|
Manuel García (tenor)
Manuel del Pópulo Vicente Rodriguez García (also known as Manuel García the Senior; 21 January 1775 – 10 June 1832) was a Spanish opera singer, composer, impresario, and singing teacher. He is often credited as a key figure in the development of modern vocal technique and vocal pedagogy. Biography García was born in Seville, Spain, on 21 January 1775. In 1808, he went to Paris, with previous experience as a tenor at Madrid and Cadiz. By that year, when he appeared in the opera '' Griselda'' in Paris, he was already a composer of light operas. He lived in Naples, Italy, performing in Gioachino Rossini's operas. These included the premières of ''Elisabetta, regina d'Inghilterra'', in which he portrayed The Duke of Norfolk and ''The Barber of Seville'', in which he portrayed the role of Count Almaviva. In 1816, he visited Paris and London, England. Between 1819 and 1823, he lived in Paris, and sang in operas such as ''The Barber of Seville'', ''Otello'', and ''Don Giovanni'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel Vicente Del Popolo Rodriguez (Garcia)
Manuel may refer to: People * Manuel (name), a given name and surname * Manuel (Fawlty Towers), Manuel (''Fawlty Towers''), a fictional character from the sitcom ''Fawlty Towers'' * Manuel I Komnenos, emperor of the Byzantine Empire * Manuel I of Portugal, king of Portugal * Manuel I of Trebizond, Emperor of Trebizond Places *Manuel, Valencia, a municipality in the province of Valencia, Spain *Manuel Junction, railway station near Falkirk, Scotland Other * Manuel (American horse), a thoroughbred racehorse * Manuel (Australian horse), a thoroughbred racehorse * Manuel and The Music of The Mountains, a musical ensemble * Manuel (album), ''Manuel'' (album), music album by Dalida, 1974 See also *Manny (other), a common nickname for those named Manuel *Manoel (other) *Immanuel (other) *Emmanuel (other) *Emanuel (other) *Emmanuelle (other) *Manuela (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Giovanni
''Don Giovanni'' (; K. 527; full title: , literally ''The Rake Punished, or Don Giovanni'') is an opera in two acts with music by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart to an Italian libretto by Lorenzo Da Ponte. Its subject is a centuries-old Spanish legend about a libertine as told by playwright Tirso de Molina in his 1630 play '' El burlador de Sevilla y convidado de piedra''. It is a ''dramma giocoso'' blending comedy, melodrama and supernatural elements (although the composer entered it into his catalogue simply as ''opera buffa''). It was premiered by the Prague Italian opera at the National Theatre (of Bohemia), now called the Estates Theatre, on 29 October 1787. ''Don Giovanni'' is regarded as one of the greatest operas of all time and has proved a fruitful subject for commentary in its own right; critic Fiona Maddocks has described it as one of Mozart's "trio of masterpieces with librettos by Da Ponte". Composition and premiere The opera was commissioned after the success of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenzo Da Ponte
Lorenzo Da Ponte (; 10 March 174917 August 1838) was an Italians, Italian, later American, opera libretto, librettist, poet and Catholic Church, Roman Catholic priest. He wrote the libretti for 28 operas by 11 composers, including three of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Mozart's most celebrated operas: ''The Marriage of Figaro'' (1786), ''Don Giovanni'' (1787), and ''Così fan tutte'' (1790). He was the first professor of Italian literature at Columbia University, and with Manuel García (tenor), Manuel Garcia, the first to introduce Italian opera#Gluck's reforms and Mozart, Italian opera to America.Music View, Did Casanova Lend a Helping Hand? The New York Times, Donald Henahan, Nov. 10, 1985Smith, Howard Jay (2022) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Pedagogy
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how singing technique is accomplished. Vocal pedagogy covers a broad range of aspects of singing, ranging from the physiological process of vocal production to the artistic aspects of interpretation of songs from different genres or historical eras. Typical areas of study include: : * Human anatomy and Human physiology, physiology as it relates to the physical process of singing. * Breathing and air support for singing * Human position, Posture for singing * Phonation * Vocal resonation or voice projection * Diction, vowels and articulation * Vocal registration * Sostenuto and legato for singing * Other singing elements, such as range extension, tone quality, vibrato, coloratura * Vocal health and voice disorders related to singing * Vocal styles, such as learning to sing opera, belt (music), belt, or art son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical music, classical male singing human voice, voice whose vocal range lies between the bass (voice type), bass and the tenor voice type, voice-types. It is the most common male voice. The term originates from the Greek language, Greek (), meaning "low sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below C (musical note), middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. Scientific pitch notation, F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second G below middle C to the G above middle C (G2 to G4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French Religious music, sacred Polyphony, polyphonic music. At t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel García (baritone)
Manuel Patricio Rodríguez García (17 March 1805 – 1 July 1906), was a Spanish singer, music educator, and vocal pedagogue. He invented the first laryngoscope. Biography García was born on 17 March 1805 either in Madrid, as has been traditionally stated, or in the town of Zafra in the province of Badajoz, Spain. His father was singer and teacher Manuel del Pópulo Vicente Rodriguez García (Manuel García I, 1775–1832). His sisters were Maria Malibran (1808–1836) and Pauline Viardot (1821–1910). After abandoning his onstage career as a baritone, García began to teach at the Paris Conservatory (1830–48) and the Royal Academy of Music, London (1848–95). Jessie Bond, Camille Everardi, Erminia Frezzolini, Julius Günther, Jenny Lind, Mathilde Marchesi, Christina Nilsson, Julia Ettie Crane, Georgina Schubert, Julius Stockhausen, Marie Tempest, Charles Santley and Henry Wood were among his pupils. He invented a laryngoscope in 1854 and the next year publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt (22 October 1811 – 31 July 1886) was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic music, Romantic period. With a diverse List of compositions by Franz Liszt, body of work spanning more than six decades, he is considered to be one of the most prolific and influential composers of his era, and his piano works continue to be widely performed and recorded. Liszt achieved success as a concert pianist from an early age, and received lessons from the esteemed musicians Carl Czerny and Antonio Salieri. He gained further renown for his performances during tours of Europe in the 1830s and 1840s, developing a reputation for technical brilliance as well as physical attractiveness. In a phenomenon dubbed "Lisztomania", he rose to a degree of stardom and popularity among the public not experienced by the virtuosos who preceded him. During this period and into his later life, Liszt was a friend, musical promoter and benefactor to many composer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
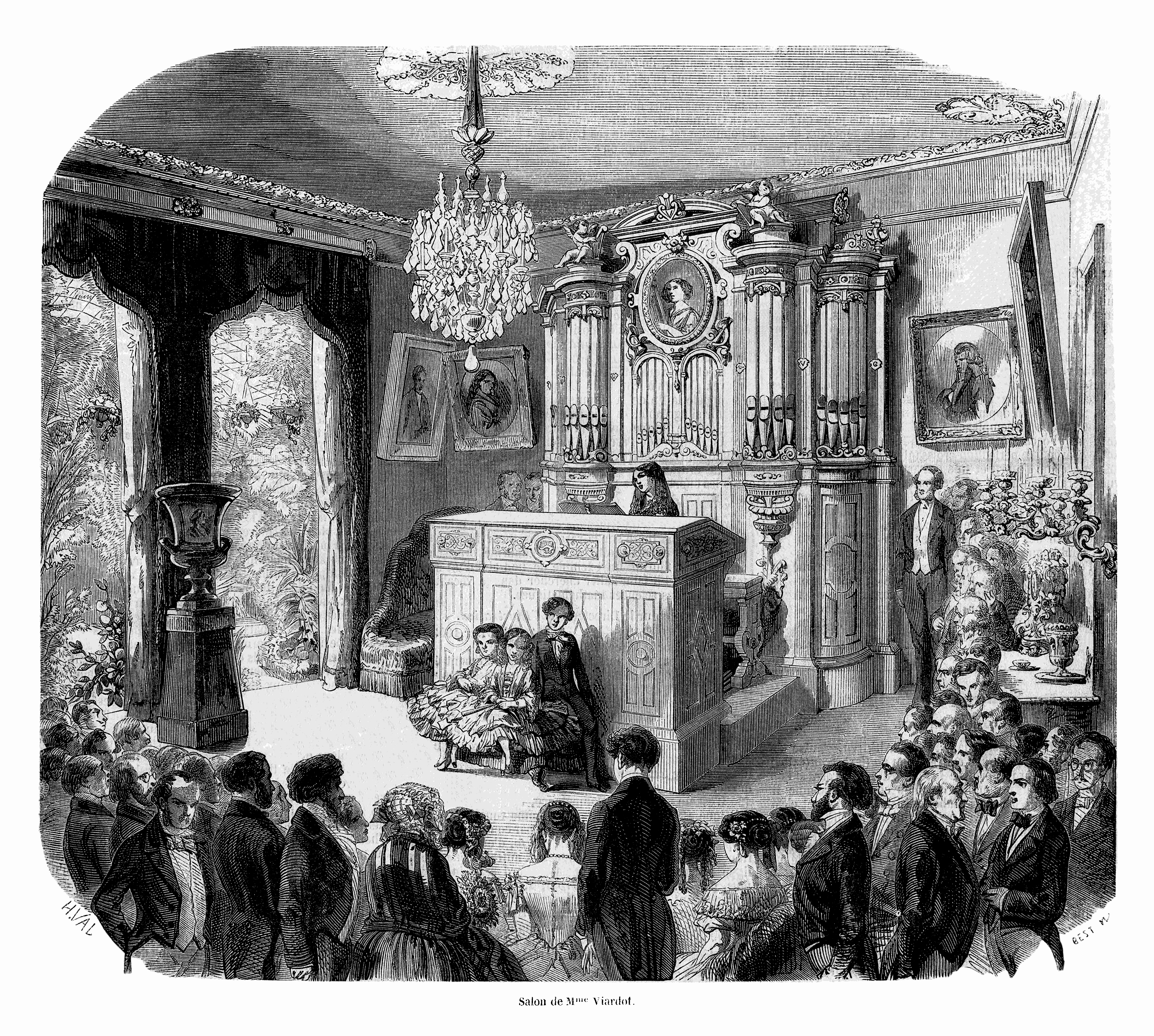
Pauline Viardot
Pauline Viardot (; 18 July 1821 – 18 May 1910) was a French dramatic mezzo-soprano, composer and pedagogue of Spanish descent. Born Michelle Ferdinande Pauline García,FitzLyon, p. 15, referring to the baptismal name. Thbirth recorddigitized at Paris's ''État civil reconstitué (XVIe-1859)'' reads instead: "Michelle Pauline Ferdinande Laurence Garcia". she came from a musical family and took up music at a young age. She began performing as a teenager and had a long and illustrious career as a star performer. Name Her name appears in various forms. When it is not simply "Pauline Viardot", it most commonly appears in association with her maiden name García or the unaccented form, Garcia. This name sometimes precedes Viardot and sometimes follows it. Sometimes the words are hyphenated; sometimes they are not. She achieved initial fame as "Pauline García"; the accent was dropped at some point, but exactly when is not clear. After her marriage, she referred to herself simply as " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Malibran
Maria Felicia Malibran (; 24 March 1808 – 23 September 1836) was a Spanish singer who commonly sang both contralto and soprano parts, and was one of the best-known opera singers of the 19th century. Malibran was known for her stormy personality and dramatic intensity, becoming a legendary figure after her death in Manchester, England, at age 28. Contemporary accounts of her voice describe its range, power and flexibility as extraordinary. Early life María Felicitas García Sitches was born into a famous Spanish musical family in Paris. Her mother was Joaquina Sitches, an actress and operatic singer. Her father Manuel García was a celebrated tenor much admired by Rossini, having created the role of Count Almaviva in his ''The Barber of Seville''. García was also a composer and an influential vocal instructor, and he was her first voice teacher. He was described as inflexible and tyrannical; the lessons he gave his daughter became constant quarrels between two powerful egos. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezzo-soprano
A mezzo-soprano (, ), or mezzo ( ), is a type of classical music, classical female singing human voice, voice whose vocal range lies between the soprano and the contralto voice types. The mezzo-soprano's vocal range usually extends from the A below middle C to the A two octaves above (i.e. A3–A5 in scientific pitch notation, where middle C = C4; 220–880 Hz). In the lower and upper extremes, some mezzo-sopranos may extend down to the F below middle C (F3, 175 Hz) and as high as "high C" (C6, 1047 Hz). The mezzo-soprano voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, lyric, and dramatic. History While mezzo-sopranos typically sing secondary roles in operas, notable exceptions include the title role in Georges Bizet, Bizet's ''Carmen'', Angelina (Cinderella) in Gioachino Rossini, Rossini's ''La Cenerentola'', and Rosina in Rossini's ''The Barber of Seville, Barber of Seville'' (all of which are also sung by sopranos and contraltos). Many 19th-century French- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théâtre Du Gymnase Marie Bell
The Théâtre du Gymnase or Théâtre du Gymnase Marie Bell, is a theatre in Paris, at 38 Boulevard Bonne-Nouvelle in the 10th arrondissement (métro : Bonne Nouvelle). History Inaugurated on December 23, 1820 by Delestre-Poirson, the théâtre du Gymnase came to serve as a training-theatre for students of the conservatoire, where they could appear solely in one-act plays or adaptations of longer plays into one-act plays. Poirson quickly added two-act plays to the theatre's repertoire, then 3-act plays, and drew up an exclusive contract with Eugène Scribe to supply them. He installed gas lighting in 1823 and in the following year, with the permission of the duchesse de Berry, the theatre was granted the title of ''théâtre de Madame''. Closed for renovation in 1830, the theatre reopened after the July Revolution under the name ''Gymnase Dramatique''. In 1844, Montigny took over as director of the theatre, and to attract a wider audience abandoned somewhat the moral and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |