|
McCabe–Thiele Method
The McCabe–Thiele method is a technique that is commonly employed in the field of chemical engineering to model the separation of two substances by a distillation column. It uses the fact that the composition at each theoretical tray is completely determined by the mole fraction of one of the two components. This method is based on the assumptions that the distillation column is isobaric—i.e the pressure remains constant—and that the flow rates of liquid and vapor do not change throughout the column (i.e., constant molar overflow). The assumption of constant molar overflow requires that: * The heat needed to vaporize a certain amount of liquid of the feed components are equal, * For every mole of liquid vaporized, a mole of vapor is condensed, and * Heat effects such as heat needed to dissolve the substance(s) are negligible. The method was first published by Warren L. McCabe and Ernest Thiele in 1925, both of whom were working at the Massachusetts Institute of Tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of the operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials into useful products. Chemical engineering uses principles of chemistry, physics, mathematics, biology, and economics to efficiently use, produce, design, transport and transform energy and materials. The work of chemical engineers can range from the utilization of nanotechnology and nanomaterials in the laboratory to large-scale industrial processes that convert chemicals, raw materials, living cells, microorganisms, and energy into useful forms and products. Chemical engineers are involved in many aspects of plant design and operation, including safety and hazard assessments, process engineering, process design and analysis, modeling and simulation, modeling, control engineering, chemical reaction engineering, nuclear engineering, biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
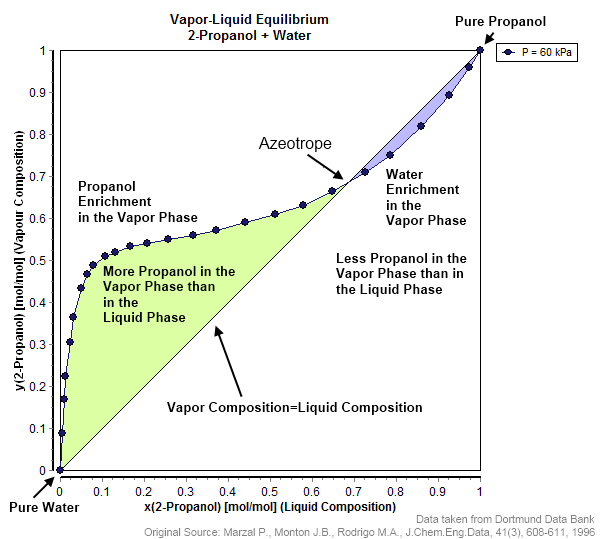
Vapor–liquid Equilibrium
In thermodynamics and chemical engineering, the vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) describes the distribution of a chemical species between the vapor phase and a liquid phase. The Vapor quality, concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid, especially at Thermodynamic equilibrium, equilibrium, is often expressed in terms of vapor pressure, which will be a partial pressure (a part of the total gas pressure) if any other gas(es) are present with the vapor. The equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid is in general strongly dependent on temperature. At vapor–liquid equilibrium, a liquid with individual components in certain concentrations will have an equilibrium vapor in which the concentrations or partial pressures of the vapor components have certain values depending on all of the liquid component concentrations and the temperature. The converse is also true: if a vapor with components at certain concentrations or partial pressures is in vapor–liquid equilibrium with its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azeotropic Distillation
In chemistry, azeotropic distillation is any of a range of techniques used to break an azeotrope in distillation. In chemical engineering, ''azeotropic distillation'' usually refers to the specific technique of adding another component to generate a new, lower-boiling azeotrope that is heterogeneous (e.g. producing two, immiscible liquid phases), such as the example below with the addition of benzene to water and ethanol. This practice of adding an entrainer which forms a separate phase is a specific sub-set of (industrial) Azeotrope#Azeotropy in fluid separation processes, azeotropic distillation methods, or combination thereof. In some senses, adding an entrainer is similar to extractive distillation. Material separation agent The addition of a material separation agent, such as benzene to an ethanol/water mixture, changes the molecular interactions and eliminates the azeotrope. Added in the liquid phase, the new component can alter the activity coefficient of various comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to fractionate. Generally the component parts have boiling points that differ by less than 25 °C (45 °F) from each other under a pressure of one atmosphere. If the difference in boiling points is greater than 25 °C, a simple distillation is typically used. A crude oil distillation unit uses fractional distillation in the process of refining crude oil. History The fractional distillation of organic substances played an important role in the 9th-century works attributed to the Islamic alchemist Jabir ibn Hayyan, as for example in the ('The Book of Seventy'), translated into Latin by Gerard of Cremona (c. 1114–1187) under the title . The Jabirian experiments with fractional distillation of animal and vegetable subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azeotrope
An azeotrope () or a constant heating point mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation.Moore, Walter J. ''Physical Chemistry'', 3rd e Prentice-Hall 1962, pp. 140–142 This happens because when an azeotrope is boiled, the vapour has the same proportions of constituents as the unboiled mixture. Knowing an azeotrope's behavior is important for distillation. Each azeotrope has a characteristic boiling point. The boiling point of an azeotrope is either less than the boiling point temperatures of any of its constituents (a positive azeotrope), or greater than the boiling point of any of its constituents (a negative azeotrope). For both positive and negative azeotropes, it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. For technical applications, the pressure-temperature-composition behavior of a mixture is the most important, but other important ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Distillation
Continuous distillation, a form of distillation, is an ongoing separation in which a mixture is continuously (without interruption) fed into the process and separated fractions are removed continuously as output streams. Distillation is the separation or partial separation of a liquid feed mixture into components or fractions by selective boiling (or evaporation) and condensation. The process produces at least two output fractions. These fractions include at least one '' volatile'' distillate fraction, which has boiled and been separately captured as a vapor condensed to a liquid, and practically always a ''bottoms'' (or ''residuum'') fraction, which is the least volatile residue that has not been separately captured as a condensed vapor. An alternative to continuous distillation is batch distillation, where the mixture is added to the unit at the start of the distillation, distillate fractions are taken out sequentially in time (one after another) during the distillation, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Vapor
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's thermodynamic tendency to evaporate. It relates to the balance of particles escaping from the liquid (or solid) in equilibrium with those in a coexisting vapor phase. A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as '' volatile''. The pressure exhibited by vapor present above a liquid surface is known as vapor pressure. As the temperature of a liquid increases, the attractive interactions between liquid molecules become less significant in comparison to the entropy of those molecules in the gas phase, increasing the vapor pressure. Thus, liquids with strong intermolecular interactions are likely to have smaller vapor pressures, with the reverse true for weaker interactions. The vapor pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturated Liquid
Saturation, saturated, unsaturation or unsaturated may refer to: Chemistry *Saturated and unsaturated compounds, a classification of compounds related to their ability to resist addition reactions ** Degree of unsaturation **Saturated fat or saturated fatty acid **Unsaturated fat or unsaturated fatty acid ** Non-susceptibility of an organometallic compound to oxidative addition * Saturation of protein binding sites * Saturation of enzymes with a substrate * Saturation of a solute in a solution, as related to the solute's maximum solubility at equilibrium ** Supersaturation, where the concentration of a solute exceeds its maximum solubility at equilibrium ** Undersaturation, where the concentration of a solute is less than its maximum solubility at equilibrium Biology * Oxygen saturation, a clinical measure of the amount of oxygen in a patient's blood * Saturation pollination, a pollination technique * Saturated mutagenesis, a form of site-directed mutagenesis * Saturation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-line Slopes
An IRCd, short for Internet Relay Chat daemon, is server software that implements the IRC protocol, enabling people to talk to each other via the Internet (exchanging textual messages in real time). It is distinct from an IRC bot that connects outbound to an IRC channel. The server listens to connections from IRC clients on a set of TCP ports. When the server is part of an IRC network, it also keeps one or more established connections to other servers/daemons. The term ''ircd'' originally referred to only one single piece of software, but it eventually became a generic reference to any implementation of an IRC daemon. However, the original version is still distributed under the same name, and this article discusses both uses. History The original IRCd was known as 'ircd', and was authored by Jarkko Oikarinen (WiZ on IRC) in 1988. He received help from a number of others, such as Markku Savela (msa on IRC), who helped with the 2.2+msa release, etc. In its first revisions, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to Chemical reaction, reactions over a long period of time. Reflux in industrial distillation The term ''reflux'' is very widely used in industries that utilize large-scale Fractionating column, distillation columns and Fractional distillation, fractionators such as oil refinery, petroleum refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants, and natural gas processing plants. In that context, reflux refers to the portion of the overhead liquid product from a distillation column or fractionator that is returned to the upper part of the column as shown in the schematic diagram of a typical industrial distillation column. Inside the column, the downflowing reflux liquid provides cooling and condensation of the upflowing vapors thereby increasing the effi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and science. In response to the increasing Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialization of the United States, William Barton Rogers organized a school in Boston to create "useful knowledge." Initially funded by a land-grant universities, federal land grant, the institute adopted a Polytechnic, polytechnic model that stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT moved from Boston to Cambridge in 1916 and grew rapidly through collaboration with private industry, military branches, and new federal basic research agencies, the formation of which was influenced by MIT faculty like Vannevar Bush. In the late twentieth century, MIT became a leading center for research in compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |