|
Manhattan, Nevada
Manhattan is an unincorporated town in Nye County, Nevada, located at the end of Nevada State Route 377, about north of Tonopah, the county seat. History It originally was founded in 1867 as part of the silver mining boom. George Wheeler found the district abandoned in 1871. Then, in 1905, as part of the gold boom, "4,000 people flood(ed) into the region". The Nye and Ormsby County Bank, the only stone structure to be built in the town, was erected in 1906, but a decline followed the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1907 depression. The bank was soon forced to close following these events. In 1904, "Mom" Ronzone first started selling socks to Manhattan miners, the beginning of a retail career that would result in Ronzone's department stores in Tonopah, then Las Vegas Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unincorporated Towns In Nevada
Nevada state law allows for governance of unincorporated area, unincorporated towns under two different systems. The Unincorporated Town Government Law, adopted in 1975, applies to counties of 100,000 people or more, and any other county that opts in. For other counties, a patchwork system of laws applies. A 1975 study by the state Legislative Commission identified 39 unincorporated towns in Nevada. As of 2014, the state Demographer's Office listed 44 unincorporated towns. Unincorporated Town Government Law The Unincorporated Town Government Law, adopted in 1975, applies to counties with a population over 100,000 (Clark County, Nevada, Clark and Washoe County, Nevada, Washoe Counties), and any other county whose commissioners pass an ordinance adopting the law. Under this law, unincorporated towns are provided extra services by the county, paid for by property taxes or other revenue sources from the town. A town can be formed by an initiative petition by residents, or by the coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yerington, Nevada
Yerington is a city in Lyon County, Nevada, United States. The population was 3,121 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the current county seat of Lyon County, with the first county seat having been established at Dayton, Nevada, Dayton on November 29, 1861. It is named after Henry M. Yerington, superintendent of the Virginia and Truckee Railroad from 1868 to 1910. History Native people The Yerington Paiute Tribe of the Yerington Colony and Campbell Ranch is headquartered in Yerington. The people, known as ''Numu'' (human beings) in their own language, have lived in the Smith and Mason Valleys in Northwestern Nevada, since around 1000 A.D. City The community was formerly named Greenfield, Mason Valley, and Pizen Switch (irreverent nickname from the time where Yerington was a transfer - or switch - stop; and the local whiskey was so bad that it was called "poison". "Poison" came out sounding like "pizen" because of local vernacular, and the name "Pizen Switch" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
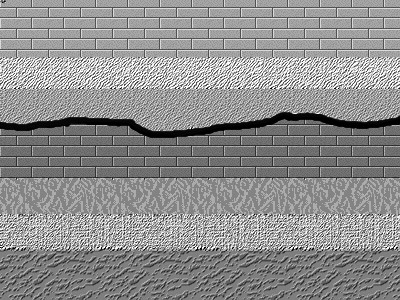
Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in Berwickshire in 1788, both in Scotland. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Permian Period, Ma. It is the fifth and penultimate period of the Paleozoic era and the fifth period of the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon. In North America, the Carboniferous is often treated as two separate geological periods, the earlier Mississippian (geology), Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin ("coal") and ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern "system" names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare (geologist), William Conybeare and William Phillips (geologist), William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. Carboniferous is the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts, and hence quartzite is a metasandstone. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture (geology), texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as mica, talc, chlorite group, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz. Schist typically forms during regional metamorphism accompanying the process of mountain building (orogeny) and usually reflects a medium Metamorphism#Metamorphic grades, grade of metamorphism. Schist can form from many different kinds of rocks, including sedimentary rocks such as mudstones and igneous rocks such as tuffs. Schist metamorphosed from mudstone is particularly common and is often very rich in mica (a ''mica schis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic rock. Foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering, but instead is in planes perpendicular to the direction of metamorphic compression. The foliation in slate, called " slaty cleavage", is caused by strong compression in which fine-grained clay forms flakes to regrow in planes perpendicular to the compression. When expertly "cut" by striking parallel to the foliation with a specialized tool in the quarry, many slates display a property called fissility, forming smooth, flat sheets of stone which have long been used for roofing, floor tiles, and other purposes. Slate is frequently grey in color, especially when seen ''en masse'' covering roofs. However, slate occurs in a variety of colors even from a single locality; for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoshone Range
The Shoshone Range is a mountain range in Lander County, Nevada. The northeast end of the range extends into Eureka County at Shoshone Point on the Humboldt River.''Crescent Valley, Nevada,'' 30x60 Minute Quadrangle, USGS, 1987 (40116-A1-TM-100)''Battle Mountain, Nevada,'' 30x60 Minute Quadrangle, USGS, 1988 (40116-E1-TM-100) The range was named from the Shoshoni language Shoshoni, also written as Shoshoni-Gosiute and Shoshone ( ; Shoshoni: soni ta̲i̲kwappe'', ''newe ta̲i̲kwappe'' or ''neme ta̲i̲kwappeh''), is a Numic language of the Uto-Aztecan family, spoken in the Western United States by the Shoshon ... meaning "grass". References Mountain ranges of Nevada Mountain ranges of Eureka County, Nevada Mountain ranges of Lander County, Nevada Range, Shoshone {{LanderCountyNV-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Period
The Tertiary ( ) is an obsolete Period (geology), geologic period spanning 66 million to 2.6 or 1.8 million years ago. The period began with the extinction of the non-bird, avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start of the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era, and extended to the beginning of the Quaternary glaciation at the end of the Pliocene, Pliocene Epoch. The Tertiary has not been recognised by the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) since the late 1980s, with the timespan of the Tertiary now being split in to the earlier Paleogene and the more recent Neogene periods, though the Tertiary continues to be used in some scientific publications. Historical use of the term The term Tertiary was first used by Giovanni Arduino (geologist), Giovanni Arduino during the mid-18th century. He classified geologic time into primitive (or primary), secondary, and tertiary periods based on observations of geology in Northern Italy. Later a fourth period, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than to almost . Alluvial fans typically form where a flow of sediment or rocks emerge from a confined channel and are suddenly free to spread out in many directions. For example, many alluvial fans form when steep mountain valleys meet a flat plain. The transition from a narrow channel to a wide open area reduces the carrying capacity of flow and results in Deposition (geology), deposition of sediments. The flow can take the form of infrequent debris flows like in a landslide, or can be carried by an intermittent stream or creek. The reduction of flow is key to the formation of alluvial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |