|
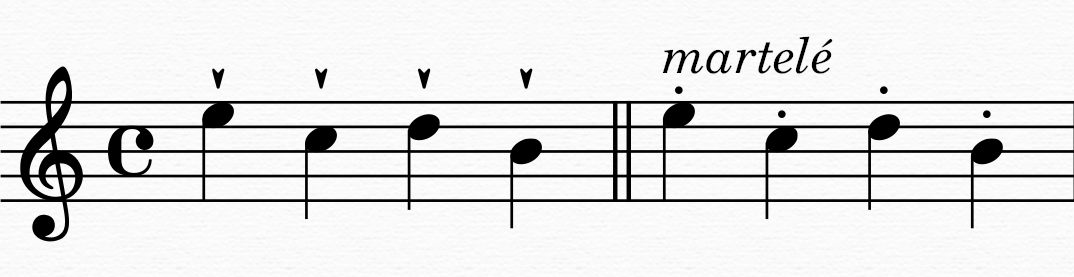
Marcato
''Marcato'' (short form: Marc.; Italian for ''marked'') is a musical instruction indicating a note, chord, or passage is to be played louder or more forcefully than the surrounding music. The instruction may involve the word ''marcato'' itself written above or below the staff or it may take the form of the symbol ∧, an open vertical wedge. The marcato is essentially a louder and often shorter version of the regular accent > (an open horizontal wedge). Like the regular accent, however, the marcato is often interpreted to suggest a sharp attack tapering to the original dynamic, an interpretation which applies only to instruments capable of altering the dynamic level of a single sustained pitch. According to author James Mark Jordan, "the ''marcato'' sound is characterized by a rhythmic ''thrust'' followed by a decay of the sound." The instruction ''marcato'' or ''marcatissimo'' (extreme marcato), among various other instructions, symbols, and expression marks may prompt a str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accent (music)
In music, an accent is an emphasis, stress, or stronger attack placed on a particular note or set of notes, or chord, either because of its context or specifically indicated by an accent mark. Accents contribute to the articulation and prosody of a performance of a musical phrase. Accents may be written into a score or part by a composer, or added by the performer as part of their interpretation of a musical piece. Compared to surrounding notes: * A dynamic accent or stress accent is an emphasis using louder sound or stronger sound; typically, most pronounced on the attack of the sound. * A tonic accent is an emphasis on notes by virtue of them being higher in pitch, as opposed to higher in volume. * An agogic accent is an emphasis by virtue of notes being longer in duration. Accents that don't correspond to the stressed beats of the prevailing meter are said to be syncopated. For example, in common time, also called 4/4, the most common metre in popular music, the stresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Musical Symbols
Musical symbols are marks and symbols in musical notation that indicate various aspects of how a piece of music is to be performed. There are symbols to communicate information about many musical elements, including Pitch (music), pitch, Duration (music), duration, Dynamics (music), dynamics, or articulation (music), articulation of musical notes; tempo, metre (music), metre, Musical form, form (e.g., whether sections are repeated), and details about specific playing techniques (e.g., which fingers, keys, or pedals are to be used, whether a string instrument should be bowed or plucked, or whether the bow of a string instrument should move up or down). Lines Clefs A clef assigns one particular pitch to one particular line of the staff on which it is placed. This also effectively defines the pitch range or tessitura of the music on that staff. A clef is usually the leftmost symbol on a staff, although a different clef may appear elsewhere to indicate a change in register. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Note
In music, notes are distinct and isolatable sounds that act as the most basic building blocks for nearly all of music. This musical analysis#Discretization, discretization facilitates performance, comprehension, and musical analysis, analysis. Notes may be visually communicated by writing them in musical notation. Notes can distinguish the general pitch class or the specific Pitch (music), pitch played by a pitched Musical instrument, instrument. Although this article focuses on pitch, notes for unpitched percussion instruments distinguish between different percussion instruments (and/or different manners to sound them) instead of pitch. Note value expresses the relative Duration (music), duration of the note in time. Dynamics (music), Dynamics for a note indicate how Loudness, loud to play them. Articulation (music), Articulations may further indicate how performers should shape the Envelope (music), attack and decay of the note and express fluctuations in a note's timbre and Pit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (music)
In Western music theory, a chord is a group of notes played together for their harmony, harmonic Consonance and dissonance, consonance or dissonance. The most basic type of chord is a Triad (music), triad, so called because it consists of three distinct notes: the Root (chord), root note along with Interval (music), intervals of a Third (chord), third and a Fifth (chord), fifth above the root note. Chords with more than three notes include added tone chords, extended chords and tone clusters, which are used in contemporary classical music, jazz, and other genres. Chords are the building blocks of harmony and form the harmonic foundation of a piece of music. They provide the harmonic support and coloration that accompany melodies and contribute to the overall sound and mood of a musical composition. The factor (chord), factors, or component notes, of a chord are often sounded simultaneously but can instead be sounded consecutively, as in an arpeggio. A succession of chords is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, hymns, marches, vaudeville song, and dance music. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major form of musical expression in traditional and popular music. Jazz is characterized by swing and blue notes, complex chords, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation. As jazz spread around the world, it drew on national, regional, and local musical cultures, which gave rise to different styles. New Orleans jazz began in the early 1910s, combining earlier brass band marches, French quadrilles, biguine, ragtime and blues with collective polyphonic improvisation. However, jazz did not begin as a single musical tradition in New Orleans or elsewhere. In the 1930s, arranged dance-oriented swing big bands, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martelé (bowstroke)
''Martelé'' (; literally meaning "hammered") is a percussive bow stroke used when playing bowed string instruments, though the Italian ''martellando'' and ''martellato'' are also applied to piano and vocal technique, and even (by Franz Liszt Franz Liszt (22 October 1811 – 31 July 1886) was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic music, Romantic period. With a diverse List of compositions by Franz Liszt, body of work spanning more than six ...) to the organ. The effect is usually produced by holding the bow against the string with pressure, then releasing it explosively to produce a sharp, biting attack with a rest between strokes. History Bows made in the 18th century and earlier, due to their lack of a ferrule, were unable to support the pressure needed to perform the martelé stroke. It wasn't until François Tourte made changes to the bow between 1785 and 1790, including the addition of a ferrule, that the bow was suited f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articulations (music)
Articulation may refer to: Linguistics * Articulatory phonetics, the study of how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of physiological structures ** Manner of articulation, how speech organs involved in making a sound make contact ** Place of articulation, positions of speech organs to create distinctive speech sounds * Articulatory gestures, the actions necessary to enunciate language * Articulatory phonology, a theory that attempts to unify phonetics and phonology * Articulatory speech recognition, the recovery of speech from acoustic signals * Articulatory synthesis, computational techniques for synthesizing speech based on models of human articulation processes * Topic–focus articulation, a field of study concerned with marking old and new information in a clause Engineering * Articulated vehicle, which have a pivoted joint allowing them to turn more sharply * Articulation score, in telecommunications, a subjective measure of the intelligibility of a vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |