|
Marcell Experimental Forest
Marcell Experimental Forest (MEF) is a 1,140 ha long-term ecosystem research site operated by the Northern Research Station of the U.S. Forest Service. It is located 40 km north of Grand Rapids, Minnesota within the Chippewa National Forest and was formally established in 1962 to study the ecology and hydrology of peatland watersheds. There are six experimental watersheds each of which consist of an upland portion, a peatland, and an outlet stream. The range of these six watersheds provide a variety of hydrological environments to study. Climatic and hydrologic data have been continuously monitored since 1961. Some notable research areas have been hydrology, nutrient and mercury cycling and behavior, and release of organic carbon and acidity. MEF is the longest running National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) site in the nation. Climate and physical characteristics Peatlands and lakes comprise 30% of the forest landscape at the MEF. The peatlands include fens and bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcell Experimental Forest Entrance Sign In Bovey, Minnesota
Marcell may refer to: * Joseph Marcell, an actor from St. Lucia * Marcell, Minnesota, an unincorporated town * Marcell Township, Minnesota See also * Marcel (other) * Marcelle (other) Marcelle may refer to: *Marcelle, a French feminine version of Marcel Given name * Marcelle Auclair (1899–1983), French novelist, biographer, journalist and poet * Marcelle Arnold (1917–2010), French film, stage and television actress * ... * Marcelling, a hair styling technique {{disambig, geo, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ericaceous Heathland
The Ericaceae () are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the heath or heather family, found most commonly in acidic and infertile growing conditions. The family is large, with about 4,250 known species spread across 124 genera, making it the 14th most species-rich family of flowering plants. The many well known and economically important members of the Ericaceae include the cranberry, blueberry, huckleberry, rhododendron (including azaleas), and various common heaths and heathers (''Erica'', ''Cassiope'', ''Daboecia'', and ''Calluna'' for example). Description The Ericaceae contain a morphologically diverse range of taxa, including herbs, dwarf shrubs, shrubs, and trees. Their leaves are usually evergreen, alternate or whorled, simple and without stipules. Their flowers are hermaphrodite and show considerable variability. The petals are often fused (sympetalous) with shapes ranging from narrowly tubular to funnelform or widely urn-shaped. The corollas are usually r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Forests Of Minnesota
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Book Store, a bookstore and office supplies chain in the Philippines * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900–1924 * National Radio Company, Malden, Massachusetts, USA 1914–1991 * National Supermarket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1943, the laboratory is sponsored by the United States Department of Energy and administered by UT–Battelle, UT–Battelle, LLC. Established in 1943, ORNL is the largest science and energy national laboratory in the Department of Energy system by size and third largest by annual budget. It is located in the Roane County, Tennessee, Roane County section of Oak Ridge. Its scientific programs focus on materials science, materials, nuclear power, nuclear science, neutron science, energy, high-performance computing, environmental science, systems biology and national security, sometimes in partnership with the state of Tennessee, universities and other industries. ORNL has several of the world's top supercomputers, including Frontier (supercomputer), Frontier, ranked by the TOP500 as the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and energy production, the research and development of nuclear power, the military's nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the secretary of energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current secretary of energy is Chris Wright, who has served in the position since February 2025. The department's headquarters are in sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
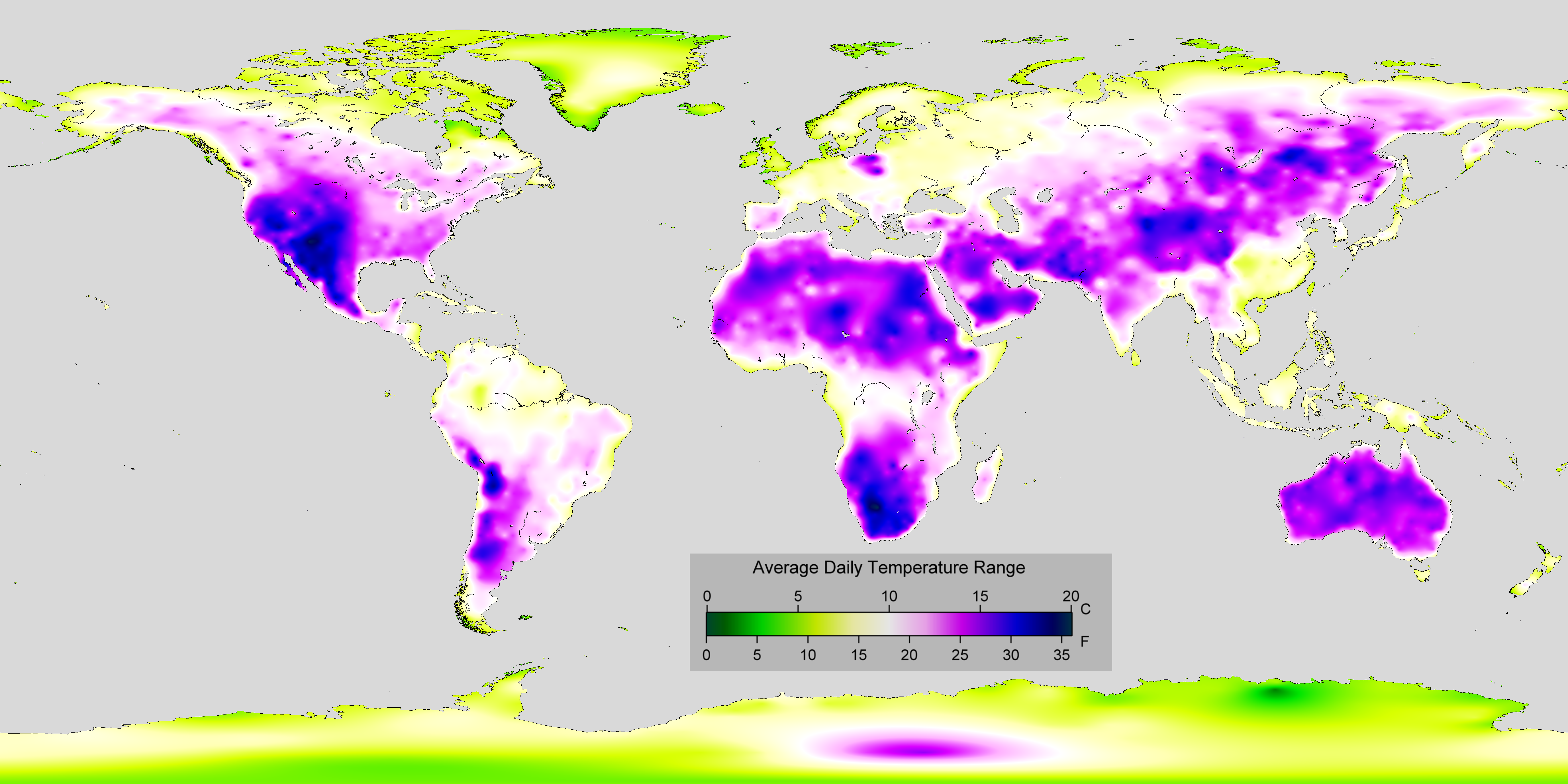
Diurnal Temperature Variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag, also known as thermal inertia, is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation. Peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps absorbing net heat for a period of time from morning through noon and some time thereafter. Similarly, minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraxinus
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae, and comprises 45–65 species of usually medium-to-large trees, most of which are deciduous trees, although some Subtropics, subtropical species are evergreen trees. The genus is widespread throughout much of Europe, Asia, and North America. The leaves are opposite leaves, opposite (rarely in Whorl (botany), whorls of three), and mostly pinnate, pinnately compound, though simple in a few species. The seeds, popularly known as "keys" or "helicopter seeds", are a type of fruit known as a samara (fruit), samara. Some ''Fraxinus'' species are Dioecy, dioecious, having male and female flowers on separate plants but sex in ash is expressed as a continuum between male and female individuals, dominated by unisexual trees. With age, ash may change their sexual function from predominantly male and hermaphrodite towards femaleness; if grown as an ornamental and both sexes are present, ashes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuja Occidentalis
''Thuja occidentalis'', also known as northern white-cedar, eastern white-cedar, or arborvitae, is an evergreen coniferous tree, in the cypress family Cupressaceae, which is native to eastern Canada and much of the north-central and northeastern United States. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant. It is not to be confused with ''Juniperus virginiana'' (eastern red cedar). Common names Its additional common names include swamp cedar, American arborvitae, and eastern arborvitae. The name arborvitae is particularly used in the horticultural trade in the United States; it is Latin for 'tree of life' – due to the supposed medicinal properties of the sap, bark, and twigs.''Thuja'', American Cancer Society, last revised 6/19/2007available online/ref> It is sometimes called white-cedar (hyphenated) or whitecedar (one word) to distinguish it from ''Cedrus'', the true cedars. Description Unlike the closely related western red cedar (''Thuja plicata''), northern white cedar i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225–229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As ''Sphagnum'' moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, ''Sphagnum'' can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing ''Sphagnum'' as 'habitat manipulators' or 'autogenic ecosystem engineers'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuge, ericaceous shrubs, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Forest
An experimental forest, or experimental range, as defined by the United States Forest Service, is "an area administered ... 'to provide for the research necessary for the management of the land.'" Size and relation to other areas According to the USFS, "Most Experimental Forests are large enough to contain significant stream systems and several dozen contain experimental watershed study sites with multiple paired basins." Individual experimental forests range from in area. Experimental forests are distinguished from research natural areas and intensive monitoring sites. History The present system of 80 experimental forests and ranges began in 1908. Many experimental forest are more than 50 years old. The system provides places for long-term science and management studies in major vegetation types of the of public land administered by the Forest Service. Experimental forests and ranges in the United States * Alum Creek Experimental Forest, Arkansas * Argonne Experimental Fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larix Laricina
''Larix laricina'', commonly known as the tamarack, hackmatack, eastern larch, black larch, red larch, or American larch, is a species of larch native to Canada, from eastern Yukon and Inuvik, Northwest Territories east to Newfoundland, and also south into the upper northeastern United States from Minnesota to Cranesville Swamp, West Virginia; there is also an isolated population in central Alaska. Description ''Larix laricina'' is a small to medium-size boreal deciduous conifer tree reaching tall, with a trunk up to diameter. The bark of mature trees is reddish, the young trees are gray with smooth bark. The leaves are needle-like, long, light blue-green, turning bright yellow before they fall in the autumn, leaving the shoots bare until the next spring. The needles are produced in clusters on long woody spur shoots. The cones are the smallest of any larch, only long, with 12-25 seed scales; they are bright red, turning brown and opening to release the seeds when matu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |