|
Małomice
Małomice () is a town in western Poland, located in Żagań County, Lubusz Voivodeship, with 3,467 inhabitants (2019). It is situated on the Bóbr river between Szprotawa and Żagań. Located in the historical region of Lower Silesia, Małomice had been a centre of smelting bog iron by bloomery hearths since medieval times. History Małomice originated as a Slavic settlement. After a deer antler tool was found on the Bober river in 1877, excavations in the 1930s showed probable age from between 1000 and 1200 on the basis of pottery finds. The area formed part of the Medieval Kingdom of Poland and from the 13th century, as a result of the fragmentation of Poland, it was part of the Piast-ruled duchies of Głogów and Żagań. The first written mention of the village under the Old Polish name ''Małymicz'' dates from 1329. The village existed on agriculture and the production of bog iron. Around 1572, the lords of Schoenaich Mallmitz conferred limited town privileges. A chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Małomice
__NOTOC__ Gmina Małomice is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Żagań County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland. Its seat is the town of Małomice, which lies approximately south-east of Żagań and south of Zielona Góra. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2019 its total population is 5,181. Villages Apart from the town of Małomice, Gmina Małomice contains the villages and settlements of Bobrzany, Chichy, Lubiechów, Lubusz Voivodeship, Lubiechów, Śliwnik and Żelisław, Lubusz Voivodeship, Żelisław. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Małomice is bordered by the gminas of Gmina Osiecznica, Osiecznica, Gmina Szprotawa, Szprotawa and Gmina Żagań, Żagań. Twin towns – sister cities Gmina Małomice is Sister city, twinned with: * Zeuthen, Germany References {{DEFAULTSORT:Gmina Malomice Gminas in Lubusz Voivodeship, Malomice Żagań County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Żagań County
__NOTOC__ Żagań County () is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Żagań, which lies south of Zielona Góra and south of Gorzów Wielkopolski. The county contains four other towns: Szprotawa, lying south-east of Żagań, Iłowa, lying south-west of Żagań, Małomice, lying south-east of Żagań, and Gozdnica, south-west of Żagań. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 79,297. The most populated towns are Żagań with 25,731 inhabitants and Szprotawa with 11,820 inhabitants. Neighbouring counties Żagań County is bordered by Zielona Góra County to the north, Nowa Sól County to the north-east, Głogów County and Polkowice County to the east, Bolesławiec County and Zgorzelec County to the south, and Żary County to the west. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubusz Voivodeship
Lubusz Voivodeship ( ) is a voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) in western Poland with a population of 972,140. Its regional capitals are Gorzów Wielkopolski and Zielona Góra. The region is characterized by a landscape of forests, lakes, and rivers, and is Germany–Poland border, bordered by Germany to the west. The functions of regional capital are shared between two citiesGorzów Wielkopolski and Zielona Góra. Gorzów serves as the seat of the centrally-appointed voivode (''wojewoda''), or governor, and Zielona Góra is the seat of the elected regional assembly (Voivodeship sejmik, ''sejmik'') and the executive elected by that assembly, headed by a marshal (''marszałek''). In addition, the voivodeship includes a third city (Nowa Sól) and a number of towns. Lubusz Voivodeship borders West Pomeranian Voivodeship to the north, Greater Poland Voivodeship to the east, Lower Silesian Voivodeship to the south, and Germany (Brandenburg and Saxony) to the west. It was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bóbr
The Bóbr (; ; ) is a river which flows through the north of the Czech Republic and the southwest of Poland. It is a left tributary of the Oder. Its Polish name translates directly to ' beaver'. Course The Bóbr has a length of (3 in Czech Republic, 276 in Poland, 10th longest Polish river) and a basin area of (44 in Czech Republic and 5,830 in Poland). Statistics Poland, p. 85-86 It originates on a slope of the Rýchory mountains in the southeast of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Żagań
The Duchy of Żagań (, ) or Duchy of Sagan () was one of the duchies of Silesia ruled by the Silesian Piasts. Its capital was Żagań in Lower Silesia, the territory stretched to the town of Nowogród Bobrzański in the north and reached the Lusatian Neisse at Przewóz, Żary County, Przewóz in the west, including two villages beyond the river (Pechern and Neudorf). It was formed in 1274 from the western part of the Duchy of Głogów and existed under Silesian Piasts, Piast rule until 1304, then again from 1322 to 1394 and from 1413 to 1472. Since 1329 it was under the suzerainty of Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia; it was acquired by the Electorate of Saxony, Saxon House of House of Wettin, Wettin in 1472, before it was finally seized by the Bohemian king in 1549. The Żagań ducal title later passed to Bohemian and French nobility, in 1742 it was annexed by Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia. Re-established as a fief of the Prussian throne in 1844, it formally existed until its official t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Poland (1025-1385)
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the medieval period from 1025 until 1385. Background The West Slavic tribe of Polans who lived in what is today the historic region of Greater Poland, gave rise to a state in the early 10th century, which would become the nascent predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland. Following the Christianization of Poland in 966, and the emergence of the Duchy of Poland during the rule of Mieszko I, his eldest son Bolesław I the Brave inherited his father's dukedom and subsequently was crowned as king. History Establishment In 1025, Bolesław I the Brave of the Piast dynasty was crowned as the first King of Poland at the cathedral in Gniezno and elevated the status of Poland from a duchy to a kingdom after receiving permission for his coronation from Pope John XIX. Following the death of Bolesław, his son Mieszko II Lambert inherited the crown and a vast territory after his father, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piast Dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of King Casimir III the Great. Branches of the Piast dynasty continued to rule in the Duchy of Masovia (until 1526) and in the Duchies of Silesia until the last male Silesian Piast died in 1675. The Piasts intermarried with several noble lines of Europe, and possessed numerous titles, some within the Holy Roman Empire. The Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings ruling after the death of Casimir IV of Poland were also descended in the female line from Casimir III's daughter. Origin of the name The early dukes and kings of Poland are said to have regarded themselves as descendants of the semi-legendary Piast the Wheelwright (''Piast Kołodziej''), first mentioned in the ''Cronicae et gesta ducum sive pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Głogów
The Duchy of Głogów (, ) or Duchy of Glogau () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed in course of the medieval fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia. It existed in 1177–1185 and 1251–1506 and was ruled by the Silesian Piasts, followed by John Corvinus and the Jagiellonian dynasty. History In 1177, under the rule of Konrad Spindleshanks, the youngest son of High Duke Władysław II the Exile of Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Poland, the town of Głogów had already become the capital of a duchy in its own right. However, when Konrad died between 1180 and 1190, his duchy was again inherited by his elder brother Bolesław I the Tall, and re-incorporated to the Duchy of Silesia/Wrocław. After the death of Bolesław's grandson Duke Henry II the Pious at the 1241 Battle of Legnica his sons in 1248 divided the Lower Silesian Duchy of Wrocław among themselves. Konrad I, Duke of Głogów, Konrad I, a child when his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Privileges
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the traditions of the self-administration of Roman cities. Judicially, a borough (or burgh) was distinguished from the countryside by means of a charter from the ruling monarch that defined its privileges and laws. Common privileges involved trade (marketplace, the storing of goods, etc.) and the establishment of guilds. Some of these privileges were permanent and could imply that the town obtained the right to be called a borough, hence the term "borough rights" (; ). Some degree of self-government, representation by diet, and tax-relief could also be granted. Multiple tiers existed; for example, in Sweden, the basic royal charter establishing a borough enabled trade, but not foreign trade, which required a higher-tier charter granting staple ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Polish
The Old Polish language () was a period in the history of the Polish language between the 10th and the 16th centuries. It was followed by the Middle Polish language. The sources for the study of the Old Polish language are the data of the comparative-historical grammar of Slavic languages, the material of Polish dialects, several Latin manuscripts with Polish glosses, as well as – most importantly – monuments written in Old Polish: the Holy Cross Sermons (), the Florian Psalter (), Bogurodzica (), the Sharoshpatak Bible ( or ) and some others. The Old Polish language was spoken mainly on the territory of modern Poland. It was the main vernacular of medieval Polish states under the Piasts and early Jagiellons, although it was not the state language (that being Latin). History The Polish language started to change after the baptism of Poland, which caused an influx of Latin words, such as ''kościół'' "church" (Latin , "castle"), ''anioł'' "angel" (Latin ). Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
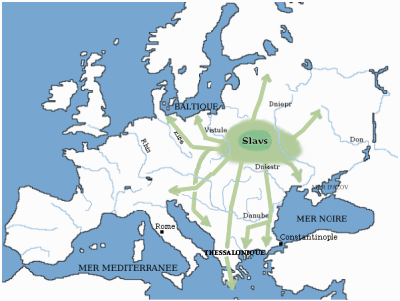
Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the Bulgarian Empire, the Principality of Serbia, the Duchy of Croatia and the Banate of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |