|
Maude Abbott Medical Museum
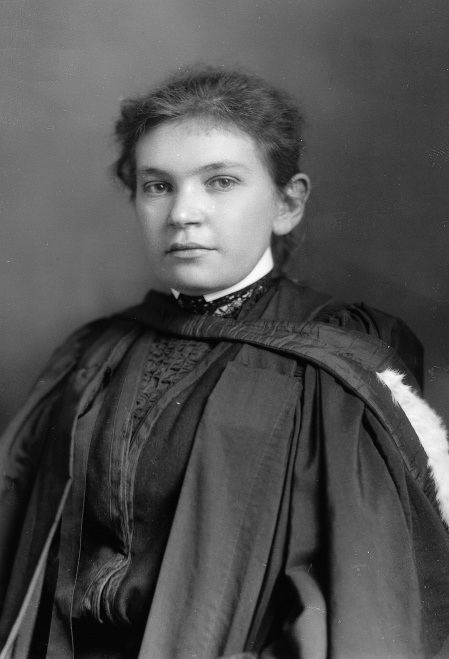
The Maude Abbott Medical Museum () is a medical museum located at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The museum is named after Canadian doctor Maude Abbott, who served as its curator in the late 19th century. History The museum originally consisted of collections of "interesting specimens," owned by university professors. In the late 19th century, the collection included dissection room specimens from the collection of F.J. Shepherd, skeletons, bones, and models made of papier-mâché, wax, and plaster. William Osler donated almost 500 post-mortem specimens. The specimens came from the Université de Montréal Faculty of Veterinary Medicine and the Montreal General Hospital. Wyatt Johnson also contributed to the collection. The museum was curated by a junior faculty member. In 1894, the museum was located in two rooms at the medical building. In 1898, Maude Abbott Maude Elizabeth Seymour Abbott (March 18, 1868Sources disagree on the date of Abbott's birth. The Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Osler
Sir William Osler, 1st Baronet, (; July 12, 1849 – December 29, 1919) was a Canadian physician and one of the "Big Four" founding professors of Johns Hopkins Hospital. Osler created the first Residency (medicine), residency program for specialty training of physicians. He has frequently been described as the ''Father of Modern Medicine'' and one of the "greatest diagnosticians ever to wield a stethoscope". In addition to being a physician he was a bibliophile, historian, author, and renowned practical joker. He was passionate about medical libraries and medical history, having founded the History of Medicine Society (formally "section"), at the Royal Society of Medicine, London. He was also instrumental in founding the Medical Library Association of Great Britain and Ireland, and the (North American) Association of Medical Librarians (later the Medical Library Association) along with three other people, including Margaret Ridley Charlton, Margaret Charlton, the medical librari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In Montreal
Montreal was referred to as "''Canada's Cultural Capital''" by Monocle (2007 magazine), Monocle Magazine. The city is Canada's centre for French-language television productions, radio, theatre, film, multimedia, and print publishing. The ''Quartier Latin, Montreal, Quartier Latin'' is a neighbourhood crowded with cafés animated by this literary and musical activity. Montreal's many cultural communities have given it a distinct local culture. As a North American city, Montreal shares many of the cultural features characteristic of the other metropolis on the continent, including representations in all traditional manifestations of high culture, a long-lasting tradition of jazz and rock music, and tentative experimentation in visual arts, theatre, music, and dance. Yet, being at the confluence of the French and the English traditions, Montreal has developed a unique and distinguished cultural face in the world. Another distinctive characteristic of Montreal culture life is to be f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Museums In Canada
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religion, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal General Hospital
The Montreal General Hospital (MGH) () is a hospital in Montreal, Quebec, Canada established in the years 1818–1820. The hospital received its charter in 1823. It is currently part of the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC) and is located on Mount Royal, at the intersection of Pine Avenue (Avenue des Pins) and Côte-des-Neiges Road. It has six pavilions: A, B, C, D, E and Livingston (L); plus a research centre in a separate building next to the L pavilion. The first MGH was built at the corner of Craig Street (today St. Antoine) and St. Lawrence Boulevard and only had 24 beds. Having outgrown this space, it moved to a new 72-bed building on Dorchester Boulevard (now René-Lévesque) between St. Dominique and De Bullion Streets; today this facility is a long-term care centre. In 1924, the hospital merged with the Western General Hospital (currently the D & E wings of the former Montreal Children's Hospital) building at the corner of Tupper Street and Atwater Avenue. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Université De Montréal Faculty Of Veterinary Medicine
The Faculty of Veterinary Medicine () at Université de Montréal is one of five veterinary medical schools in Canada. It is the only French-language veterinary college in North America. The faculty is part of the Université de Montréal and is located in Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec near Montreal. The veterinary college was located in Oka, Quebec before moving to Saint-Hyacinthe in 1947. In Oka, the veterinary college formed part of an agricultural-veterinary educational centre operated by the Trappists. This centre was financed by the Quebec Department of Agriculture. The Centre became the direct responsibility of the Québec Department of Agriculture from 1947 to 1969. In 1969, the Centre became a Université de Montréal faculty. Considerable development in staff and facilities has taken place. The FMV holds a full accreditation of the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and is one of 15 faculties and affiliated schools of Université de Montréal Studies Doctorate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Université De Montréal
The Université de Montréal (; UdeM; ) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university's main campus is located in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood of Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce on Mount Royal near the Outremont Summit (also called Mount Murray), in the borough of Outremont, Quebec, Outremont. The institution comprises thirteen faculties, more than sixty departments and two affiliated schools: the Polytechnique Montréal (School of Engineering; formerly the École polytechnique de Montréal) and HEC Montréal (School of Business, formerly École des Hautes études commerciales). It offers more than 650 undergraduate programmes and graduate programmes, including 71 doctoral programmes. The university was founded as a satellite campus of the Université Laval in 1878. It became an independent institution after it was issued a papal charter in 1919 and a provincial charter in 1920. moved from Montreal's Quartier Latin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-mortem
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death; or the exam may be performed to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. The term ''necropsy'' is generally used for non-human animals. Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathology, pathologist. Only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Manner of death must be determined ** Determine if death was natural or unnatural ** Injury source and extent on the corpse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papier-mâché
file:JacmelMardiGras.jpg, upright=1.3, Mardi Gras papier-mâché masks, Haiti Papier-mâché ( , , - the French term "mâché" here means "crushed and ground") is a versatile craft technique with roots in ancient China, in which waste paper is shredded and mixed with water and a binder to produce a pulp ideal for modelling or moulding, which dries to a hard surface and allows the creation of light, strong and inexpensive objects of any shape, even very complicated ones. There are various recipes, including those using cardboard and some mineral elements such as chalk or clay (carton-pierre, a building material). Papier-mâché reinforced with textiles or boiled cardboard (carton bouilli) can be used for durable, sturdy objects. There is even carton-cuir (cardboard and leather) There is also a "laminating process", a method in which strips of paper are glued together in layers. Binding agents include glue, starch or wallpaper paste. "Carton-paille" or strawboard was already describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum
A museum is an institution dedicated to displaying or Preservation (library and archive), preserving culturally or scientifically significant objects. Many museums have exhibitions of these objects on public display, and some have private collections that are used by researchers and specialists. Museums host a much wider range of objects than a library, and they usually focus on a specific theme, such as the art museums, arts, science museums, science, natural history museums, natural history or Local museum, local history. Public museums that host exhibitions and interactive demonstrations are often tourist attractions, and many draw large numbers of visitors from outside of their host country, with the List of most-visited museums, most visited museums in the world attracting millions of visitors annually. Since the establishment of Ennigaldi-Nanna's museum, the earliest known museum in ancient history, ancient times, museums have been associated with academia and the preserva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids. Vertebrates are animals with an endoskeleton centered around an axial vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bones and cartilages. Invertebrates are other animals that lack a vertebral column, and their skeletons vary, including hard-shelled exoskeleton (arthropods and most molluscs), plated internal shells (e.g. cuttlebones in some cephalopods) or rods (e.g. ossicles in echinoderms), hydrostatically supported body cavities (most), and spicules (sponges). Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab. Dissection has been used for centuries to explore anatomy. Objections to the use of cadavers have led to the use of alternatives including virtual dissection of computational anatomy, computer models. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |