|
Major Atmospheric Gamma Ray Imaging Cherenkov
MAGIC (Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov Telescopes, later renamed to MAGIC Florian Goebel Telescopes) is a system of two IACT, Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes situated at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on La Palma, one of the Canary Islands, at about 2200 m above sea level. MAGIC detects particle showers released by gamma rays, using the Cherenkov radiation, i.e., faint light radiated by the charged particles in the showers. With a diameter of 17 meters for the reflecting surface, it was the largest in the world before the construction of High Energy Stereoscopic System, H.E.S.S. II. The first telescope was built in 2004 and operated for five years in standalone mode. A second MAGIC telescope (MAGIC-II), at a distance of 85 m from the first one, started taking data in July 2009. Together they integrate the MAGIC telescope stereoscopic system. MAGIC is sensitive to cosmic gamma rays with photon energy, photon energies between 50 GeV (later lowered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz () and wavelengths less than 10 picometers (), gamma ray photons have the highest photon energy of any form of electromagnetic radiation. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900, he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Binaries
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for broken bones) and materials science (e.g., identification of some chemical elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Foam
Quantum foam (or spacetime foam, or spacetime bubble) is a theoretical quantum fluctuation of spacetime on very small scales due to quantum mechanics. The theory predicts that at this small scale, particles of matter and antimatter are constantly created and destroyed. These subatomic objects are called virtual particles. The idea was devised by John Wheeler in 1955. Background With an incomplete theory of quantum gravity, it is impossible to be certain what spacetime looks like at small scales. However, there is no definitive reason that spacetime needs to be fundamentally smooth. It is possible that instead, in a quantum theory of gravity, spacetime would consist of many small, ever-changing regions in which space and time are not definite, but fluctuate in a foam-like manner. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markarian 501
Markarian 501 (or Mrk 501) is a galaxy with a spectrum extending to the highest energy gamma rays. It is a blazar or BL Lac object, which is an active galactic nucleus with a jet that is shooting towards the Earth. The object has a redshift of z = 0.034. Mrk 501 is an extremely variable source of gamma rays, undergoing violent outbursts. During an outburst in 1997, it was the brightest object in the sky in the very-high-energy gamma ray region of the spectrum, at photon energy, energies above 1011 electronvolt, eV (100 GeV). The galaxy hosting the blazar was studied and Markarian galaxies, catalogued by Benjamin Markarian in 1974. It was first determined to be a very high energy gamma ray emitter in 1996 by John Quinn at the Whipple Observatory. Galaxy The elliptical galaxy is located in the constellation of Hercules (constellation), Hercules at right ascension 16h 53.9m and declination +39° 45'. Its visible size appears to be 1.2 by 1 minute of arc. Gamma rays The gamma r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blazar
A blazar is an active galactic nucleus (AGN) with a relativistic jet (a jet composed of ionized matter traveling at nearly the speed of light) directed very nearly towards an observer. Relativistic beaming of electromagnetic radiation from the jet makes blazars appear much brighter than they would be if the jet were pointed in a direction away from Earth. Blazars are powerful sources of emission across the electromagnetic spectrum and are observed to be sources of high-energy gamma ray photons. Blazars are highly variable sources, often undergoing rapid and dramatic fluctuations in brightness on short timescales (hours to days). Some blazar jets appear to exhibit superluminal motion, another consequence of material in the jet traveling toward the observer at nearly the speed of light. The blazar category includes BL Lac objects and optically violently variable (OVV) quasars. The generally accepted theory is that BL Lac objects are intrinsically low-power radio galaxies while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco Dwarf
The Draco Dwarf is a spheroidal galaxy which was discovered by Albert George Wilson of Lowell Observatory in 1954 on photographic plates of the National Geographic Society's Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS). It is part of the Local Group and a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way galaxy. The Draco Dwarf is situated in the direction of the Draco Constellation at 34.6° above the galactic plane. Characteristics Paul W. Hodge analyzed the distribution of its stars in 1964 and concluded that its ellipticity was 0.29 ± 0.04. Recent studies have indicated that the galaxy may potentially hold large amounts of dark matter. Having an absolute magnitude of −8.6 and a total luminosity of only , it is one of the faintest companions to our Milky Way. Draco Dwarf contains many red giant branch (RGB) stars; five carbon stars have been identified in Draco Dwarf and four likely asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars have been detected. The Draco Dwarf is estimated to be 80 ± 10 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Galaxy
A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition. Formation One theory states that most galaxies, including dwarf galaxies, form in association with dark matter, or from gas that contains metals. However, NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer space probe identified new dwarf galaxies forming out of gases with low metallicity. These galaxies were located in the Leo Ring, a cloud of hydrogen and helium around two massive galaxies in the constellation Leo (constellation), Leo. Because of their small size, dwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3C 279
3C 279 (also known as 4C–05.55, NRAO 413, and PKS 1253–05) is an OVV quasar, optically violent variable quasar (OVV), which is known in the astronomical community for its variations in the Visible spectrum, visible, Radio frequency, radio and X-ray bands. The quasar was observed to have undergone a period of extreme activity from 1987 until 1991. The Rosemary Hill Observatory (RHO) started observing 3C 279 in 1971, the object was further observed by the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory in 1991, when it was unexpectedly discovered to be one of the brightest gamma ray objects in the sky. It is also one of the brightest and most variable sources in the gamma ray sky monitored by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. It was used as a calibrator source for Event Horizon Telescope observations of M87* that resulted in the first image of a black hole. Observations * The apparent Superluminal#Astronomical observations, superluminal motion was detected during observations first made in 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasar
A quasar ( ) is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. The emission from an AGN is powered by accretion onto a supermassive black hole with a mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses, surrounded by a gaseous Accretion disk, accretion disc. Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. The radiant energy of quasars is enormous; the most powerful quasars have luminosity, luminosities thousands of times greater than that of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Quasars are usually categorized as a subclass of the more general category of AGN. The redshifts of quasars are of Expansion of the universe, cosmological origin. The term originated as a Contraction (grammar), contraction of "quasi-stellar ''[star-like]'' radio source"—because they were first identified during the 1950s as sources of radio-wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo theory, dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body with a dipole magnetic field such as Earth, the field lines resemble a simple magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma (physics), plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation. Interactions of particles and atmospheres with magnetospheres are studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics, and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert (astronomer), W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab Pulsar
The Crab Pulsar (PSR B0531+21 or Baade's Star) is a relatively young neutron star. The star is the central star in the Crab Nebula, a remnant of the supernova SN 1054, which was widely observed on Earth in the year 1054.Supernova 1054 – Creation of the Crab Nebula Discovered in 1968, the was the first to be connected with a supernova remnant. 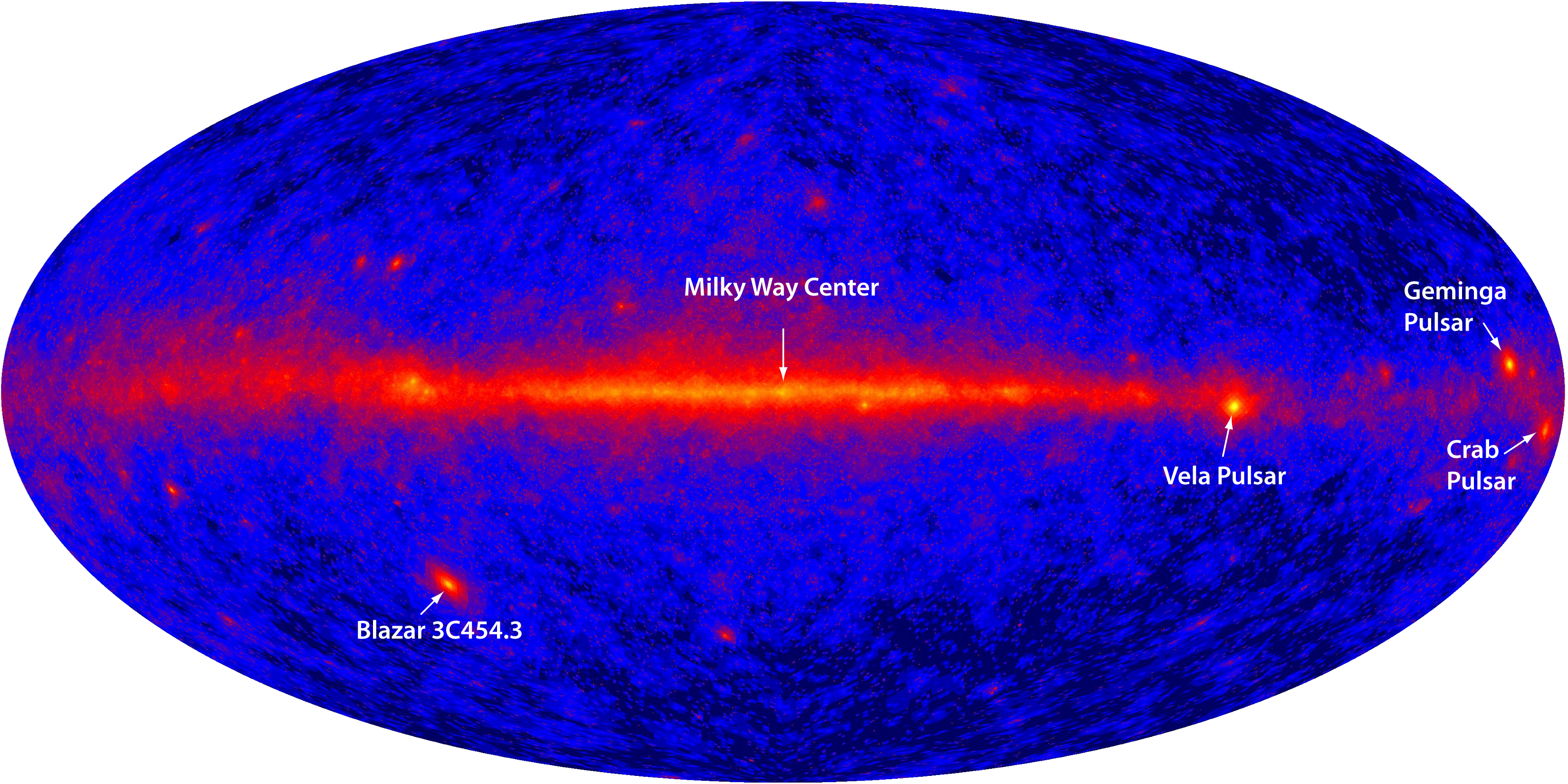 The Crab Pulsar is one of very few pulsars to be identified optically. The
The Crab Pulsar is one of very few pulsars to be identified optically. The [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relativity unless more matter is present than can be observed. Such effects occur in the context of Galaxy formation and evolution, formation and evolution of galaxies, gravitational lensing, the observable universe's current structure, mass position in galactic collisions, the motion of galaxies within galaxy clusters, and cosmic microwave background Anisotropy, anisotropies. Dark matter is thought to serve as gravitational scaffolding for cosmic structures. After the Big Bang, dark matter clumped into blobs along narrow filaments with superclusters of galaxies forming a cosmic web at scales on which entire galaxies appear like tiny particles. In the standard Lambda-CDM model of cosmology, the mass–energy equivalence, mass–energy content o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









