|
MacCarthy Reagh
The MacCarthy Reagh (Irish: ''Mac Cárthaigh Riabhach'') dynasty are a branch of the MacCarthy dynasty, Kings of Desmond, deriving from the Eóganacht Chaisil sept. History The Mac Cárthaigh Riabhach seated themselves as kings of Carbery in what is now southwestern County Cork including Rosscarbery in the 13th century.Butler, "The Barony of Carbery" Their primary allies in the initially small territory itself were O'Donovans, and members of the Ui Chairpre; both were recent arrivals, gaining their lands from the O'Mahonys of Eóganacht Raithlind and the O'Driscolls of Corcu Loígde. The historical record for this period is very confused and a precise sequence of events cannot be reconstructed. A portion of Carbery was conquered around 1232 by Donal Gott MacCarthy, King of Desmond, from whom the dynasty descend. His son Donal Maol Mac Carthaigh, was the first ruler of the new principality. Their descendants would expand their territories considerably and forge a small, wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
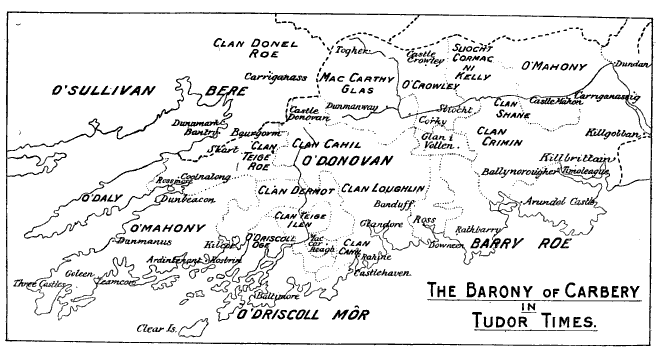
Barony Of Carbery
Carbery, or the Barony of Carbery, was once the largest barony in Ireland, and essentially a small, semi-independent kingdom on the southwestern coast of Munster, in what is now County Cork, from its founding in the 1230s by Donal Gott MacCarthy to its gradual decline in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. His descendants, the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty, were its ruling family. The kingdom officially ended in 1606 when Donal of the Pipes, 17th Prince of Carbery chose to surrender his territories to the Crown of England; but his descendants maintained their position in Carbery until the Cromwellian confiscations, following their participation in the Irish Rebellion of 1641 after which some emigrated to the Chesapeake Colonies. Its modern descendants in name are the baronies of Carbery West and Carbery East, but Carbery once included territories from several of the surrounding baronies as well. To the north/northwest it shared a long and shifting border with the Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence MacCarthy
Finnin MacCarthy () (1560–1640), was an Irish clan chief and member of the Gaelic nobility of Ireland () of the late 16th-century and the last credible claimant to the Mac Carthaig Mór title before its suppression by English authority. Mac Carthaig's involvement in the Nine Years' War (1595–1603) led to his arrest by the Crown, and he spent the last 40 years of his life in custody in London. His clan's lands were divided among his relatives and Anglo-Irish colonialists. Early life Mac Carthaig was born in 1560 at Kilbrittain Castle near Kinsale in the province of Munster in Ireland, into the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty, rulers of Carbery, the son of Donogh MacCarthy Reagh, 15th Prince of Carbery. His grandfather was Donal MacCarthy Reagh, 12th Prince of Carbery. The significance of Mac Carthaig's career lies in his command of territories in west Munster, at a time when the Tudor conquest of Ireland was underway. Southwest Munster was the area most open to Spanish inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finghin MacCarthy Reagh, 8th Prince Of Carbery
Finghin MacCarthy Reagh () was the 10th Prince of Carbery from 1478 to his death in 1505. He belonged to the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty,Irish Pedigrees: MacCarthy Reagh, Prince of Carbery (#118) and was the eldest son of Dermod an Duna MacCarthy Reagh, 8th Prince of Carbery. He was born in 1425 or 1430. Life He was held in high regard by , who in 1484 "authorized" (encouraged) him, along with his kinsman Cormac MacTeige, Lord of Muskerry, to receive the homage of the various Irish lords and chiefs of the region. It was for Finghin and his wife Katherine that the famous |
Book Of Lismore
The Book of Lismore, also known as the Book of Mac Carthaigh Riabhach, is a late fifteenth-century Gaelic manuscript that was created at Kilbrittain in County Cork, Ireland, for Fínghean Mac Carthaigh, Lord of Carbery (1478–1505). Defective at beginning and end, 198 leaves survive today, containing a miscellany of religious and secular texts written entirely in Irish. The main scribe of the manuscript did not sign his name. A second scribe, who wrote eleven leaves, signed himself Aonghus Ó Callanáin, and was probably a member of a well-known family of medical scholars from West Cork. Other relief scribes contribute short stints throughout the book. The book also contains a reference (f. 158v) to a second manuscript, a ''duanaire'' or anthology of poetry dedicated to Mac Carthaigh, but this manuscript is now lost. Contents While poetry is well represented throughout the manuscript, the dominant form is prose, dating linguistically from the high through late Middle Ages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac Carthaigh's Book
''Mac Carthaigh’s Book'' is a collection of annals of the period AD 1114 in Ireland, 1114–1437 in Ireland, 1437 inclusive. It was compiled from earlier material by Florence MacCarthy, Fínghin Mac Carthaigh Mór (c. 1560–1640) an Irish nobleman who was imprisoned for years in London. He was a patron of learning and a scholar in his own right. While in London in 1633 he employed Diarmaid Ó Súilleabháin (writer), Diarmaid Ó Súilleabháin who also kept the book in his castle until it was sacked by Radhulbh MacAmlaoibh, then his clan took control of it, they copied and compiled these annals for him. The original manuscript is currently preserved in the National Library of Ireland. The annals were edited and translated by Séamus Ó hInnse and published in 1947 by the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies under the title ‘Miscellaneous Irish Annals’. Mac Carthaigh's Book is important as one of the few native records of events in southern Ireland for the period it covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscounts
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status. The status and any domain held by a viscount is a viscounty. In the case of French viscounts, the title is sometimes left untranslated as ''vicomte'' . Etymology The word ''viscount'' comes from Old French (French language">Modern French: ), itself from Medieval Latin , accusative case, accusative of , from Vulgar Latin, Late Latin "deputy" + Latin (originally "companion"; later Roman imperial courtier or trusted appointee, ultimately count). History During the Carolingian Empire, the kings appointed counts to administer provinces and other smaller regions, as governors and military commanders. Viscounts were appointed to assist the counts in their running of the province, and often took on judicial responsibility. The kings strictly prevented the offices of their counts and viscounts from becoming hereditary, in order to consolidate their po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Owen MacCarthy Reagh, 12th Prince Of Carbery
Owen MacCarthy Reagh () (1520–1594) was the 16th Prince of Carbery from 1576 to 1593. He belonged to the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty. Owen was commonly referred to as "Sir" Owen MacCarthy (McCartie) in the English court records. Owen was the fourth son of Donal MacCarthy Reagh, 12th Prince of Carbery (r. 1505–1531) by his wife Lady Eleanor, daughter of Gerald FitzGerald, 8th Earl of Kildare, Owen became tánaiste in 1567, when his next elder brother Donogh MacCarthy Reagh, 15th Prince of Carbery (r. 1567–1576), father of Florence MacCarthy, succeeded their elder brother Cormac na Haoine MacCarthy Reagh, 13th Prince of Carbery (r. 1531–1567). He was succeeded by the son of his brother Cormac na Haoine, Donal of the Pipes, 17th Prince of Carbery. Career Owen did not support Gerald FitzGerald, 15th Earl of Desmond during the Second Desmond Rebellion. Instead he allowed his forces of around 1200 fighting men to be employed by the Crown, and thus prevented much of the destru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Tuite MacCarthy
Nicholas Tuite MacCarthy (May 1769 – 3 May 1833) was a renowned Jesuit preacher in late-18th- and early-19th-century France. He was known also as the Abbé de Lévignac. He was of noble birth, being a member of the MacCarthy Reagh family of Springhouse, Bansha, County Tipperary in Ireland who were Princes of Carbery and who subsequently became Counts of Toulouse in France. Biography Nicholas was born in Dublin, but left Ireland for Toulouse with his parents when he was four years of age. Over the succeeding six decades he dedicated his life to preaching throughout France and Europe. Tuite MacCarthy, who grew up at the family's palatial townhouse at 3, Rue Mage in the city of Toulouse was profoundly affected by the death in childbirth of a sister-in-law, wife of Viscount (later Count) Robert MacCarthy, deputy for the Drome in 1815–20. He then resolved to study for the priesthood, which he did, firstly in the College du Plessis, and afterwards at the Sorbonne, Paris. On account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote Ecumenism, ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patron saint, patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a Superior General of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Toulouse
The count of Toulouse (, ) was the ruler of county of Toulouse, Toulouse during the 8th to 13th centuries. Originating as vassals of the kingdom of the Franks, Frankish kings, the hereditary counts ruled the city of Toulouse and its surrounding County of Toulouse, county from the late 9th century until 1270. The counts and other family members were also at various times counts of Quercy, Rouergue, Albi, and Nîmes, and sometimes margraves (military defenders of the Holy Roman Empire) of Septimania and Provence. Count Raymond IV, Count of Toulouse, Raymond IV founded the Crusader state of County of Tripoli, Tripoli, and his descendants were also counts there. They reached the zenith of their power during the 11th and 12th centuries, but after the Albigensian Crusade the county fell to the kingdom of France, nominally in 1229 and ''de facto'' in 1271. Later the title was revived for Louis Alexandre, Count of Toulouse, a bastard of Louis XIV (1678–1737). History Carolingian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Paris. It is the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, fourth-largest city in France after Paris, Marseille and Lyon, with 511,684 inhabitants within its municipal boundaries (2022); its Functional area (France), metropolitan area has a population of 1,513,396 inhabitants (2022). Toulouse is the central city of one of the 22 Métropole, metropolitan councils of France. Between the 2014 and 2020 censuses, its metropolitan area was the third fastest growing among metropolitan areas larger than 500,000 inhabitants in France. Toulouse is the centre of the European aerospace industry, with the headquarters of Airbus, the SPOT (satellites), SPOT satellite system, ATR ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donal Of The Pipes, 17th Prince Of Carbery
Donal na Pipi MacCarthy Reagh (Irish language, Irish: ''Domhnall na bpíopaí Mac Cárthaigh Riabhach'') (died 10 October 1612) was the 17th Prince of Carbery from 1593 to 1606, when he surrendered the principality to the English Crown under the policy of Surrender and regrant, Surrender and Regrant. He belonged to the MacCarthy Reagh dynasty as a son of Cormac na Haoine MacCarthy Reagh, Cormac na Haoine, the 13th Prince of Carbery. His epithet "of the Pipes" (''na bpíopaí'' in Irish) originates from when several English wine cask units, pipes of wine washed up on the beach at Burren, which was traditionally believed to be a sign of good fortune for him. Birth and origins Donal was born the eldest son of Cormac na Haoine MacCarthy Reagh, Cormac MacCarthy Reagh and his wife Julia MacCarthy. His father was the 13th Prince of Carbery. His father's family were the MacCarthy Reagh, a Gaelic Irish dynasty that branched from the MacCarthy Mor dynasty, MacCarthy-Mor line with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |