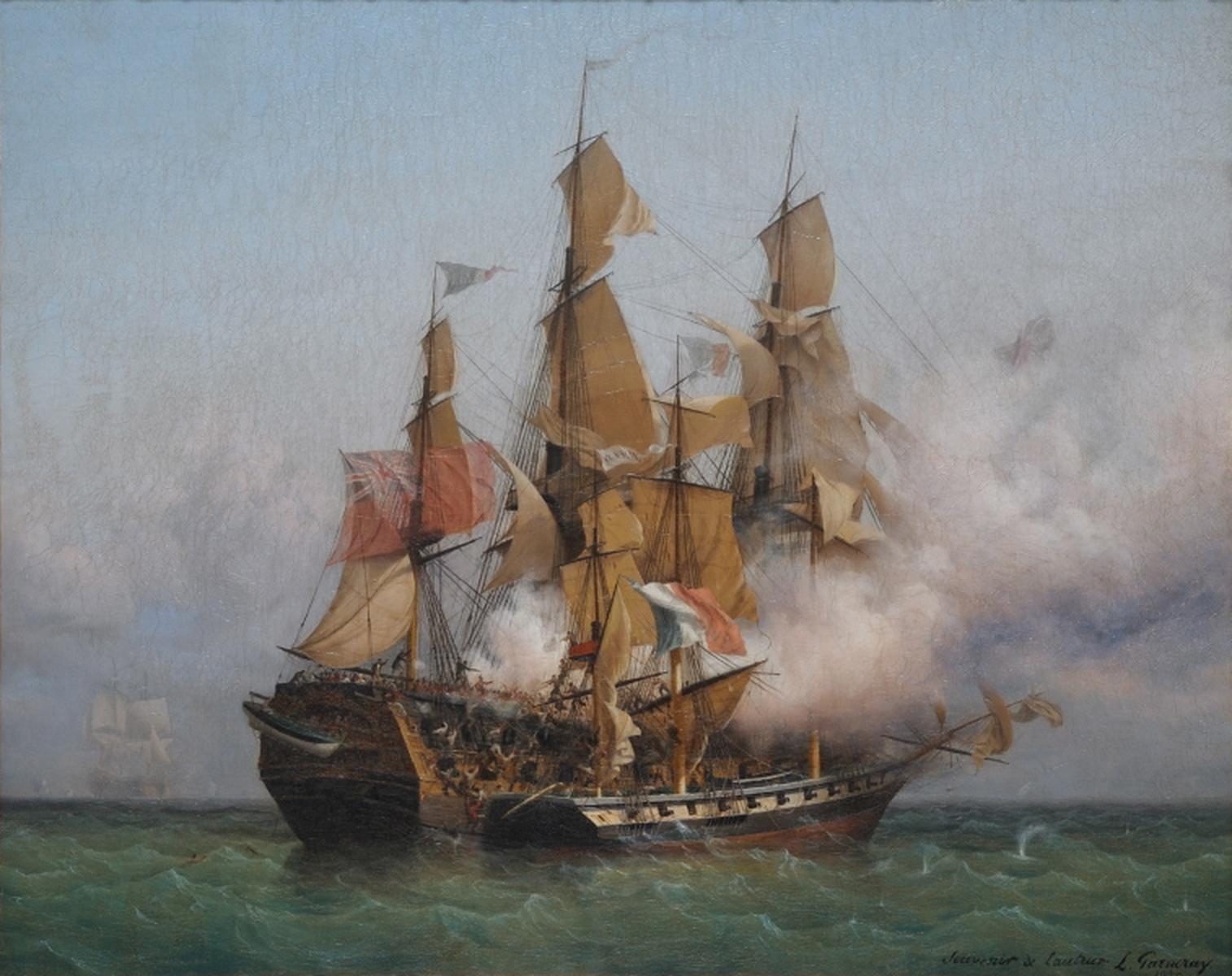
Privateers
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as letters of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes and taking crews prisoner for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission (i.e. the sovereign). Most colonial powers, as well as other countries, engaged in privateering. Privateering allowed sovereigns to multiply their naval forces at relatively low cost by mobilizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604)
The Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) was an intermittent conflict between the Habsburg Spain, Habsburg Kingdom of Spain and the Kingdom of England that was never formally declared. It began with England's military expedition in 1585 to what was then the Spanish Netherlands under the command of Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester, Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester, in support of the Eighty Years' War, Dutch rebellion against Spanish Habsburg rule. In large-scale campaigns, the English repelled the Spanish Armada in 1588, while Spain repelled the English Armada in 1589. The war included much English privateering against Spanish ships, and several widely separated battles. The war dragged on towards the end of the sixteenth century; England and Spain intervened French Wars of Religion#War with Spain (1595–1598), in France in the 1590s and in Nine Years War (Ireland), Ireland from 1601. The Eighty Years' War, 1599–1609, campaign in the Netherlands saw a Spanish veteran force defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |