|
Mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into action potential, electrical signals that, in animals, are sent to the central nervous system. Vertebrate mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli that result from physical interaction, including pressure and vibration. They are located in the skin, like other cutaneous receptors. They are all innervated by Aβ fibers, except the mechanorecepting free nerve endings, which are innervated by A delta fiber, Aδ fibers. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors can be categorized by what kind of sensation they perceive, by the rate of adaptation, and by morphology. Furthermore, each has a different receptive field. By sensation * The Slowly Adapting type 1 (SA1) mechanoreceptor, with the Merkel corpuscle end-organ (also known as M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Receptor
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded receptor potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord. The sensory information travels on the afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve, to the brain via the spinal cord. Spinal nerves transmit external sensations via sensory nerves to the brain through the spinal cord. The stimulus can come from exteroreceptors outside the body, for example those that detect light and sound, or from interoreceptors inside the body, for example those that are responsive to blood pressure or the sense of body position. Types and function Sensory neurons in vertebrates are predominantly pseudounipolar or bipolar, and different types of sensory neurons have different sensory receptors that respond to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkel Corpuscle End-organ
Merkel nerve endings (also Merkel's disks, or Merkel tactile endings) are mechanoreceptors situated in the basal epidermis as well as around the apical ends or some hair follicles. They are slowly adapting. They have small receptive fields measuring some millimeters in diameter. Most are associated with fast-conducting large myelinated axons. A single afferent nerve fibre branches to innervate up to 90 such endings. Merkel nerve endings respond to light touch. They respond to sustained pressure, and are sensitive to edges of objects. Their exact functions remain controversial. The Merkel nerve endings consist of a nerve ending associated with a flattened epithelial cell (Merkel cell); both the nerve ending and Merkel cell are independently mechanosensitive. The Merkel cell expresses the PIEZO2 mechanosensitive ion channels; mechanical activation of the channel causes depolarisation of the Merkel cell and consequent release of serotonin into a synapse with the associated nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissner Corpuscle End-organ
Tactile corpuscles or Meissner's corpuscles are a type of mechanoreceptor discovered by anatomist Georg Meissner (1829–1905) and Rudolf Wagner. This corpuscle is a type of nerve ending in the skin that is responsible for sensitivity to pressure. In particular, they have their highest sensitivity (lowest threshold) when sensing vibrations between 10 and 50 hertz. They are rapidly adaptive receptors. They are most concentrated in thick hairless skin, especially at the finger pads. Structure Tactile corpuscles are encapsulated myelinated nerve endings, surrounded by Schwann cells. The encapsulation consists of flattened supportive cells arranged as horizontal lamellae surrounded by a connective tissue capsule. The corpuscle is 30–140 μm in length and 40–60 μm in diameter. A single nerve fiber meanders between the lamellae and throughout the corpuscle. Location They are distributed on various areas of the skin, but concentrated in areas especially sensitive to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous Receptors
A cutaneous receptor is a sensory receptor found in the skin that provides information about temperature, touch (including vibration and pain), spatial orientation,pressure (stretching or squeezing), and metabolic circumstances (including those induced by external chemical substances). The main four types of cutaneous receptors are tactile corpuscles, bulbous corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, and Merkel nerve endings, although the latter do not qualify as sensory corpuscles in the narrow sense. Types The sensory receptors in the skin are: *Mechanoreceptors **Bulbous corpuscles (skin stretch) **Bulboid corpuscles (Cold) **Tactile corpuscles (changes in texture, slow vibrations) **Pacinian corpuscles (deep pressure, fast vibrations) **Merkel nerve endings (sustained touch and pressure) **Free nerve endings *thermoreceptor *nociceptors *chemoreceptors Modalities With the above-mentioned receptor types the skin can sense the modalities touch, pressure, vibration, temperature and pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Delta Fiber
Group A nerve fibers are one of the three classes of nerve fiber as ''generally classified'' by Erlanger and Gasser. The other two classes are the group B nerve fibers, and the group C nerve fibers. Group A are heavily myelinated, group B are moderately myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. The other classification is a sensory grouping that uses the terms '' type Ia and type Ib'', '' type II'', ''type III'', and ''type IV'', sensory fibers. Types There are four subdivisions of group A nerve fibers: alpha (α) Aα; beta (β) Aβ; , gamma (γ) Aγ, and delta (δ) Aδ. These subdivisions have different amounts of myelination and axon thickness and therefore transmit signals at different speeds. Larger diameter axons and more myelin insulation lead to faster signal propagation. Group A nerves are found in both motor and sensory pathways. Different sensory receptors are innervated by different types of nerve fibers. Proprioceptors are innervated by type Ia, Ib and II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacinian Corpuscle End-organs
The Pacinian corpuscle (also lamellar corpuscle, or Vater–Pacini corpuscle) is a low-threshold mechanoreceptor responsive to vibration or pressure, found in the skin and other internal organs. In the skin it is one of the four main types of cutaneous receptors. The corpuscles are present in skin notably on both surfaces of the hands and feet, arms, and neck. Pacinian corpuscles are also found on bone periosteum, joint capsules, the pancreas and other internal organs, the breast, genitals, and lymph nodes. Pacinian corpuscles are rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors. As phasic receptors they respond quickly but briefly to a stimulus with the response diminishing even when the stimulus is maintained. They primarily respond to vibration, and deep pressure. They are especially sensitive to high-frequency vibrations. Groups of corpuscles sense pressure changes (such as on grasping or releasing an object). They are additionally crucially involved in proprioception. The vibrational r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellar Corpuscle
The Pacinian corpuscle (also lamellar corpuscle, or Vater–Pacini corpuscle) is a low-threshold mechanoreceptor responsive to vibration or pressure, found in the skin and other internal organs. In the skin it is one of the four main types of cutaneous receptors. The corpuscles are present in skin notably on both surfaces of the hands and feet, arms, and neck. Pacinian corpuscles are also found on bone periosteum, joint capsules, the pancreas and other internal organs, the breast, genitals, and lymph nodes. Pacinian corpuscles are rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors. As phasic receptors they respond quickly but briefly to a stimulus with the response diminishing even when the stimulus is maintained. They primarily respond to vibration, and deep pressure. They are especially sensitive to high-frequency vibrations. Groups of corpuscles sense pressure changes (such as on grasping or releasing an object). They are additionally crucially involved in proprioception. The vibrational rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of Membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cells, which include animal cells like neurons and myocyte, muscle cells, as well as some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell–cell interaction, cell–cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward axon terminal, synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
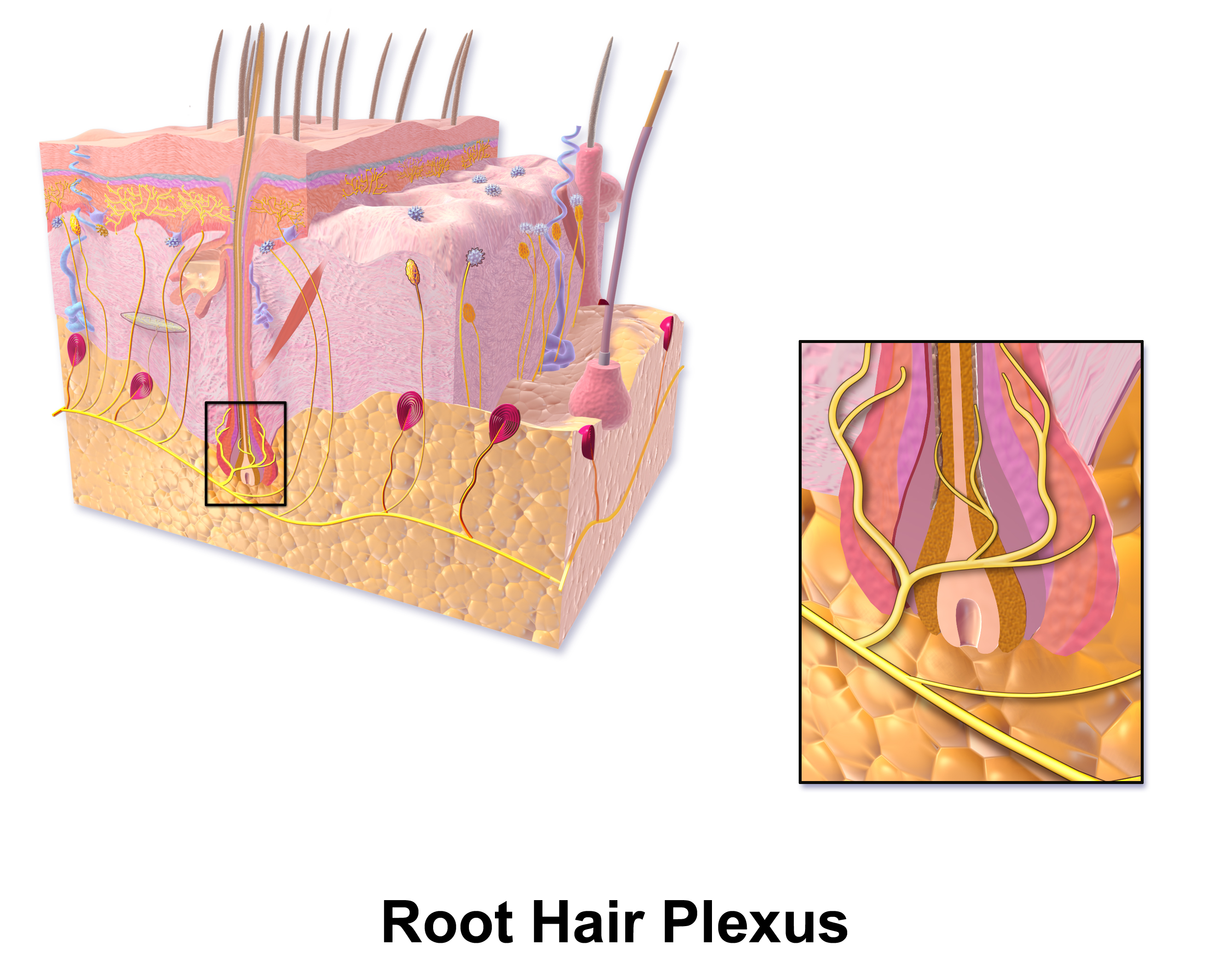
Hair Follicle Receptors
A hair plexus or root hair plexus is a special group of nerve fiber endings and serves as a very sensitive mechanoreceptor for touch sensation. Hair contains a number of different types of nerve endings. They are specialized for the detection of different kinds of stimuli and thus different types of neuron innervate these structures within the skin. In particular there are neurons innervating the hair that detect, deflection of the hair (i.e. to detect stroking), and pulling of the hair (i.e. noxious stimuli). The hair follicles are innervated by at least 5 classes of low threshold mechanical receptors. They are mechanoreceptors conveying touch sensation with cell bodies located inside of either dorsal root ganglia or trigeminal root ganglia. For most of the body (excluding the head and neck), crude touch and noxious stimuli from these receptors are further conveyed by the spinothalamic tract whereas discriminative and light touch are conveyed to via the dorsal column medial lem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |