|
Matrix (music)
In music, especially folk and popular music, a matrix is an element of variations which does not change. The term was derived from use in musical writings and from Arthur Koestler's '' The Act of Creation'', who defines creativity as the bisociation of two sets of ideas or matrices. Musical matrices may be combined in any number, usually more than two, and may be — and must be for analysis — broken down into smaller ones. They are not necessarily intended by the composer or perceived by the listener, and they may be purposefully ambiguous. The simplest examples given by van der Merwe are fixed notes, definite intervals, and regular beats, while the most complex given are the Baroque fugue, Classical tonality, and Romantic chromaticism. The following examples are some matrices which are part of " Pop Goes the Weasel": * major mode *6/8 time *four-bar phrasing *regular beat *rhyming tune structure *ending both halves of the tune with the same figure *melodic climax *perfect ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all human societies. Definitions of music vary widely in substance and approach. While scholars agree that music is defined by a small number of elements of music, specific elements, there is no consensus as to what these necessary elements are. Music is often characterized as a highly versatile medium for expressing human creativity. Diverse activities are involved in the creation of music, and are often divided into categories of musical composition, composition, musical improvisation, improvisation, and performance. Music may be performed using a wide variety of musical instruments, including the human voice. It can also be composed, sequenced, or otherwise produced to be indirectly played mechanically or electronically, such as via a music box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pop Goes The Weasel Melody
Pop or POP may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * Pop music, a musical genre Artists * POP, a Japanese idol group now known as Gang Parade * Pop! (British group), a UK pop group * Pop! featuring Angie Hart, an Australian band Albums * ''Pop'' (Gas album) * ''Pop'' (Joachim Witt album) * ''Pop'' (Mao Abe album) * ''Pop'' (Same Difference album) * ''Pop'' (Tones on Tail album) * ''Pop'' (U2 album) * ''Pop'', an album by Topi Sorsakoski and Agents * '' P.O.P'', The Mad Capsule Markets album * '' Pop! The First 20 Hits'', an album by English duo Erasure EPs * ''P.O.P.'' (EP), a 2024 EP by Marina Satti Songs * "Pop" (NSYNC song), a 2001 song * "Pop!" (Nayeon song), a song from the album ''Im Nayeon'' * "Pop", a song by A.R. Kane * "Pop", a song by Ari Lennox from '' Shea Butter Baby'' * "Pop", a song by La Oreja de Van Gogh from '' El viaje de Copperpot'' * "Pop", a song by Death Grips from '' No Love Deep Web'' * "Pop!", a song from ''The Wedding Singe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Music
Popular music is music with wide appeal that is typically distributed to large audiences through the music industry. These forms and styles can be enjoyed and performed by people with little or no musical training.Popular Music. (2015). ''Funk & Wagnalls New World Encyclopedia'' As a kind of popular art, it stands in contrast to art music. Art music was historically disseminated through the performances of written music, although since the beginning of the recording industry, it is also disseminated through sound recording, recordings. Traditional music forms such as early blues songs or hymns were passed along orally, or to smaller, local audiences. The original application of the term is to music of the 1880s Tin Pan Alley period in the United States. Although popular music sometimes is known as "pop music", the two terms are not interchangeable. Popular music is a generic term for a wide variety of genres of music that appeal to the tastes of a large segment of the populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banjo Roll
In bluegrass music, a banjo roll or roll is a pattern played by the banjo that uses a repeating eighth-note arpeggio – a broken chord – that by subdividing the beat 'keeps time'. "Each standard"roll pattern is a ''right hand'' fingering pattern, consisting of eight (eighth) notes, which can be played while holding ''any'' chord position with the left hand." "When used as back-up, the same pattern can be repeated over and over throughout an entire song, (... ith chord changesas required), or the roll patterns can be combined with one another and with ack-up licks.. The roll patterns can also be used to embellish the vamping style of back-up, especially when the chords are played high... These roll patterns can be used as back-up for any song played at any tempo." The banjo is commonly played in open tunings, such as open G (as are all of the examples): G′DGBD′, allowing rolls to be practiced on all open strings (without fretting). Rolls are a distinguishing cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
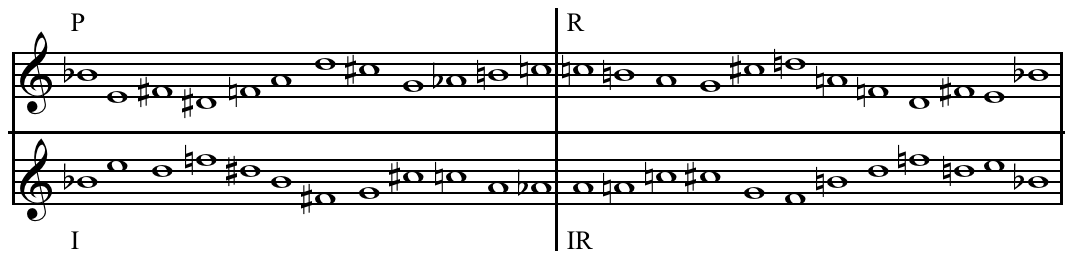
Serialism
In music, serialism is a method of composition using series of pitches, rhythms, dynamics, timbres or other musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique, though some of his contemporaries were also working to establish serialism as a form of post-tonal thinking. Twelve-tone technique orders the twelve notes of the chromatic scale, forming a row or series and providing a unifying basis for a composition's melody, harmony, structural progressions, and variations. Other types of serialism also work with sets, collections of objects, but not necessarily with fixed-order series, and extend the technique to other musical dimensions (often called " parameters"), such as duration, dynamics, and timbre. The idea of serialism is also applied in various ways in the visual arts, design, and architecture, and the musical concept has also been adapted in literature. Integral serialism or total serialism is the use of series for aspects su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Tone Technique
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition. The technique is a means of ensuring that all 12 notes of the chromatic scale are sounded equally often in a piece of music while preventing the emphasis of any one notePerle 1977, 2. through the use of tone rows, orderings of the 12 pitch classes. All 12 notes are thus given more or less equal importance, and the music avoids being in a key. The technique was first devised by Austrian composer Josef Matthias Hauer, who published his "law of the twelve tones" in 1919. In 1923, Arnold Schoenberg (1874–1951) developed his own, better-known version of 12-tone technique, which became associated with the " Second Viennese School" composers, who were the primary users of the technique in the first decades of its existence. Over time, the technique increased greatly in popularity and eventually became widely influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
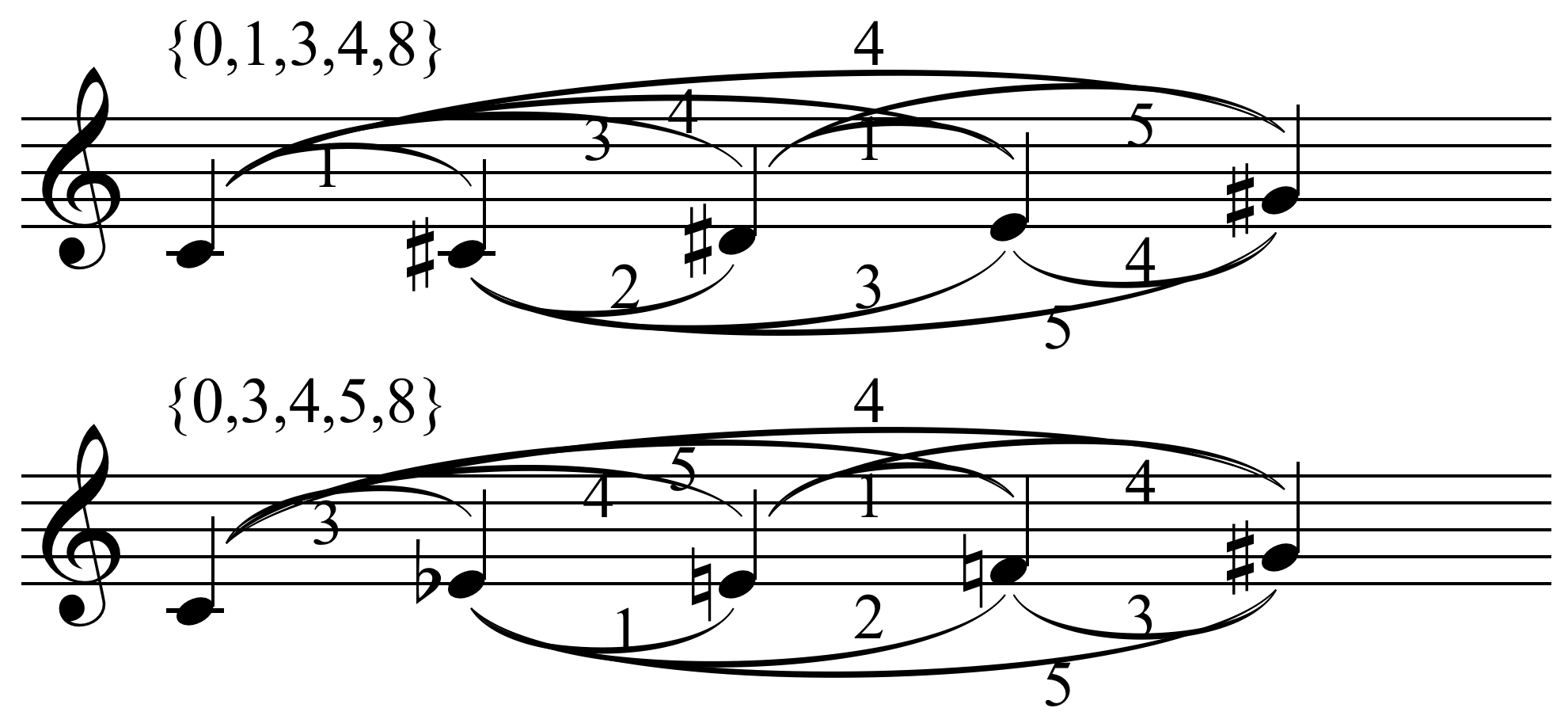
Set Theory (music)
Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Howard Hanson first elaborated many of the concepts for analyzing tonal music. Other theorists, such as Allen Forte, further developed the theory for analyzing atonal music, drawing on the twelve-tone theory of Milton Babbitt. The concepts of musical set theory are very general and can be applied to tonal and atonal styles in any equal temperament tuning system, and to some extent more generally than that. One branch of musical set theory deals with collections ( sets and permutations) of pitches and pitch classes (pitch-class set theory), which may be ordered or unordered, and can be related by musical operations such as transposition, melodic inversion, and complementation. Some theorists apply the methods of musical set theory to the analysis of rhythm as well. Comparison with mathematical set theory Although musical set theory is often thought to involve the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone Row
In music, a tone row or note row ( or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets are sometimes found. History and usage Tone rows are the basis of Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique and most types of serial music. Tone rows were widely used in 20th-century contemporary music, like Dmitri Shostakovich's use of twelve-tone rows, "without dodecaphonic transformations." A tone row has been identified in the A minor prelude, BWV 889, from book II of J.S. Bach's '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'' (1742) and by the late eighteenth century it is found in works such as Mozart's C major String Quartet, K. 157 (1772), String Quartet in E-flat major, K. 428, String Quintet in G minor, K. 516 (1790), and the Symphony in G minor, K. 550 (1788). Beethoven also used the technique but, on the whole, "Mozart seems to have employed seria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permutation
In mathematics, a permutation of a set can mean one of two different things: * an arrangement of its members in a sequence or linear order, or * the act or process of changing the linear order of an ordered set. An example of the first meaning is the six permutations (orderings) of the set : written as tuples, they are (1, 2, 3), (1, 3, 2), (2, 1, 3), (2, 3, 1), (3, 1, 2), and (3, 2, 1). Anagrams of a word whose letters are all different are also permutations: the letters are already ordered in the original word, and the anagram reorders them. The study of permutations of finite sets is an important topic in combinatorics and group theory. Permutations are used in almost every branch of mathematics and in many other fields of science. In computer science, they are used for analyzing sorting algorithms; in quantum physics, for describing states of particles; and in biology, for describing RNA sequences. The number of permutations of distinct objects is factorial, us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Triad
In music, a primary triad is one of the three triads, or three-note chords built from major or minor thirds, most important in tonal and diatonic music, as opposed to an auxiliary triad or secondary triad. Each triad found in a diatonic key corresponds to a particular diatonic function. Functional harmony tends to rely heavily on the primary triads: triads built on the tonic, subdominant, and dominant degrees.Harrison, Daniel (1994). ''Harmonic Function in Chromatic Music: A Renewed Dualist Theory and an Account of its Precedents'', p.45. . Cited in Deborah Rifkin. "A Theory of Motives for Prokofiev's Music", p.274, ''Music Theory Spectrum'', Vol. 26, No. 2 (Autumn, 2004), pp. 265-289. University of California Press on behalf of the Society for Music Theory The roots of these triads begin on the first, fourth, and fifth degrees (respectively) of the diatonic scale, otherwise symbolized: I, IV, and V (again, respectively). Primary triads, "express function clearly and unamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |