|
Marathonisi, Gytheio
Cranae or Kranai ( ) (also Marathonisi) is an island off the coast of Gytheio (ancient Gythium) connected to the land by a causeway built in 1898. Etymology Some believe that the etymology for the name Cranae (Kranai) comes from the legendary king of Athens Kranaos, the successor of King Kekropas (Cecrops) as Athens was also known as "Kranaa". However the word Kranaos according to Homer it has the following meanings: 'Rocky', 'ragged', 'hard'. Therefore, some believe that the word Kranai literally means 'rocky', 'rock'. The name "Marathonisi" translates to 'fennel-island', as the herb fennel was naturally growing on this island. History According to legend, when Paris of Troy abducted Helen from Sparta they spent their first night in Cranae. When Gythium became the major port of ancient Sparta, Cranae became a resting spot for traders. When Greece became a part of the Ottoman Empire, the beys of Mani fortified Cranae with a Maniot tower. The tower built by the Tzannetakis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
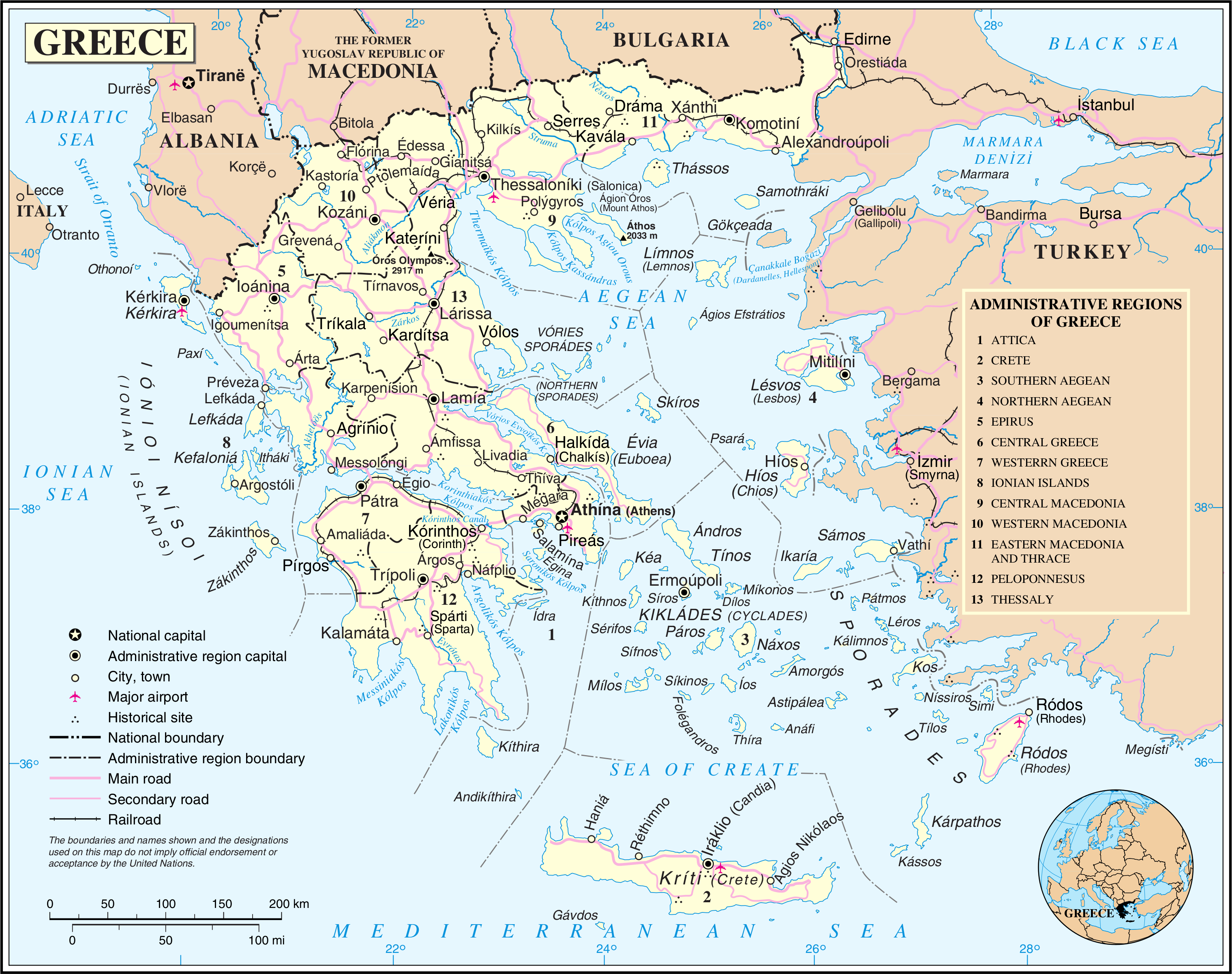
Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece () are the country's thirteen second-level administrative divisions of Greece, administrative entities, counting decentralized administrations of Greece as first-level. Regions are divided into regional units of Greece, regional units, known as prefectures of Greece, prefectures until 2011. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the Prefectures of Greece, prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad geographic regions of Greece, historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the valley of Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered much autonomy after the Roman conquest of Greece in 146 BC and prospered during the Roman Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laconian Mythology
Laconia or Lakonia may refer to: Places * Laconia, a region of Greece * Laconia (constituency), an electoral district of Greece ** Laconian Greek, a dialect of Doric Greek United States * Laconia, Indiana * Laconia, New Hampshire * Laconia, Tennessee Ships * , 1911–1917, sunk in the First World War * 1921–1942, sunk in the Second World War ** Laconia incident, sinking of RMS ''Laconia'' and being attacked while rescuing survivors. * TSMS ''Lakonia'', 1929–1963, caught fire, evacuated and sank in 1963 See also * Laconian (dog) The Laconian (), also known as the Spartan or the Castorian, is an extinct dog breed from Ancient Greece, famous for their sense of smell, typically used for Hunting dog, hunting. The breed originated in Laconia, a region of Ancient Greece, famo ..., an extinct dog breed * Laconia Car Company a one time American rolling stock builder * Loconia, a village in Apulia, Italy {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Ancient Laconia
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Laconia
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( ; ; ) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his '' Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology, which is providing evidence of the sites and cultural details he mentions although knowledge of their existence may have become lost or relegated to myth or legend. Biography Nothing is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is probable that he was born into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From until his death around 180, Pausanias travelled throughout the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing his '' Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
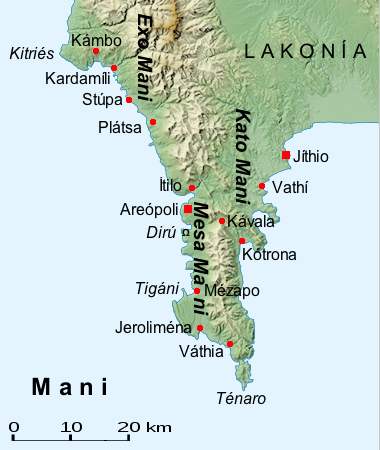
Mani Peninsula
The Mani Peninsula (), also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (), is a geographical and cultural region in the Peloponnese of Southern Greece and home to the Maniots (), who claim descent from the ancient Spartans. The capital city of Mani is Areopoli. Mani is the central of three peninsulas which extend southwards from the Peloponnese. To the east is the Laconian Gulf, to the west the Messenian Gulf. The Mani peninsula forms a continuation of the Taygetos mountain range, the western spine of the Peloponnese. Etymology There are many theories regarding the etymology of the word Mani. The most accepted one is that it represents the natural evolution of the medieval name of the region, which was Maini, of uncertain origin. The name "Mani" may come from the name of the Frankish castle ''le Grand Magne''. Geography The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible. Until recent years many Mani villages could be reached only by sea. Today a narrow and winding road ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tainaro
Cape Matapan (, Maniot dialect: Ματαπά), also called Cape Tainaron or Taenarum (), or Cape Tenaro, is situated at the end of the Mani Peninsula, Greece. Cape Matapan is the southernmost point of mainland Greece, and the second southernmost point in mainland Europe. It separates the Messenian Gulf in the west from the Laconian Gulf in the east. Cape Taenarum in classical antiquity was the site of the city of Taenarum (Ancient Greek: Ταίναρον), now in ruins. In ancient Greek mythology the eponymous founder-hero of the city was Taenarus (Ταίναρος), who was credited with establishing the city's important temple of Poseidon. Greeks used the proverb Tainarian evil (), meaning a great and unlawful evil affecting suppliants, for the Spartans killed the Helots who had fled into Tainaron and were suppliants in the temple of Poseidon. History Cape Matapan has been an important place for thousands of years. Near Taenarum, there is a cave that Greek legends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He appears repeatedly and prominently in all four New Testament gospels, as well as the Acts of the Apostles. Catholic and Orthodox tradition treats Peter as the first bishop of Rome – or pope – and also as the first bishop of Antioch. Peter's leadership of the early believers is estimated to have spanned from AD 30 or 33 to his death; these dates suggest that he could have been the longest-reigning pope, for anywhere from 31 to 38 years; however, this has never been verified. According to Christian tradition, Peter was crucified in Rome under Emperor Nero. The ancient Christian churches all venerate Peter as a major saint and the founder of the Church of Antioch and the Church of Rome, but they differ in their attitudes regarding the autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical And Cultural Museum Of Mani
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower
A tower is a tall Nonbuilding structure, structure, taller than it is wide, often by a significant factor. Towers are distinguished from guyed mast, masts by their lack of guy-wires and are therefore, along with tall buildings, self-supporting structures. Towers are specifically distinguished from buildings in that they are built not to be habitable but to serve other functions using the height of the tower. For example, the height of a clock tower improves the visibility of the clock, and the height of a tower in a fortified building such as a castle increases the visibility of the surroundings for defensive purposes. Towers may also be built for observation tower, observation, leisure, or telecommunication purposes. A tower can stand alone or be supported by adjacent buildings, or it may be a feature on top of a larger structure or building. Etymology Old English ''torr'' is from Latin ''turris'' via Old French ''tor''. The Latin term together with Greek language, Greek τύ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |