|
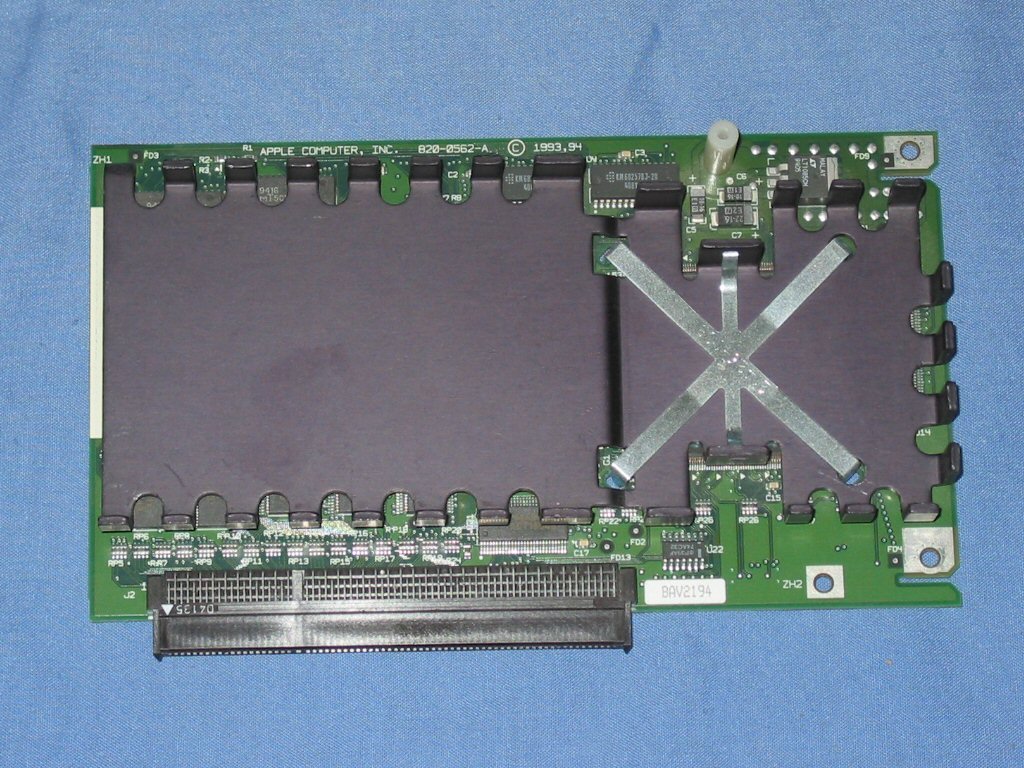
Macintosh Processor Upgrade Card
The generically named Macintosh Processor Upgrade Card (code named STP) is a central processing unit upgrade card sold by Apple Computer, designed for many Motorola 68040-powered Macintosh LC, Quadra and Performa models. The card contains a PowerPC 601 CPU and plugs into the 68040 CPU socket of the upgraded machine. The Processor Upgrade card required the original CPU be plugged back into the card itself, and gave the machine the ability to run in its original 68040 configuration, or through the use of a software configuration utility allowed booting as a PowerPC 601 computer running at twice the original speed in MHz (50 MHz or 66 MHz) with 32 KB of L1 Cache, 256 KB of L2 Cache and a PowerPC Floating Point Unit available to software. The Macintosh Processor Upgrade requires and shipped with System 7.5. Development of the card started in July 1993. The upgrade card was announced in January 1994 at the MacWorld Expo in San Francisco. Apple described the Macintosh Proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Macintosh Upgrade Card Front
Power may refer to: Common meanings * Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work" ** Engine power, the power put out by an engine ** Electric power, a type of energy * Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events Mathematics, science and technology Computing * IBM POWER (software), an IBM operating system enhancement package * IBM POWER architecture, a RISC instruction set architecture * Power ISA, a RISC instruction set architecture derived from PowerPC * IBM Power microprocessors, made by IBM, which implement those RISC architectures * Power.org, a predecessor to the OpenPOWER Foundation Mathematics * Exponentiation, "''x'' to the power of ''y''" * Power function * Power of a point * Statistical power Physics * Magnification, the factor by which an optical system enlarges an image * Optical power, the degree to which a lens converges or diverges light Social sciences and politics * Economic power, encompassing several concepts that economists use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison-Wesley
Addison–Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson plc, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison–Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison–Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison–Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include '' The Art of Computer Programming'', '' The C++ Programming Language'', '' The Mythical Man-Month'', and '' Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison–Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison–Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, in Silicon Valley. It is best known for its consumer electronics, software, and services. Founded in 1976 as Apple Computer Company by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne, the company was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. the following year. It was renamed Apple Inc. in 2007 as the company had expanded its focus from computers to consumer electronics. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue, with billion in the 2024 fiscal year. The company was founded to produce and market Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. Its second computer, the Apple II, became a best seller as one of the first mass-produced microcomputers. Apple introduced the Lisa in 1983 and the Macintosh in 1984, as some of the first computers to use a graphical user interface and a mouse. By 1985, internal company problems led to Jobs leaving to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 68040
The Motorola 68040 ("''sixty-eight-oh-forty''") is a 32-bit microprocessor in the Motorola 68000 series, released in 1990. It is the successor to the 68030 and is followed by the 68060, skipping the 68050. In keeping with general Motorola naming, the 68040 is often referred to as simply the '040 (pronounced ''oh-four-oh'' or ''oh-forty''). The 68040 was the first 680x0 family member with an on-chip Floating-Point Unit (FPU). It thus included all of the functionality that previously required external chips, namely the FPU and Memory Management Unit (MMU), which was added in the 68030. It also had split instruction and data caches of 4 kilobytes each. It was fully pipelined, with six stages. Versions of the 68040 were created for specific market segments, including the 68LC040, which removed the FPU, and the 68EC040, which removed both the FPU and MMU. Motorola had intended the EC variant for embedded use, but embedded processors during the 68040's time did not need t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
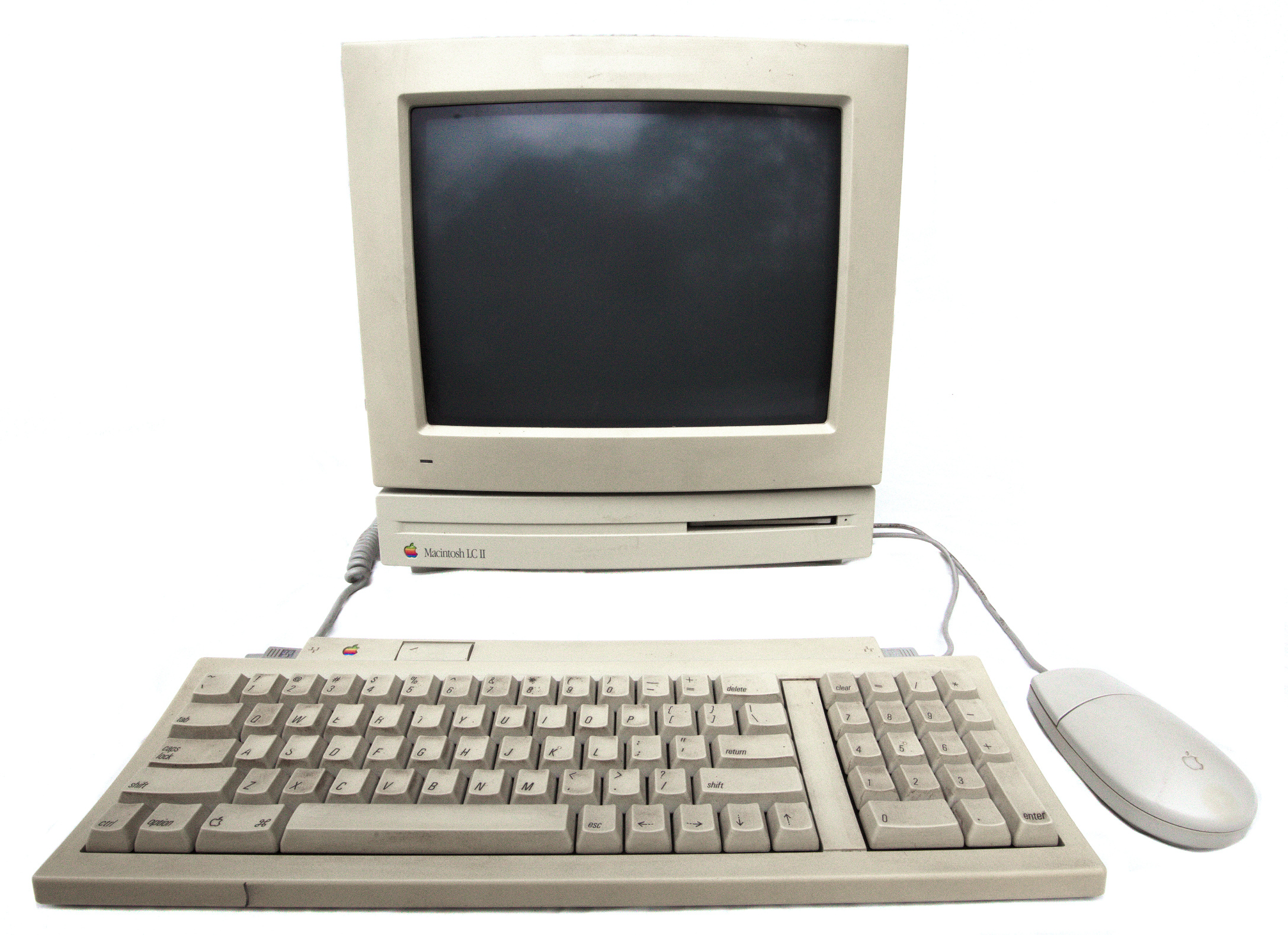
Macintosh LC Family
The Macintosh LC is a family of personal computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Inc., Apple Computer, Inc. from 1990 to 1997. Introduced alongside the Macintosh IIsi and Macintosh Classic as part of a new wave of lower-priced Macintosh computers, the LC offered the same overall performance as the Macintosh II for half the price. Part of Apple's goal was to produce a machine that could be sold to school boards for the same price as an Apple IIGS, Apple IIGS, a machine that was very successful in the education market. Not long after the Apple IIe Card was introduced for the LC, Apple officially announced the retirement of the IIGS, as the company wanted to focus its sales and marketing efforts on the LC. The original Macintosh LC was introduced in October 1990, with updates in the form of the Macintosh LC II, LC II and Macintosh LC III, LC III in 1992 and early 1993. These early models all shared the same pizza box form factor, and were joined by the Macintosh LC 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macintosh Quadra
The Macintosh Quadra is a family of personal computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Inc., Apple Computer, Inc. from October 1991 to October 1995. The Quadra, named for the Motorola 68040 central processing unit, replaced the Macintosh II family as the high-end Mac (computer), Macintosh model. The first models were the Macintosh Quadra 700, Quadra 700 and Macintosh Quadra 900, Quadra 900, both introduced in October 1991, with the latter discontinued after six months and replaced by the Macintosh Quadra 950, Quadra 950. The Macintosh Quadra 800, Quadra 800 was added in February 1993 (succeeding the Quadra 700), followed the multimedia-focused Macintosh Quadra 840AV, 840AV at the end of July 1993. The Macintosh Centris line was merged with the Quadra in October 1993, adding the Macintosh Quadra 610, 610, Macintosh Quadra 650, 650 and Macintosh Quadra 660AV, 660AV to the range. The Macintosh Quadra 605, 605 (also sold as the Performa 475 or LC 475) was also introduced in Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performa
The Macintosh Performa is a family of personal computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from 1992 to 1997. The Performa brand re-used models from Apple's Quadra, Centris, LC, Classic, and Power Macintosh families with model numbers that denoted included software packages or hard drive sizes. Whereas non-Performa Macintosh computers were sold by Apple Authorized Resellers, the Performa was sold through big-box stores and mass-market retailers such as Good Guys, Circuit City, and Sears. The initial series of models consisted of the Macintosh Classic II-based Performa 200, the LC II-based Performa 400, and the IIvi-based Performa 600. After releasing a total of sixty-four different models, Apple retired the Performa brand in early 1997, shortly after release of the Power Macintosh 5500, 6500, 8600 and 9600, as well as the return of Steve Jobs to the company. The Performa brand's lifespan coincided with a period of significant financial turmoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerPC 600
The PowerPC 600 family was the first family of PowerPC processors built. They were designed at the Somerset facility in Austin, Texas, jointly funded and staffed by engineers from IBM and Motorola as a part of the AIM alliance. Somerset was opened in 1992 and its goal was to make the first PowerPC processor and then keep designing general purpose PowerPC processors for personal computers. The first incarnation became the PowerPC 601 in 1993, and the second generation soon followed with the PowerPC 603, PowerPC 604 and the 64-bit PowerPC 620. Nuclear family PowerPC 601 The PowerPC 601 was the first generation of microprocessors to support the basic 32-bit PowerPC instruction set. The design effort started in earnest in mid-1991 and the first prototype chips were available in October 1992. The first 601 processors were introduced in an IBM RS/6000 workstation in October 1993 (alongside its more powerful multichip cousin IBM POWER2 line of processors) and the first Apple Power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating Point Unit
A floating-point unit (FPU), numeric processing unit (NPU), colloquially math coprocessor, is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating-point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root. Modern designs generally include a fused multiply-add instruction, which was found to be very common in real-world code. Some FPUs can also perform various transcendental functions such as exponential or trigonometric calculations, but the accuracy can be low, so some systems prefer to compute these functions in software. Floating-point operations were originally handled in software in early computers. Over time, manufacturers began to provide standardized floating-point libraries as part of their software collections. Some machines, those dedicated to scientific processing, would include specialized hardware to perform some of these tasks with much greater speed. The introduction of microcode in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System 7
System 7 (later named Mac OS 7) is the seventh major release of the classic Mac OS operating system for Macintosh computers, made by Apple Computer. It was launched on May 13, 1991, to succeed System 6 with virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, TrueType fonts, the Force Quit dialog, and an improved user interface. It was code-named "Big Bang" in development and the initial release was named "The System" or "System" like all earlier versions. With version 7.5.1, the name "Mac OS" debuted on the boot screen, and the operating system was officially renamed to Mac OS in 1997 with version 7.6. The Mac OS 7 line was the longest-lasting major version of the Classic Mac OSes due to the troubled development of Copland, an operating system intended to be the successor to OS 7 before its cancellation and replacement with Mac OS 8. Development By 1988, the Macintosh had been on the market for four years. Some aspects of the operating system were beginning to fall behind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processor Direct Slot
A processor direct slot (PDS) is a slot incorporated into many older Macintosh models that allowed direct access to the signal pins of a CPU, similar to the functionality of a local bus in PCs. This would result in much higher speeds than having to go through a bus layer, such as NuBus, which typically ran at a slower 10 MHz speed. Overview Typically, if a machine had bus expansion slots it would feature multiple bus expansions slots. However, there was never more than one PDS slot, as rather than providing a sophisticated communication protocol with ''arbitration'' between different bits of hardware that might be trying to use the communication channel at the same time, the PDS slot, for the most part, just gave direct access to signal pins on the CPU, making it closer in nature to a local bus. Thus, PDS slots tended to be CPU-specific, and therefore a card designed for the PDS slot in the Motorola 68030-based Macintosh SE/30, for example, would not work in the Moto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |