|
Manchán Of Lemanaghan
Saint Manchán mac Silláin (died 664), ''Manchianus'' in Latin sources, is the name of an early List of saints of Ireland, Irish saint, patron of Liath Mancháin, now Lemanaghan, in County Offaly.Stalmans and Charles-Edwards, "Meath, saints of (act. ''c''.400–''c''.900)". ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography''.Breen, "Manchán, Manchianus, Manchíne". ''Dictionary of Irish Biography''. He is not to be confused with the scholar Manchán of Min Droichit, Manchán or Manchéne, abbot of Min Droichit (Co. Offaly). There are variant traditions concerning the saint's pedigree, possibly owing to confusion with one of several churchmen named Manchán or Mainchín. The most reliable genealogy makes him a son of Sillán son of Conall, who is said be a descendant of Rudraige Mór of Ulster, and names his mother Mella. Foundation of the monastery Manchán's church, Liath Mancháin, was located in the kingdom of Delbnae Bethra and its remains now lie approximately two kilometres from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Saints Of Ireland
In Christianity, certain deceased Christians are recognized as saints, including some from Ireland. The vast majority of these saints lived during the 4th–10th centuries, the period of early Christian Ireland, when Celtic Christianity produced many missionaries to Great Britain and the European continent. The exact number of Irish saints is not known but the Martyrology of Donegal lists 1000 saints, male and female. For this reason, Ireland in a 19th-century adage is described as "the land of saints and scholars".''The Monthly Packet of Evening Readings for Members of the English Church'', Volume 3, John and Charles Mozley (1852)p. 215 Christianity was introduced into Ireland toward the end of the 4th century. The details of the introduction are obscure, though the strict ascetic nature of monasticism in Ireland is said to be derived from the practices of the Desert Fathers. Although there were some Christians in Ireland before Patrick, who was a native of Roman Britain, he pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martyrology Of Tallaght
The ''Martyrology of Tallaght'', which is closely related to the ''Félire Óengusso'' or ''Martyrology of Óengus the Culdee'', is an eighth- or ninth-century Irish-language martyrology, a list of saints and their feast days assembled by Maelruain, Máel Ruain and/or Óengus of Tallaght, Óengus the Culdee at Tallaght Monastery, near Dublin. The '' Martyrology of Tallaght'' is in prose and contains two sections for each day of the year, one general and one for Irish saints. It also has a prologue and an epilogue. ''Prologue'' and Irish paganism The prologue contains a famous verse on the declining pagan faith in Ireland: ''Senchatraig na ngente/iman roerud rudad/itfossa can adrad/amail Lathrach Lugdach.'' ''Ind locáin rogabtha/dessib ocus trírib/it rúama co ndálib/co cétaib, co mílib.'' which reads in translation as ''The old cities of the pagans to which length of occupation has refused are deserts without worship like Lugaid mac Con, Lugaid's House-site.'' ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Clonmacnoise
The ''Annals of Clonmacnoise'' () are an early 17th-century Early Modern English translation of a lost Irish chronicle, which covered events in Ireland from prehistory to 1408. The work is sometimes known as ''Mageoghagan's Book'', after its translator Conall the Historian. David Sellar, who was the Lord Lyon King of Arms in Scotland, concluded that it dates from 1627. Robert Anthony Welch also stated that while it records history from the earliest times up to 1408, the original manuscript has been lost and it survives in an English translation that dates from 1627. Translation The Irish chronicle was translated into English, in the style of the Elizabethan period, in 1627 by Conall Mag Eochagáin, of Lismoyny (County Westmeath), near Clara, County Offaly. Mag Eochagáin dedicated this translation to his brother-in-law, Toirdhealbhach Mac Cochláin, whose family was among the last to uphold and practice native Irish Gaelic customs. The translation was completed on 20 Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Inisfallen
The ''Annals of Inisfallen'' () are a chronicle of the medieval history of Ireland. Overview There are more than 2,500 entries spanning the years between 433 and 1450. The manuscript is thought to have been compiled in 1092, as the chronicle is written by a single scribe down to that point but updated by many different hands thereafter. It was written by the monks of Innisfallen Abbey, on Innisfallen Island on Lough Leane, near Killarney in Munster, but made use of sources produced at different centres around Munster as well as a Clonmacnoise group text of the hypothetical Chronicle of Ireland. It is regarded as the main source for the medieval history of Munster. As well as the chronological entries, the manuscript contains a short, fragmented narrative of the history of pre-Christian Ireland, known as the ''pre-Patrician section'', from the time of Abraham to the arrival of Saint Patrick in Ireland. This has many elements in common with Lebor Gabála Érenn. It sets th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
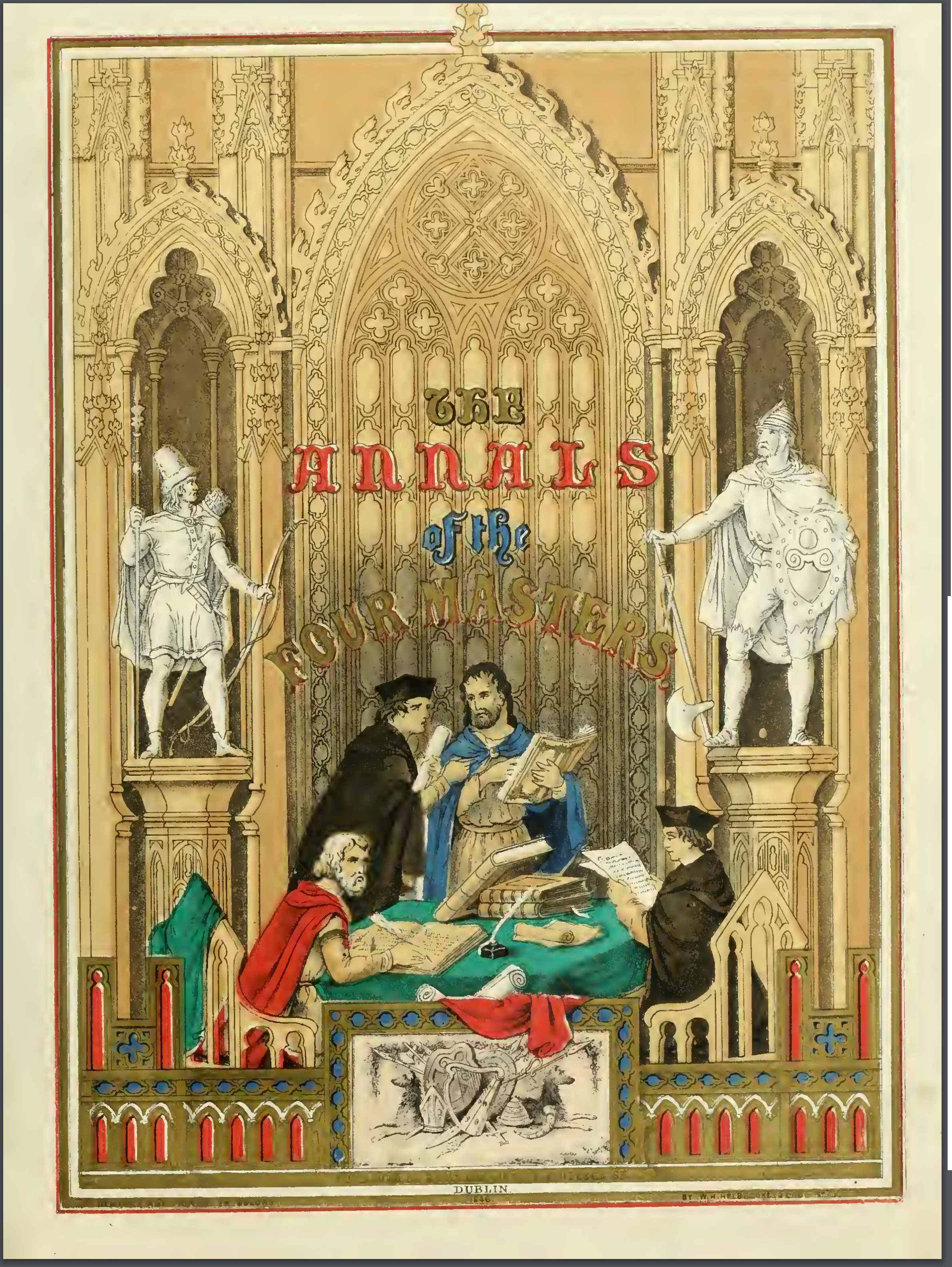
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' () or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' () are chronicles of Middle Ages, medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Genesis flood narrative, Deluge, dated as 2,242 Anno Mundi, years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th-century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal (town), Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' () are annals of History of Ireland, medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, under his patron Cathal Óg Mac Maghnusa, on the island of ''Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa'', also known as ''Senad'' or Ballymacmanus Island (now known as Belle Isle, where Belle Isle Castle is located), near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of ''Fir Manach'' (Fermanagh). Later entries (up to AD 1540) were added by others. Entries up to the mid-6th century are retrospective, drawing on earlier annalistic and historical texts, while later entries were contemporary, based on recollection and oral history. Thomas Charles-Edwards, T. M. Charles-Edwards has claimed that the main source for its records of the first millennium A.D. is a now-lost Armagh continuation of the ''Chronicle of Ireland''. The Annals used the Irish language, with some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalwork
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges, down to precise engine parts and delicate jewellery. The historical roots of metalworking predate recorded history; its use spans cultures, civilizations and millennia. It has evolved from shaping soft, native metals like gold with simple hand tools, through the smelting of ores and hot forging of harder metals like iron, up to and including highly technical modern processes such as machining and welding. It has been used as an industry, a driver of trade, individual hobbies, and in the creation of art; it can be regarded as both a science and a craft. Modern metalworking processes, though diverse and specialized, can be categorized into one of three broad areas known as forming, cuttin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Sculpture
Romanesque art is the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic style in the 12th century, or later depending on region. The preceding period is known as the Pre-Romanesque period. The term was invented by 19th-century art historians, especially for Romanesque architecture, which retained many basic features of Roman architectural style – most notably round-headed arches, but also barrel vaults, apses, and acanthus-leaf decoration – but had also developed many very different characteristics. In Southern France, Spain, and Italy there was an architectural continuity with the Late Antique, but the Romanesque style was the first style to spread across the whole of Catholic Europe, from Sicily to Scandinavia. Romanesque art was also greatly influenced by Byzantine art, especially in painting, and by the anti-classical energy of the decoration of the Insular art of the British Isles. From these elements was forged a highly innovative and coherent sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Offaly
County Offaly (; ) is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster. It is named after the Ancient Ireland, ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain. Offaly County Council is the Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local authority for the county. The county population was 82,668 at the 2022 census. Geography and political subdivisions Offaly is the 18th largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area and the 24th largest in terms of population. It is the fifth largest of Leinster's 12 counties by size and the tenth largest by population. Physical geography Tullamore is the county town and largest town in Offaly and is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, 30th largest in Ireland. Offaly borders seven counties: County Galway, Galway, County Roscommon, Roscommon, County Tipperary, Tippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Manchan's Shrine
Saint Manchan's Shrine is a large (60-cm wide) 12th-century Irish house-shaped shrine dedicated to Manchán of Lemanaghan (died 664), now in Boher Roman Catholic Church, outside Ballycumber, County Offaly. Built to hold human remains, still intact and presumably of Manchán himself, the relic container consists of a wooden core made of Taxus baccata, yew, placed on four cast bronze feet, overlain by sliver plates containing Gilding, gilt, cast copper alloy and bronze decorations, with large Boss (architecture), bosses.Murray (2003), p. 177 The shrine has a long history and has survived a number of sackings and fires. It was in poor condition when discovered in the collection of the Mooney family of Doon, County Offaly in 1821, with many of the figures and bosses missing; some of the current elements were added during late 19th century restorations.Crawford (1923), p. 83 Its style is a mixture of Irish and Viking art,Verney, Deirdre.World famous St Manchan's shrine subject of lect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |