|
Mechanistic Interpretability
Mechanistic interpretability (often shortened to "Mech Interp" or "MI") is a subfield of interpretability that seeks to reverse‑engineer neural networks, generally perceived as a black box, into human‑understandable components or "circuits", revealing the causal pathways by which models process information. The object of study generally includes but is not limited to vision models and Transformer-based large language models (LLMs). History Chris Olah is generally credited with coining the term 'Mechanistic interpretability' and spearheading its early development. In the 2018 paper ''The Building Blocks of Interpretability'', Olah (then at Google Brain) and his colleagues combined existing interpretability techniques, including feature visualization, dimensionality reduction, and attribution with human-computer interface methods to explore features represented by the neurons in the vision model, Inception v1. In the March 2020 paper ''Zoom In: An Introduction to Circuits'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accomplishes a task with very little (if any) insight into exactly how it does so. Depending on the system under consideration and the technologies employed, the knowledge gained during reverse engineering can help with repurposing obsolete objects, doing security analysis, or learning how something works. Although the process is specific to the object on which it is being performed, all reverse engineering processes consist of three basic steps: information extraction, modeling, and review. Information extraction is the practice of gathering all relevant information for performing the operation. Modeling is the practice of combining the gathered information into an abstract model, which can be used as a guide for designing the new object or syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
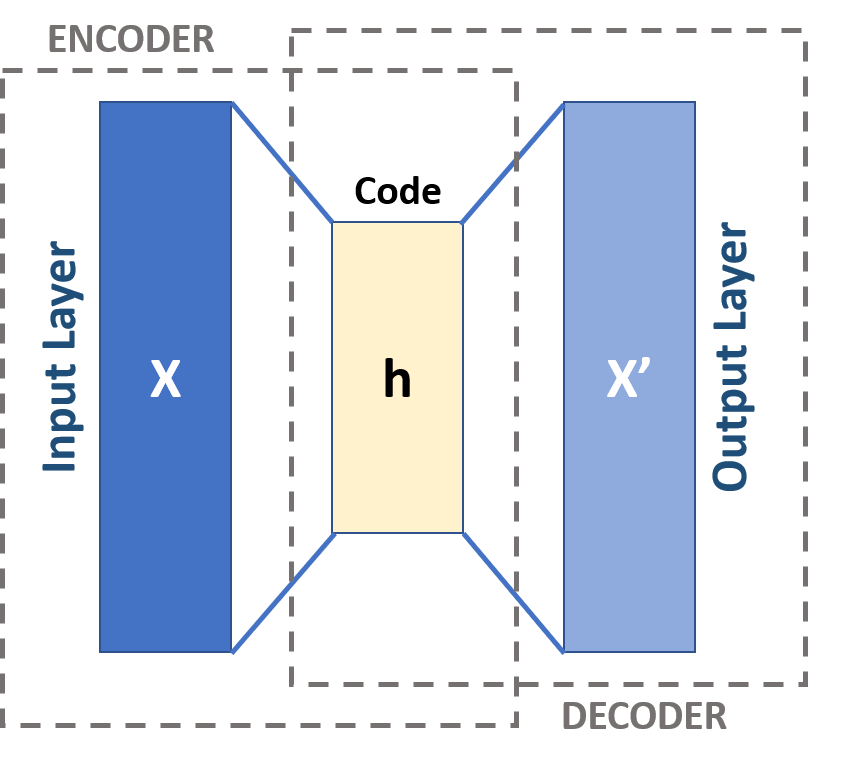
Autoencoder
An autoencoder is a type of artificial neural network used to learn efficient codings of unlabeled data (unsupervised learning). An autoencoder learns two functions: an encoding function that transforms the input data, and a decoding function that recreates the input data from the encoded representation. The autoencoder learns an efficient representation (encoding) for a set of data, typically for dimensionality reduction, to generate lower-dimensional embeddings for subsequent use by other machine learning algorithms. Variants exist which aim to make the learned representations assume useful properties. Examples are regularized autoencoders (''sparse'', ''denoising'' and ''contractive'' autoencoders), which are effective in learning representations for subsequent classification tasks, and ''variational'' autoencoders, which can be used as generative models. Autoencoders are applied to many problems, including facial recognition, feature detection, anomaly detection, and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliency Map
In computer vision, a saliency map is an image that highlights either the region on which people's eyes focus first or the most relevant regions for machine learning models. The goal of a saliency map is to reflect the degree of importance of a pixel to the human visual system or an otherwise opaque ML model. For example, in this image, a person first looks at the fort and light clouds, so they should be highlighted on the saliency map. Saliency maps engineered in artificial or computer vision are typically not the same as the actual saliency map constructed by biological or natural vision. Application Overview Saliency maps have applications in a variety of different problems. Some general applications: Human eye * Image and video compression: The human eye focuses only on a small region of interest in the frame. Therefore, it is not necessary to compress the entire frame with uniform quality. According to the authors, using a salience map reduces the final size of the vid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explainability
Explainable AI (XAI), often overlapping with interpretable AI, or explainable machine learning (XML), is a field of research within artificial intelligence (AI) that explores methods that provide humans with the ability of ''intellectual oversight'' over AI algorithms. The main focus is on the reasoning behind the decisions or predictions made by the AI algorithms, to make them more understandable and transparent. This addresses users' requirement to assess safety and scrutinize the automated decision making in applications. XAI counters the "black box" tendency of machine learning, where even the AI's designers cannot explain why it arrived at a specific decision. XAI hopes to help users of AI-powered systems perform more effectively by improving their understanding of how those systems reason. XAI may be an implementation of the social right to explanation. Even if there is no such legal right or regulatory requirement, XAI can improve the user experience of a product or servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lex Fridman
Alexei "Lex" Fridman (; born 15 August 1983) is an American computer scientist and podcaster. Since 2018, he has hosted the ''Lex Fridman Podcast'', where he interviews notable figures from various fields such as science, technology, sports, and politics. Fridman rose to prominence in 2019 after Elon Musk praised a study Fridman authored at MIT, which concluded that drivers remained focused while using Tesla's semi-autonomous driving system. The study was not peer-reviewed and was criticized by AI experts. That year Fridman transitioned to an unpaid role at MIT AgeLab, and since 2022 has worked as a research scientist at the MIT Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems (LIDS). As of February 2024, Fridman lives in Texas and is still paid by MIT. Early life and education Fridman was born in Chkalovsk, Tajik Soviet Socialist Republic, and grew up in Moscow. He is Jewish. His father, Alexander Fridman, is a plasma physicist and professor at Drexel University. His brothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICML
The International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) is a leading international academic conference in machine learning. Along with NeurIPS and ICLR, it is one of the three primary conferences of high impact in machine learning and artificial intelligence research. It is supported by the International Machine Learning Society (IMLS). Precise dates vary year to year, but paper submissions are generally due at the end of January, and the conference is generally held the following July. The first ICML was held 1980 in Pittsburgh. Locations * ICML 2026 Seoul, South Korea * ICML 2025 Vancouver, Canada * ICML 2024 Vienna, Austria * ICML 2023 Honolulu, United States * ICML 2022 Baltimore, United States * ICML 2021 Vienna, Austria (virtual conference) * ICML 2020 Vienna, Austria (virtual conference) * ICML 2019 Los Angeles, United States * ICML 2018 Stockholm, Sweden * ICML 2017 Sydney, Australia * ICML 2016 New York City, United States * ICML 2015 Lille, France * ICML ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google DeepMind
DeepMind Technologies Limited, trading as Google DeepMind or simply DeepMind, is a British–American artificial intelligence research laboratory which serves as a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Founded in the UK in 2010, it was acquired by Google in 2014 and merged with Google AI's Google Brain division to become Google DeepMind in April 2023. The company is headquartered in London, with research centres in the United States, Canada, France, Germany, and Switzerland. DeepMind introduced neural Turing machines (neural networks that can access external memory like a conventional Turing machine), resulting in a computer that loosely resembles short-term memory in the human brain. DeepMind has created neural network models to play video games and board games. It made headlines in 2016 after its AlphaGo program beat a human professional Go player Lee Sedol, a world champion, in a five-game match, which was the subject of a documentary film. A more general program, AlphaZero, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Tegmark
Max Erik Tegmark (born 5 May 1967) is a Swedish-American physicist, machine learning researcher and author. He is best known for his book ''Life 3.0'' about what the world might look like as artificial intelligence continues to improve. Tegmark is a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the president of the Future of Life Institute. Early life Tegmark was born in Sweden to Karin Tegmark and American-born professor of mathematics Harold S. Shapiro. While in high school, he and a friend created and sold a word processor written in pure machine code for the Swedish eight-bit computer ABC 80, and a 3D Tetris-like game called Frac. Tegmark left Sweden in 1990 after receiving his Master of Science in Engineering, M.S.E in engineering physics from the KTH Royal Institute of Technology and a Bachelor of Arts, B.A. in economics the previous year at the Stockholm School of Economics. His first academic venture beyond Scandinavia brought him to California, where he stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AI Alignment
In the field of artificial intelligence (AI), alignment aims to steer AI systems toward a person's or group's intended goals, preferences, or ethical principles. An AI system is considered ''aligned'' if it advances the intended objectives. A ''misaligned'' AI system pursues unintended objectives. It is often challenging for AI designers to align an AI system because it is difficult for them to specify the full range of desired and undesired behaviors. Therefore, AI designers often use simpler ''proxy goals'', such as Reinforcement learning from human feedback, gaining human approval. But proxy goals can overlook necessary constraints or reward the AI system for merely ''appearing'' aligned. AI systems may also find loopholes that allow them to accomplish their proxy goals efficiently but in unintended, sometimes harmful, ways (reward hacking). Advanced AI systems may develop unwanted Instrumental convergence, instrumental strategies, such as seeking power or survival because s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Philanthropy
Open Philanthropy is an American philanthropic advising and funding organization focused on cost-effective, high-impact giving. Its current CEO is Alexander Berger. As of June 2025, Open Philanthropy has directed more than $4 billion in grants across a variety of focus areas, including global health, scientific research, pandemic preparedness, potential risks from advanced AI, and farm animal welfare. It chooses focus areas through a process of "strategic cause selection" — looking for problems that are large, tractable, and neglected relative to their size. History While Open Philanthropy works with a range of donors, its founding and most significant ongoing partnership is with Good Ventures, the foundation of Cari Tuna and Dustin Moskovitz. Dustin Moskovitz co-founded Facebook and later Asana, becoming a billionaire in the process. He and Tuna, his wife, were inspired by Peter Singer's '' The Life You Can Save'', and became the youngest couple to sign Bill Gates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AI Safety
AI safety is an interdisciplinary field focused on preventing accidents, misuse, or other harmful consequences arising from artificial intelligence (AI) systems. It encompasses machine ethics and AI alignment, which aim to ensure AI systems are moral and beneficial, as well as monitoring AI systems for risks and enhancing their reliability . The field is particularly concerned with existential risks posed by advanced AI models. Beyond technical research, AI safety involves developing norms and policies that promote safety. It gained significant popularity in 2023, with rapid progress in generative AI and public concerns voiced by researchers and CEOs about potential dangers. During the 2023 AI Safety Summit, the United States and the United Kingdom both established their own AI Safety Institute. However, researchers have expressed concern that AI safety measures are not keeping pace with the rapid development of AI capabilities. Motivations Scholars discuss current risks from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparse Dictionary Learning
Sparse dictionary learning (also known as sparse coding or SDL) is a representation learning method which aims to find a sparse representation of the input data in the form of a linear combination of basic elements as well as those basic elements themselves. These elements are called ''atoms'', and they compose a ''dictionary''. Atoms in the dictionary are not required to be orthogonal, and they may be an over-complete spanning set. This problem setup also allows the dimensionality of the signals being represented to be higher than any one of the signals being observed. These two properties lead to having seemingly redundant atoms that allow multiple representations of the same signal, but also provide an improvement in sparsity and flexibility of the representation. One of the most important applications of sparse dictionary learning is in the field of compressed sensing or signal recovery. In compressed sensing, a high-dimensional signal can be recovered with only a few linear me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |