|
Macedonian Wars
The Macedonian Wars (214–148 BC) were a series of conflicts fought by the Roman Republic and its Greek allies in the eastern Mediterranean against several different major Greek kingdoms. They resulted in Roman control or influence over Ancient Greece, Greece and the rest of the eastern Mediterranean basin, in addition to their hegemony in the western Mediterranean after the Punic Wars. Traditionally, the "Macedonian Wars" include the four wars with Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia, in addition to one war with the Seleucid Empire, and a final minor war with the Achaean League (which is often considered to be the final stage of the final Macedonian War). The most significant war was fought with the Seleucid Empire, and both this and the wars with Macedonia effectively marked the end of these empires as major world powers, even though neither of them led immediately to overt Roman domination. Four separate wars were fought against the weaker power, Macedonia, due to its geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Macedonia And The Aegean World C
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to: * North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia * Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity * Macedonia (Greece), a former administrative region, spanning today three administrative subdivisions of northern Greece * Macedonia (region), a geographic and historical region that today includes parts of six Balkan countries (see map) Macedonia, Makedonia, Makedonija, or Makedoniya may also refer to: Other historical entities * Achaemenid Macedonia, a satrapy of Achaemenid Empire * Diocese of Macedonia, a late Roman administrative unit * Independent Macedonia (1944), a proposed puppet state of the Axis powers (1944) * Macedonia (Roman province), a province of the early Roman Empire * Macedonia (theme), a province of the Byzantine Empire * Socialist Republic of Macedonia, a part of the former Yugoslavia (1945–1991) and a predecessor of North Macedonia Other geographical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marcus Valerius Laevinus
Marcus Valerius Laevinus (c. 260 BC200 BC) was a Roman consul and commander who rose to prominence during the Second Punic War and corresponding First Macedonian War. A member of the '' gens Valeria'', an old patrician family believed to have migrated to Rome under the Sabine king T. Tatius, Laevinus played an integral role in the containment of the Macedonian threat. Background and early career Laevinus was the son of P. Valerius Laevinus, and grandson of P. Valerius Laevinus. The latter may have been the consul of 280 BC whom Pyrrhus of Epirus defeated at Heraclea. Praetor in Sicily in 227, Marcus Laevinus was first elected consul in 220. His consulship, however, was annulled, likely due to accusations of a faulty election. In 215, during the Second Punic War, Laevinus was elected praetor peregrinus with command of the Roman forces in Apulia. Stationed in Brundisium, Laevinus was appointed to act as a deterrent to any potential advance from the Macedonian king, Phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Cynoscephalae
The Battle of Cynoscephalae () was an encounter battle fought in Thessaly in 197 BC between the Roman army, led by Titus Quinctius Flamininus, and the Antigonid dynasty of Macedon, led by Philip V, during the Second Macedonian War. It was a decisive Roman victory and marked the end of the conflict. Background The First Macedonian War (started due to an alliance between Macedon and Carthage against the Romans during the Second Punic War in 215 BC) had ended in a stalemate; between the Roman alliance with Aetolia and the destruction of the Macedonian fleet early in the war, the Macedonians were unable to support Carthage and were forced into a defensive stance. A truce was signed between Macedonia and Rome in 205 BC leading to an uneasy peace. The Second Punic War would end not long after in 201 BC. Although Macedonia had limited effect in the Second Punic War, their alliance with Carthage would earn the ire of the Romans. In 202 BC, the Fifth Syrian War would break out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titus Quinctius Flamininus
Titus Quinctius Flamininus (229 – 174 BC) was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece. Family background Flamininus belonged to the minor patrician ''gens'' Quinctia. The family had a glorious place in the early history of Rome, especially the famous hero Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus, but it had somewhat lost its political influence by the middle of the fourth century BC. Flamininus' great grandfather Caeso Quinctius Claudus was still consul in 271, the last time a Quinctius is recorded as holding a curule office before 209. Lucius Quinctius, his grandfather, was '' flamen Dialis'' — the great priest of Jupiter — during the third quarter of the third century. The cognomen Flamininus borne by his descendants derives from this prestigious priesthood. Flamininus' great grandson later put an '' apex'', the head covering of the Flamen, as a symbol of his family on a denarius he minted. Flamininus' father — also named Titus — is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Ancient Macedonia, Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean, which would eventually lead to Rome's conquest of the entire region. Background In 204 BC, King Ptolemy IV Philopator of Egypt died, leaving the throne to his six-year-old son Ptolemy V. Philip V of Macedon and Antiochus the Great of the Seleucid Empire decided to exploit the weakness of the young king by taking Ptolemaic territory for themselves and they signed a secret pact defining spheres of interest, opening the Fifth Syrian War. Philip first turned his attention to the ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
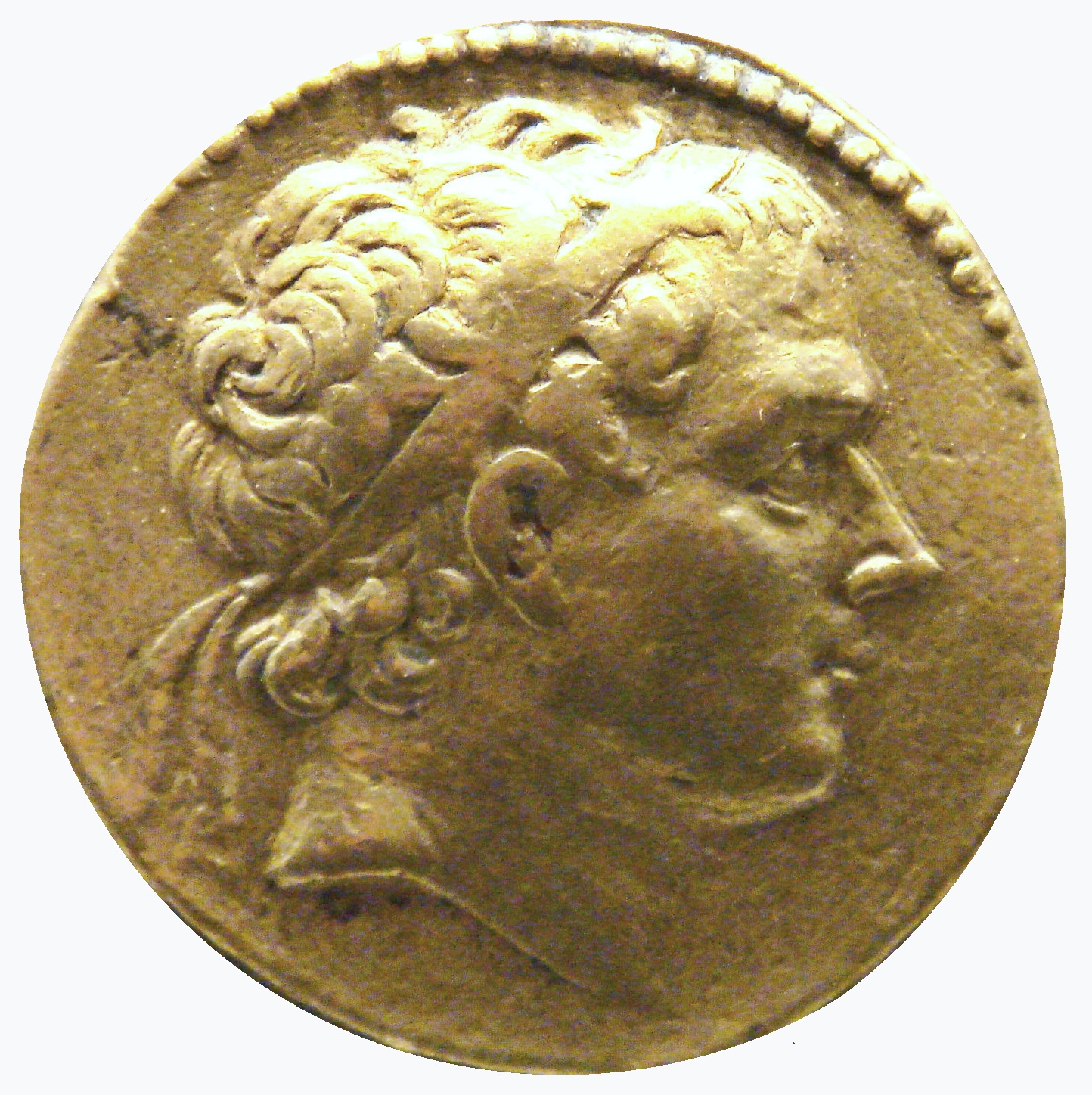
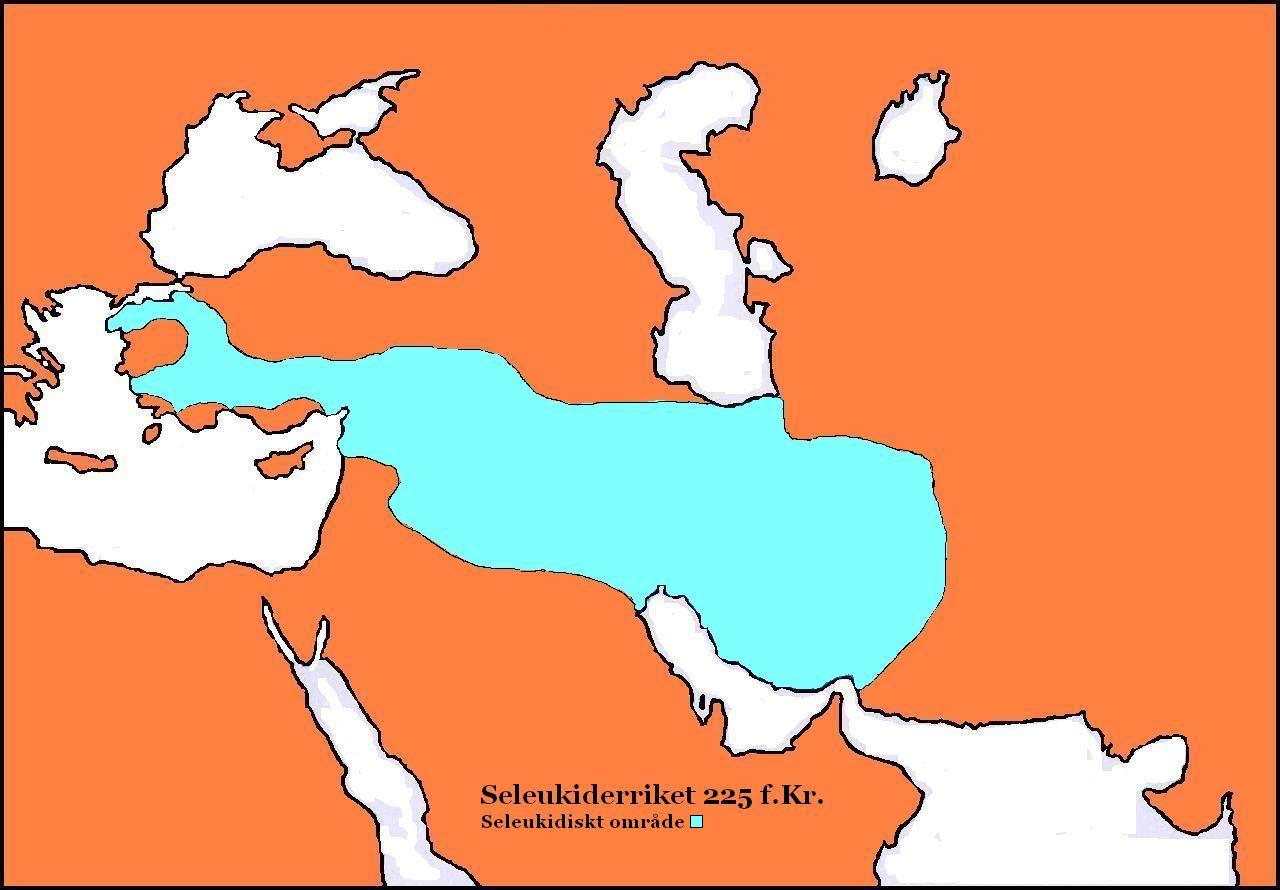
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in April/June 223 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for ' Great King'), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against the Roman Republic. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domination", he waged a four-year war against Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rhodes
Rhodes (; ) is the largest of the Dodecanese islands of Greece and is their historical capital; it is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, ninth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes (regional unit), Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean Administrative regions of Greece, administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is the Rhodes (city), city of Rhodes, which had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022, the island had a population of 125,113 people. It is located northeast of Crete and southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights Hospitaller, Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522. Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ptolemy V
Ptolemy V Epiphanes Eucharistus (, ''Ptolemaĩos Epiphanḗs Eukháristos'' "Ptolemy the Manifest, the Beneficent"; 9 October 210–September 180 BC) was the King of Ptolemaic Egypt from July or August 204 BC until his death in 180 BC. Ptolemy V, the son of Ptolemy IV and Arsinoe III, inherited the throne at the age of five when his parents died in suspicious circumstances. The new regent, Agathocles, was widely reviled and was toppled by a revolution in 202 BC, but the series of regents who followed proved incompetent and the kingdom was paralysed. The Seleucid king Antiochus III and the Antigonid king Philip V took advantage of the kingdom's weakness to begin the Fifth Syrian War (202–196 BC), in which the Ptolemies lost all their territories in Asia Minor and the Levant, as well as most of their influence in the Aegean Sea. Simultaneously, Ptolemy V faced a widespread Egyptian revolt (206–185 BC) led by the self-proclaimed pharaohs Horwennefer and Ankhwennefer, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ptolemy IV
Ptolemy IV Philopator (; "Ptolemy, lover of his Father"; May/June 244 – July/August 204 BC) was the fourth pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 221 to 204 BC. Ptolemy IV was the son of Ptolemy III and Berenice II. His succession to the throne was accompanied by a wide-ranging purge of the Ptolemaic royal family, which left control of the realm's government largely in the hands of his courtiers Sosibius and Agathocles. His reign was marked by the Fourth Syrian War (219–217 BC) with the Seleucid empire, which culminated in a decisive Ptolemaic victory at the Battle of Raphia, one of the largest battles of the whole Hellenistic Age. In the final years of his rule, control over the southern portion of the country was lost to the rebel pharaoh Hugronaphor. Ptolemy IV died in mysterious circumstances in 204 BC and was succeeded by his young son Ptolemy V Epiphanes under the regency of Sosibius and Agathocles. In ancient sources, Ptolemy IV was criticised for being more interested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Treaty Of Phoenice
The Treaty of Phoenice, also known as the Peace of Phoenice, was a treaty''Hannibal's War: A Military History of the Second Punic War'' by J. F. Lazenby, , 1998, page 178, "... the two belligerents with peace proposals, both were more than ready to talk terms. The result was the Peace of Phoinike, by which Philip agreed to surrender the territory of the Parthinoi" ending the First Macedonian War. It was drawn up at Phoenice in 205 BC. The Greek political balance between Macedon under Philip V and the Aetolian League was upset by the war between Rome and Carthage. Philip, seeking to enhance his position, raised a fleet and sent emissaries to Hannibal, then occupying part of Italy. Fearing that Philip could offer overt military assistance, Rome hoped to confine the Macedonians to the east of the Roman province of Illyria. Between 214 and 212 BC, Philip made two unsuccessful attempts to invade Illyria by sea and halting progress by ground, eventually succeeding in capturing the port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |