|
Marin Beçikemi
Marino Becichemo or Marin Beçikemi (c. 1468 – 1526) was an Albanians, Albanian scholar and orator who was a prominent Renaissance humanism, humanist in the cities of Brescia and later Padua in the Republic of Venice in the early 16th century. He maintained a humanist school and was a professor in the University of Padua. He wrote commentaries about classical Latin literature and was well known for his orations in the region of Venice. Early life Beçikemi came from an Albanian family in Shkodër, Scutari (Shkodër), then part of the Venetian Albania, Venetian possessions in Albania. He was probably born in 1468. Many of the biographical details about his family come from several orations and letters he wrote including a panegyric which he wrote in 1503 and directed to the Venetian senate as a laudation for the resettlement of 2,000 Albanian refugees from Shkodra in Italy after the fall of the city to the Ottomans. His grandfather Pietro was, together with Stefano Ionina, an Alba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marin Barleti
Marin Barleti (, ; – ) was a historian, humanist and Catholic priest from Shkodër. He is considered the first Albanian historian because of his 1504 eyewitness account of the 1478 siege of Shkodra. Barleti is better known for his second work, a biography on Skanderbeg, translated into many languages in the 16th to the 20th centuries. Life Barleti was born and raised in Scutari (modern Shkodra, Albania), then part of the Republic of Venice. Although there is no debate whether Barleti was a native Shkodran or an Albanian in a geographical sense, and although there is indirect evidence that he considered his mother tongue to be Albanian, alternatively to an Albanian ethnic origin (supported by Zeno, Fallmerayer, Jireček), some scholars have hypothesized an Italian ( DuCange, Iorga), or Dalmatian ( Giovio, Czwittinger, Fabricius) ethnic origin. In his works Barleti repeatedly calls himself Shkodran (), and then equates being Shkodran with being Epirote, a term used by ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Philosophy
This page lists some links to ancient philosophy, namely philosophical thought extending as far as early post-classical history (). Overview Genuine philosophical thought, depending upon original individual insights, arose in many cultures roughly contemporaneously. Karl Jaspers termed the intense period of philosophical development beginning around the 7th century BCE and concluding around the 3rd century BCE an Axial Age in human thought. In Western philosophy, the spread of Christianity in the Roman Empire marked the ending of Hellenistic philosophy and ushered in the beginnings of medieval philosophy, whereas in the Middle East, the spread of Islam through the Caliphate, Arab Empire marked the end of #Ancient Iranian philosophy, Old Iranian philosophy and ushered in the beginnings of early Islamic philosophy. Ancient Greek and Roman philosophy Philosophers Pre-Socratic philosophers * Milesian School :Thales (624 – c 546 BCE) :Anaximander (610 – 546 BCE) :Anaximen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists and the innovator of what became known as "Ciceronian rhetoric". Cicero was educated in Rome and in Greece. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. He greatly influenced both ancient and modern reception of the Latin language. A substantial part of his work has survived, and he was admired by both ancient and modern authors alike. Cicero adapted the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy in Latin and coined a large portion of Latin philosophical vocabulary via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girolamo Donato
Girolamo Donato, also spelled Donati, Donado or Donà ( – 20 October 1511), was a Venice, Venetian diplomat and Renaissance humanist, humanist. He made important translations of ancient Greek philosophy and the Greek Fathers into Latin. He served the Republic of Venice on embassies abroad on twelve separate occasions, most importantly at Rome four times, and also served as a governor of Ravenna (1492), Brescia (1495–97), Cremona (1503–04) and Kingdom of Candia, Crete (1506–08). Family and education Girolamo was the son of Antonio di Andrea and Lucia di Bernardo Balbi of the Patrician (post-Roman Europe), patrician class. His father belonged to the ''dalle Rose'' branch of the Donà family. His birth is usually given as around 1456 or before 1457. Giovanni degli Agostini places his birth in 1457, but also gives his age as 57 at his death. He is recorded as 18 years old when presented to the ''Avogadoria de Comùn, avogadori di Comun'' on 22 or 27 November 1474. He married Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II Of Naples
Ferdinand II (; 26 June 1467 – 7 September 1496) was Kingdom of Naples, King of Naples from 1495 to 1496. He was the son of Alfonso II of Naples and the grandson of Ferrante I of Naples. At the start of the Italian Wars in 1495, Alfonso abdicated in favor of his son, Ferdinand, when a French army led by Charles VIII of France, Charles VIII threatened Naples. Unable to effectively defend the city, Ferdinand fled with a small retinue to the island of Ischia. Charles quickly occupied the city, then split his army, leaving half of it to garrison Naples, and taking the other half to return home. By May 1495, with fresh troops and the support of Aragon allies, Ferdinand returned to the peninsula and with the assistance of the Spanish general Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba, expelled French soldiers from the entire kingdom. He died soon thereafter on 7 September 1496 and was succeeded by his uncle, Frederick IV of Naples, Frederick. Biography Birth On 26 June 1467, Ferrandino was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melchiorre Trevisan
Melchiorre may refer to: As first name *Melchiorre Cafà (1636–1667), Maltese sculptor * Melchiore Cesarotti (1730–1808), Italian poet * Melchiorre Delfico (caricaturist) (1825–1895), Italian caricaturist * Melchiorre Delfico (economist) (1744–1835), Italian economist * Melchiorre Gherardini (1607–1668), Italian painter *Melchiorre Gioia (1767–1829), Italian philosopher and economist * Melchiorre Grimaldi (died 1512), Italian Bishop * Melchiorre Luise (1896–1967), Italian opera singer *Melchiorre Martelli, regent of San Marino * Melchiorre da Montalbano, Italian architect and sculptor *Melchiorre Murenu Melchiorre Murenu (Macomer 1803 – 1854) was a blind Sardinians, Sardinian poet.Melchiorre Murenu, "Tutte le Poesie", Edizioni della Torre, 1990. Melchiorre Murenu is known as the "Homer of Sardinia"Paola Pittalis, Storia della letteratura in S ... (1803–1854), Sardinian poet * Melchiorre Zoppio (1544–1634), Italian doctor and scholar As surname * Daniela Melc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetian Patriciate
Venetian often means from or related to: * Venice, a city in Italy * Veneto, a region of Italy * Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area Venetians might refer to: * Masters of Venetian painting in 15th-16th centuries * City dwellers of Venice Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ... Venetian and the like may also refer to: * Venetian language, a Romance language spoken mostly in the Veneto region * Venice, Florida, a city in Sarasota County, United States * The Venetian Las Vegas, a resort hotel and casino in Las Vegas, Nevada * The Venetian Macao, a hotel and casino in Macau, China *Venetian blind, or Venetian, a common type of window blind similar to Persian blind *Venetian curtain, a type of theater front curtain *''The Venetian Woman' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Gučetić
Ivan () is a Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John) from Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. The earliest person known to bear the name was the Bulgarian Saint Ivan of Rila. It is very popular in Russia, Ukraine, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Slovenia, Bulgaria, Belarus, North Macedonia, and Montenegro and has also become more popular in Romance-speaking countries since the 20th century. Etymology Ivan is the common Slavic Latin spelling, while Cyrillic spelling is two-fold: in Bulgarian, Russian, Macedonian, Serbian and Montenegrin it is , while in Belarusian and Ukrainian it is . The Old Church Slavonic (or Old Cyrillic) spelling is . It is the Slavic relative of the Latin name , corresponding to English ''John''. This Slavic version of the name originates from New Testament Greek (''Iōánnēs'') rather than from the Latin . The Greek name is in turn derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
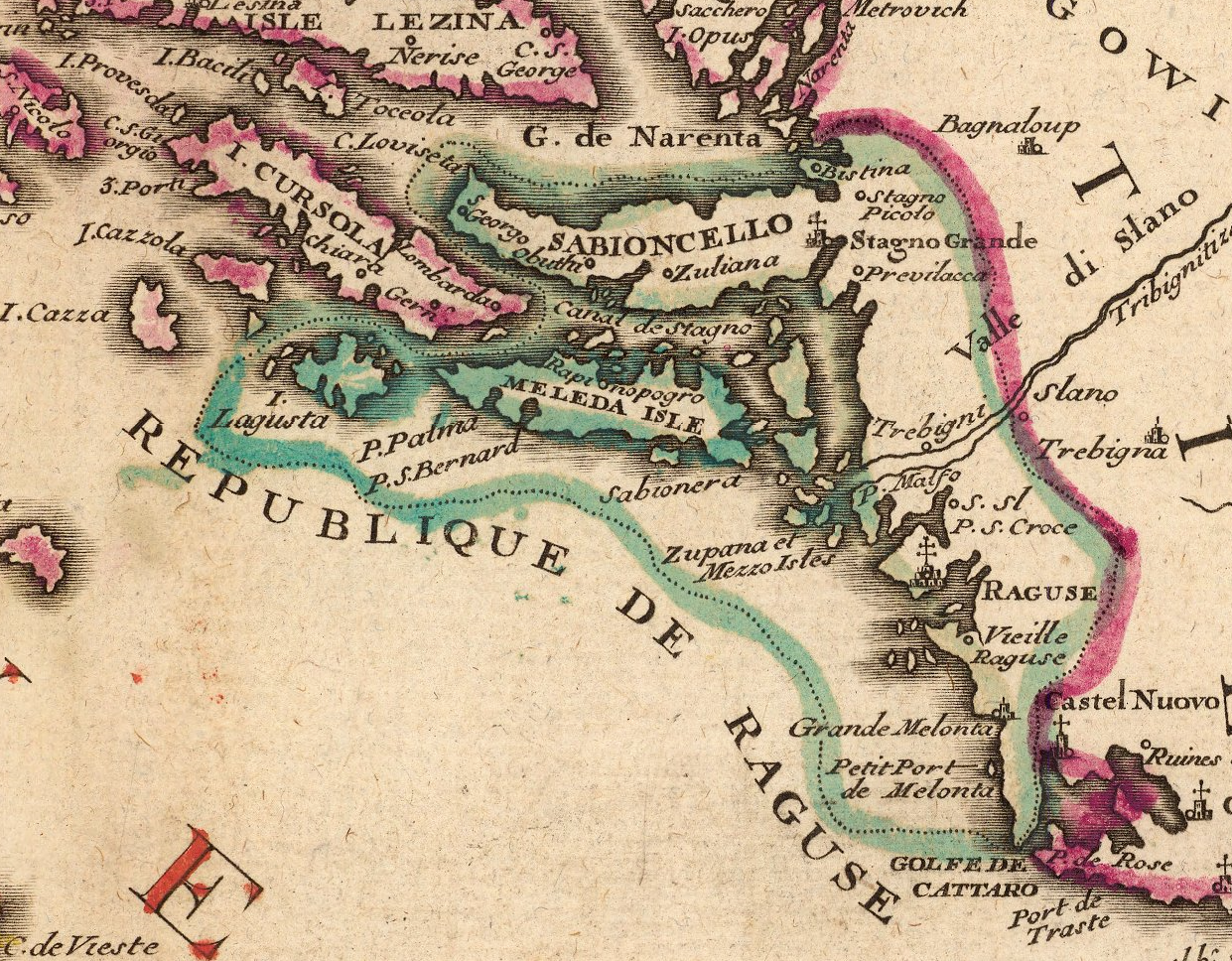
Republic Of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's First French Empire, French Empire and formally annexed by the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |