|
MEID
A mobile equipment identifier (MEID) is a globally unique number identifying a physical piece of CDMA2000 mobile station equipment. The number format is defined by th3GPP2 report S.R0048but in practical terms, it can be seen as an International Mobile Equipment Identity, IMEI but with hexadecimal digits. An MEID is 56 bits long (14 hexadecimal digits). It consists of three fields, including an 8-bit regional code (RR), a 24-bit manufacturer code, and a 24-bit manufacturer-assigned serial number. The check digit (CD) is not considered part of the MEID. The MEID was created to replace electronic serial numbers (ESNs), whose virgin form was exhausted in November 2008. As of TIA/EIA/IS-41 Revision D and TIA/EIA/IS-2000 Rev C, the ESN is still a required field in many messages—for compatibility, devices with an MEID can use a pseudo-ESN (pESN), which is a manufacturer code of 0x80 (formerly reserved) followed by the least significant 24 bits of the SHA-1 hash of the MEID. MEIDs ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Serial Number
Electronic serial numbers (ESNs) were created by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to uniquely identify mobile devices, from the days of Advanced Mobile Phone System, AMPS in the United States starting in the early 1980s. The administrative role was taken over by the Telecommunications Industry Association in 1997 and is still maintained by them. ESNs are currently mainly used with CDMA phones (and were previously used by Advanced Mobile Phone System, AMPS and digital AMPS, TDMA phones), compared to International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) numbers used by all GSM phones. The first eight bits of the ESN were originally the manufacturer code, leaving 24 bits for the manufacturer to assign up to 16,777,215 codes to mobiles. To allow more than 256 manufacturers to be identified, the manufacturer code was extended to 14 bits, leaving 18 bits for the manufacturer to assign up to 262,144 codes. Manufacturer code 0x80 is reserved from assignment and is used instead as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Mobile Equipment Identity
The International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) is a numeric identifier, usually unique, for 3GPP and iDEN mobile phones, as well as some satellite phones. It is usually found printed inside the battery compartment of the phone but can also be displayed on-screen on most phones by entering the MMI Supplementary Service code *#06# on the dialpad, or alongside other system information in the settings menu on smartphone operating systems. GSM networks use the IMEI number to identify valid devices, and can stop a stolen phone from accessing the network. For example, if a mobile phone is stolen, the owner can have their network provider use the IMEI number to blocklist the phone. This renders the phone useless on that network and sometimes other networks, even if the thief changes the phone's SIM card. Devices without a SIM card slot or eSIM capability usually do not have an IMEI, except for certain early Sprint LTE devices such as the Samsung Galaxy Nexus and S III which e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
The international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI; ) is a number that uniquely identifies every user of a cellular network. It is stored as a field and is sent by the mobile device to the network. It is also used for acquiring other details of the mobile in the home location register (HLR) or as locally copied in the visitor location register. To prevent eavesdroppers from identifying and tracking the subscriber on the radio interface, the IMSI is sent as rarely as possible and a randomly-generated TMSI is sent instead. The IMSI is used in ''any'' mobile network that interconnects with other networks. For GSM, UMTS and LTE networks, this number was provisioned in the SIM card and for cdmaOne and CDMA2000 networks, in the phone directly or in the R-UIM card (the CDMA equivalent of the SIM card). Both cards have been superseded by the UICC. An IMSI is usually presented as a 15-digit number but can be shorter. For example, MTN South Africa's old IMSIs that are still in us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDMA2000
CDMA2000 (also known as C2K or IMT Multi‑Carrier (IMT‑MC)) is a family of 3G mobile technology standards for sending voice, data, and signaling data between mobile phones and cell sites. It is developed by 3GPP2 as a backwards-compatible successor to second-generation cdmaOne (IS-95) set of standards and used especially in North America and South Korea. CDMA2000 compares to UMTS, a competing set of 3G standards, which is developed by 3GPP and used in Europe, Japan, China, and Singapore. The name CDMA2000 denotes a family of standards that represent the successive, evolutionary stages of the underlying technology. These are: *Voice: CDMA2000 1xRTT, 1X Advanced *Data: CDMA2000 1xEV-DO ( Evolution-Data Optimized): Release 0, Revision A, Revision B, Ultra Mobile Broadband (UMB) All are approved radio interfaces for the ITU's IMT-2000. In the United States, ''CDMA2000'' is a registered trademark of the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA-USA). 1X CDMA200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Technology
Mobile technology is the technology used for Cellular network, cellular communication. Mobile technology has evolved rapidly over the past few years. Since the start of this millennium, a standard mobile device has gone from being no more than a simple two-way pager to being a mobile phone, GPS navigation device, an embedded web browser and instant messaging client, and a handheld gaming console. Many experts believe that the future of computer technology rests in mobile computing with wireless networking. Mobile computing by way of tablet computers is becoming more popular. Tablets are available on the 3G and 4G networks. Mobile communication convergence Source: Nikola Tesla laid the theoretical foundation for wireless communication in 1890. Guglielmo Marconi, known as the father of radio, first transmitted wireless signals two miles away in 1894. Mobile technology gave human society great change. The use of mobile technology in government departments can also be traced back to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Identification Number
The mobile identification number (MIN) or mobile subscription identification number (MSIN) refers to the 10- digit unique number that a wireless carrier uses to identify a mobile phone, which is the last part of the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI). The MIN is a number that uniquely identifies a mobile phone working under TIA standards for cellular and PCS technologies (e.g. EIA/TIA–553 analog, IS–136 TDMA, IS–95 or IS-2000 CDMA). MIN usage became prevalent for mobile number portability to switch providers. It can also be called the MSID (Mobile Station ID) or IMSI_S (Short IMSI). MIN derivation The mobile identification number (MIN) is a number that is derived from the 10-digit directory telephone number assigned to a mobile station. The rules for deriving the MIN from the 10-digit telephone number are given in the IS-95 standard. MIN1 is the first or least significant 24 binary digits of the MIN. MIN2 is the second part of the MIN containing the 10 most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
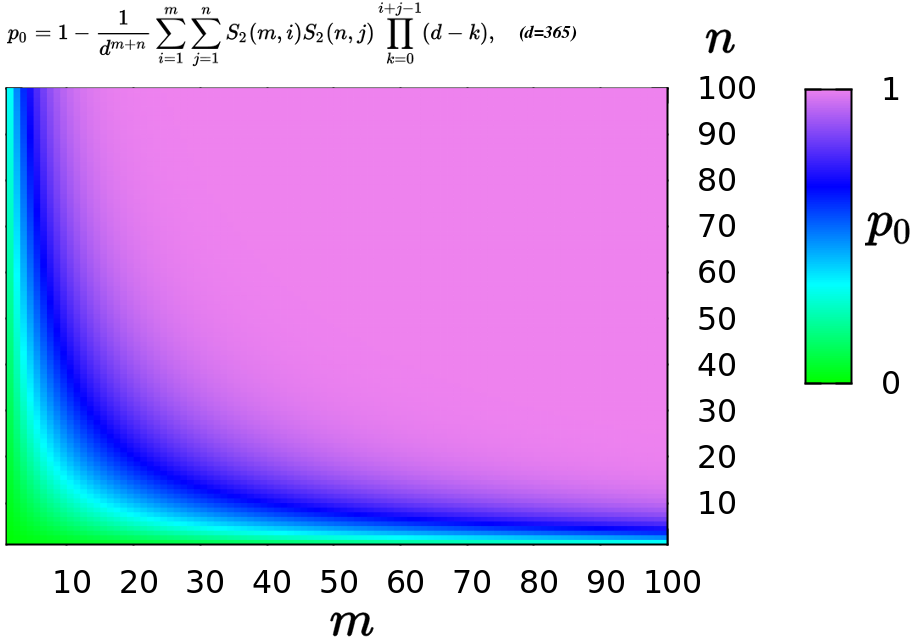
Birthday Paradox
In probability theory, the birthday problem asks for the probability that, in a set of randomly chosen people, at least two will share the same birthday. The birthday paradox is the counterintuitive fact that only 23 people are needed for that probability to exceed 50%. The birthday paradox is a veridical paradox: it seems wrong at first glance but is, in fact, true. While it may seem surprising that only 23 individuals are required to reach a 50% probability of a shared birthday, this result is made more intuitive by considering that the birthday comparisons will be made between every possible pair of individuals. With 23 individuals, there are = 253 pairs to consider. Real-world applications for the birthday problem include a cryptographic attack called the birthday attack, which uses this probabilistic model to reduce the complexity of finding a Collision attack, collision for a hash function, as well as calculating the approximate risk of a hash collision existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OTASP
An over-the-air update (or OTA update), also known as over-the-air programming (or OTA programming), is an update to an embedded system that is delivered through a wireless network, such as Wi-Fi or a cellular network. These embedded systems include mobile phones, tablets, set-top boxes, cars and telecommunications equipment. OTA updates for cars and internet of things devices can also be called firmware over-the-air (FOTA). Various components may be updated OTA, including the device's operating system, applications, configuration settings, or parameters like encryption keys. Terminology The term ''over-the-air update'' applies specifically to embedded systems, rather than non-embedded systems like computers. Before OTA updates, embedded devices could only be flashed through direct physical access (with a JTAG) or wired connections (usually through USB or a serial port). Purpose Over-the-air delivery may allow updates to be distributed at larger scales, reduce the cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar Code
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, Machine-readable data, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers, of which there are several types. Later, two-dimensional (2D) variants were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons and other patterns, called ''2D barcodes'' or ''matrix codes'', although they do not use bars as such. Both can be read using purpose-built 2D optical scanners, which exist in a few different forms. Matrix codes can also be read by a digital camera connected to a microcomputer running software that takes a photographic image of the barcode and analyzes the image to deconstruct and decode the code. A mobile device with a built-in camera, such as a smartphone, can function as the latter type of barcode reader usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huawei
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ("Huawei" sometimes stylized as "HUAWEI"; ; zh, c=华为, p= ) is a Chinese multinational corporationtechnology company in Longgang, Shenzhen, Longgang, Shenzhen, Guangdong. Its main product lines include telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics, electric vehicle self-driving car, autonomous driving systems, and rooftop solar power products. The company was founded in Shenzhen in 1987 by Ren Zhengfei, a veteran officer of the People's Liberation Army (PLA). Initially focused on manufacturing stored program control, phone switches, Huawei has expanded to more than 170 countries to include building telecommunications network infrastructures, providing equipment, operational and consulting services, and manufacturing communications devices for the consumer market. It overtook Ericsson in 2012 as the largest telecommunications equipment manufacturer in the world. Huawei surpassed Apple Inc., Apple and Samsung Electronics, Samsung, in 2018 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luhn
The Luhn algorithm or Luhn formula (creator: IBM scientist Hans Peter Luhn), also known as the " modulus 10" or "mod 10" algorithm, is a simple check digit formula used to validate a variety of identification numbers. The algorithm is in the public domain and is in wide use today. It is specified in ISO/IEC 7812-1. It is not intended to be a cryptographically secure hash function; it was designed to protect against accidental errors, not malicious attacks. Most credit card numbers and many government identification numbers use the algorithm as a simple method of distinguishing valid numbers from mistyped or otherwise incorrect numbers. Description The check digit is computed as follows: # Drop the check digit from the number (if it's already present). This leaves the payload. # Start with the payload digits. Moving from right to left, double every second digit, starting from the last digit. If doubling a digit results in a value > 9, subtract 9 from it (or sum its digits). # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |