|
Mbale District
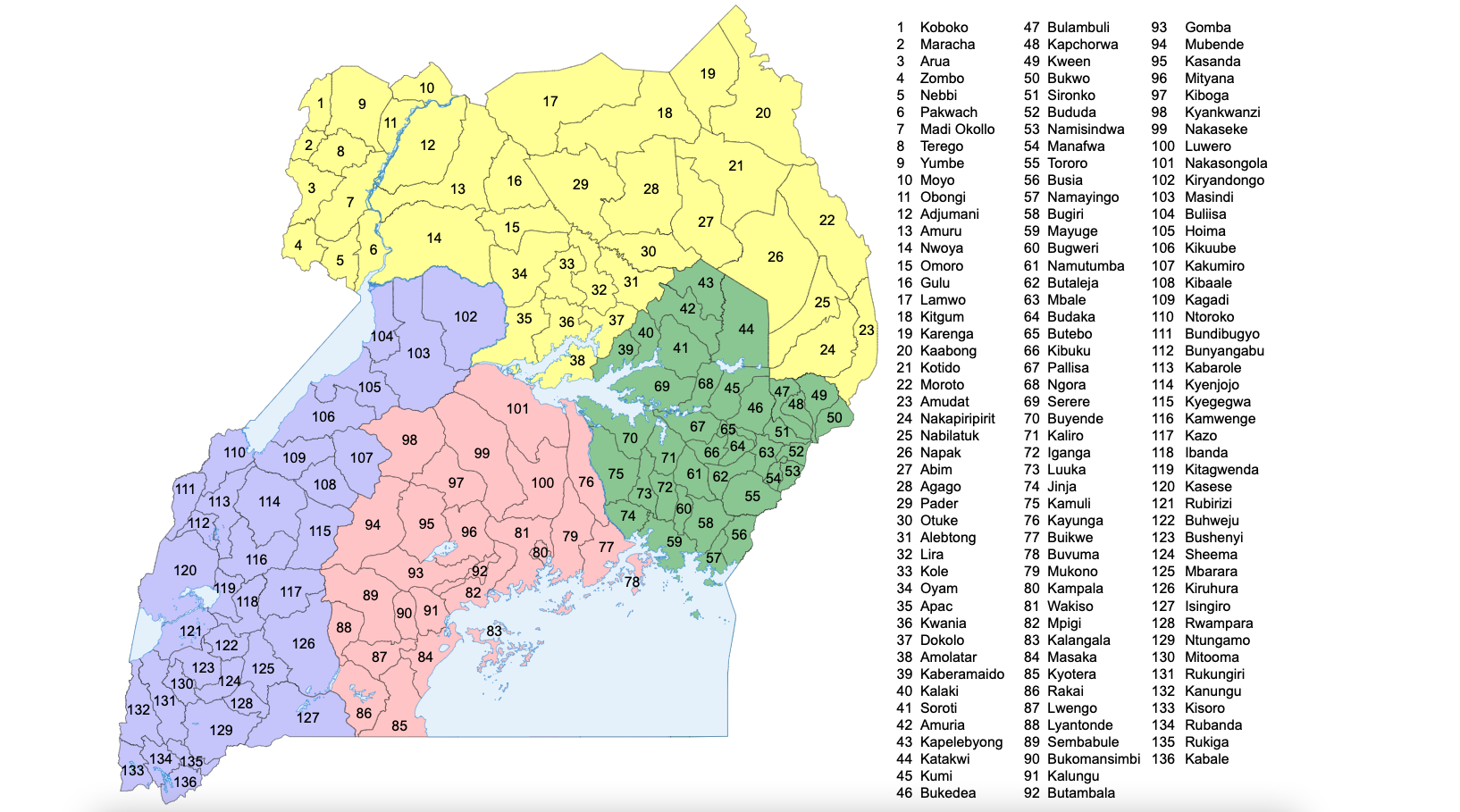
Mbale District is a district in Eastern Uganda. It is named after the largest city in the district, Mbale, which also serves as the main administrative and commercial center in the sub-region. Location Mbale District is bordered by Sironko District to the north, Bududa District to the northeast, Manafwa District to the southeast, Tororo District to the south, Butaleja District to the southwest and Budaka District to the west. Pallisa District and Kumi District lie to the northwest of Mbale District. Mbale, the largest town in the district which serves as the district headquarters, is located approximately northeast of Kampala, the capital and largest city of Uganda. The coordinates of the district are:00 57N, 34 20E. It has an area of . The districts of Bududa, Manafwa and Sironko were part of Mbale District before they were split off as independent districts. Population The 1991 census estimated the district population at about 240,900. The 2002 national census put th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Uganda
As of 1 July 2020, Uganda is divided into 135 districts plus the capital city of Kampala, which are grouped into four Regions of Uganda, geographic regions. Since 2005, the Ugandan government has been in the process of dividing districts into smaller units. This decentralization is intended to prevent resources from being distributed primarily to chief towns and leaving the remainder of each district neglected. Each district is further divided into Counties of Uganda, counties and municipalities, and each county is further divided into Sub-counties of Uganda, sub-counties. The head elected official in a district is the chairperson of the Local Council (Uganda), Local Council five (usually written with a Roman numeral V). Districts created since 2015 In September 2015, the Parliament of Uganda created 23 new districts, to be phased in over the next four years. ;Notes: See also * List of constituencies in Uganda * Regions of Uganda * Uganda Local Governments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumi District
Kumi District is a district in the Eastern Region of Uganda. The district is named after its main town, Kumi, which also hosts the district headquarters. Location Kumi District is bordered by Katakwi District to the north, Nakapiripirit District to the northeast, Bukedea District to the east, Pallisa District to the south, and Ngora District to the west. The main town in the district, Kumi, is located approximately southeast of Soroti, the largest town in Teso sub-region. The coordinates of the district are:01 30N, 33 57E. Population The 1991 national census estimated the population of the district at about 102,030. The 2002 national census estimated the district population at approximately 165,400. The annual population growth rate in the district is given as 4.5%. In 2012, the population of Kumi District was estimated at 255,500. The table below illustrates how the district population has grown between 2002 and 2012. All numbers are estimates. Transport Kumi District i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
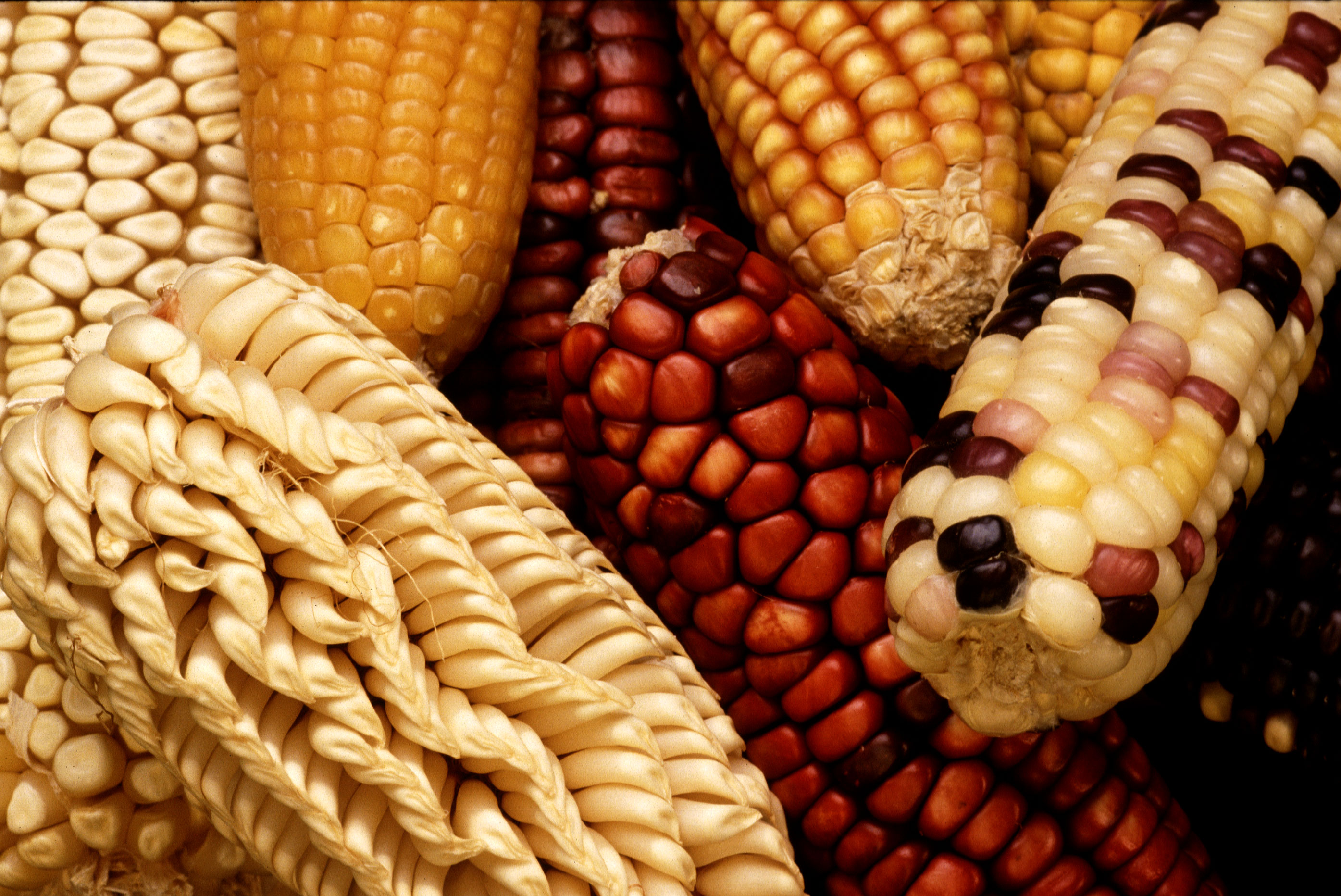
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matooke
Matoke, locally also known as matooke, amatooke in Buganda (Central Uganda), ekitookye in southwestern Uganda, ekitooke in western Uganda, kamatore in Lugisu (Eastern Uganda), ebitooke in northwestern Tanzania, igitoki in Rwanda, Burundi and by the cultivar name East African Highland banana, are a group of starchy triploid banana cultivars, originating from the African Great Lakes. The fruit is harvested green, carefully peeled, and then cooked and often mashed or pounded into a meal. In Uganda and Rwanda, the fruit is steam-cooked, and the mashed meal is considered a national dish in both countries. Matoke bananas are a staple food crop in Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania and other Great Lakes countries. They are also known as the Mutika/Lujugira subgroup. The medium-sized green fruits, which are of a specific group of banana, the East African Highland bananas (''Musa'' AAA-EA), are known in the Bantu languages of Uganda and Western Kenya as ''matoke''. Cooking bananas have long been and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditionally soaked and boiled, and used in many traditional dishes throughout the world. They can be cooked in many different ways, however, including frying and baking. The unripe seedpods of some varieties are also eaten whole as green beans or '' edamame'' (immature soybean), but many fully ripened beans contain toxins like phytohemagglutinin and require cooking. Terminology The word "bean" and its Germanic cognates (e.g. German '' Bohne'') have existed in common use in West Germanic languages since before the 12th century, referring to broad beans, chickpeas, and other pod-borne seeds. This was long before the New World genus '' Phaseolus'' was known in Europe. With the Columbian exchange of domestic plants between Europe and the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
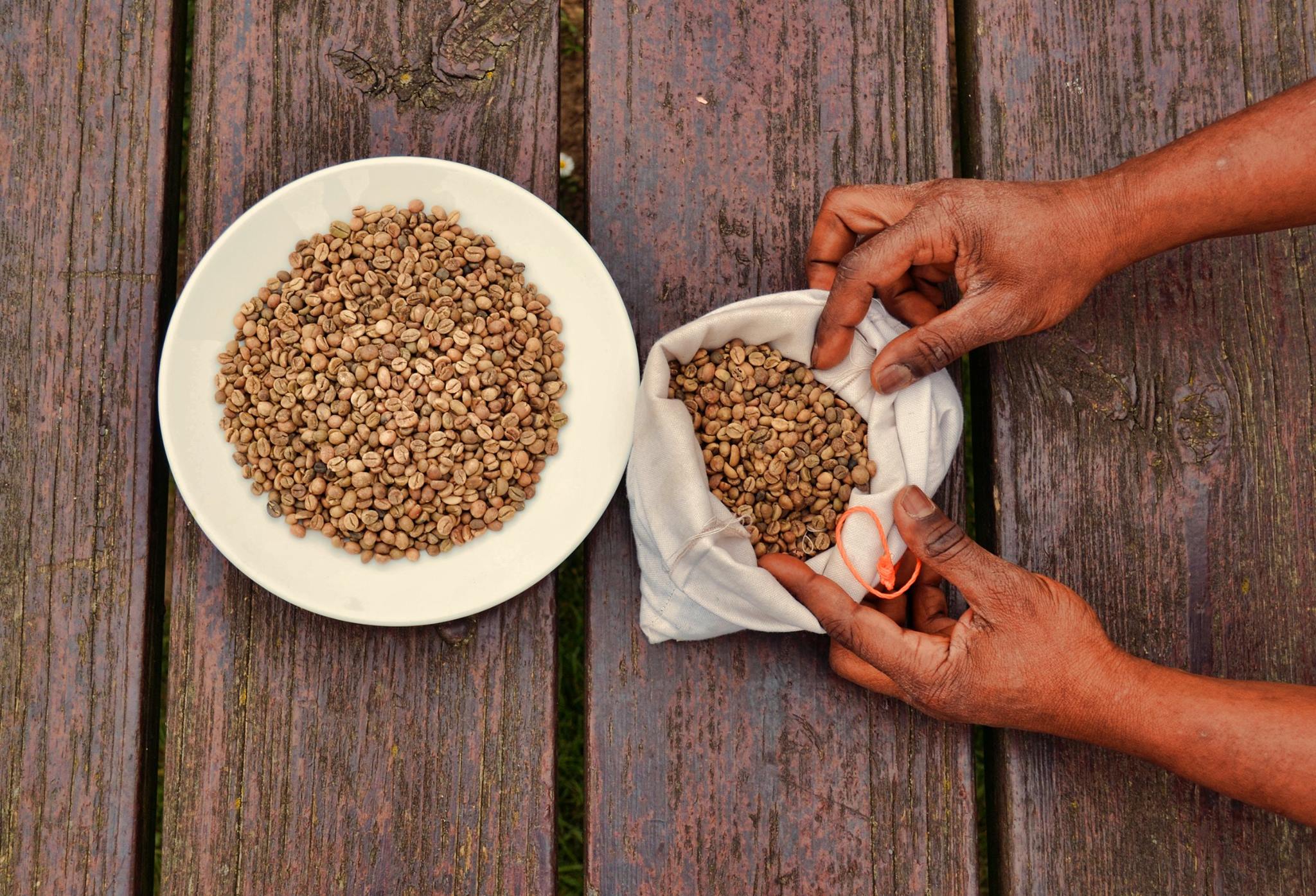
Coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially available. There are also various coffee substitutes. Typically served hot, coffee has the highest sales in the world market for hot drinks. Coffee production begins when the seeds from coffee cherries (the '' Coffea'' plant's fruits) are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The "beans" are roasted and then ground into fine particles. Coffee is brewed from the ground roasted beans, which are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often added to mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on farms larger than . However, five of every six farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumasaba
Masaba (''Lumasaaba''), sometimes known as Gisu (''Lugisu'') after one of its dialects, is a Bantu language spoken by more than two million people in East Africa. The Gisu dialect in eastern Uganda is mutually intelligible with Bukusu, spoken by ethnic Luhya in western Kenya. ''Masaba'' is the local name of Mount Elgon and the name of the son of the ancestor of the Gisu tribe. Like other Bantu languages, Lumasaba nouns are divided into several sets of noun classes. These are similar to the genders in Germanic and Romance languages, except that instead of the usual two or three, there are around eighteen different noun classes. The language has a quite complex verb morphology. Varieties Varieties of Masaba are as follows:Maho (2009) *Gisu (''Lugisu'') *Kisu *Bukusu (''Lubukusu''; ethnic Luhya) *Syan *Tachoni (''Lutachoni''; ethnic Luhya) *Dadiri (''Ludadiri'') *Buya (''Lubuya'') Dadiri is spoken in the north, Gisu in the center, and Buya in the center and south of Masaba territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagisu
The Gisu people, or ''Bamasaba'' people of Elgon, are a Bantu tribe and Bantu-speaking ethnic group of the Masaba people in eastern Uganda, closely related to the Bukusu people of Kenya. Bamasaba live mainly in the Mbale District of Uganda on the slopes of Mount Elgon. The Bagisu are estimated to be about 1,646,904 people making up 4.9% of the total population according to the 2014 National Census of Uganda. Religion The majority of the Bagisu people are Christians mainly Anglican (Church of Uganda) estimated at 45.7% while a significant percentage are Roman Catholic estimated at 29.1%. Around 14% of the Bagisu people follow Islam according to the 2002 Census of Uganda and 5.3% are Pentecostal. Ancestor The Masaba, Bukusu and Luhya people believed that their ancestors were Mundu and Sera. The people of Ethiopia and the Ethiopian Highlands have no name for Kundu, except that it is a mountain peak in Oromiya. The Bamasaba ancestor, Masaba migrated from the Ethiopian Mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masaba People
The Masaba people, or ''Bamasaaba'', are a Bantu people inhabiting the eastern Ugandan districts of Sironko, Manafwa, Bududa, Mbale, Namisindwa and Bulambuli. They are closely related to the Bukusu and Luhya of Western Kenya. They are mainly agricultural people, farming coffee, millet, bananas and sorghum on small-holder plots. Maize became popular with the coming of Europeans in the late 1890s. The name ''Bamasaaba'' is sometimes used interchangeably with the name '' Bagisu,'' even though the latter is actually a tribe of the Bamasaaba nation. The current Babukusu of western Kenya are believed to have migrated from the Bamasaaba, particularly from areas around Bubulo, in current Manafwa District. Many clans among the Babukusu have their origins among the Bamasaaba, a testimony to this linkage. Masinde Muliro, once a veteran politician and elder of the Babukusu from Kitale, was from the Bakokho clan, with its base at Sirilwa, near Bumbo in Uganda. Other clans common to bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Vision
The ''New Vision'' is a Ugandan English-language daily newspaper. It was established in its current form in 1986 by the Government of Uganda. It is the flagship newspaper of the state-owned Vision Group, a multimedia conglomerate. Along with its privately-owned competitor, the ''Daily Monitor'', the ''New Vision'' is one of the two largest national newspapers in Uganda. History The ''New Vision'' traces its origins to the colonial era. Its institutional predecessor, the ''Uganda Argus'', was founded in 1955 as a British colonial government publication. Following Uganda's independence in 1962, the government of President Milton Obote retained the ''Uganda Argus'' as its official paper. After the 1971 coup, the government of Idi Amin renamed the paper the ''Voice of Uganda''. When Amin was overthrown in 1979, the succeeding government named it the ''Uganda Times''. When the National Resistance Movement (NRM) came to power in 1986, the publication was rebranded as the ''New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |