|
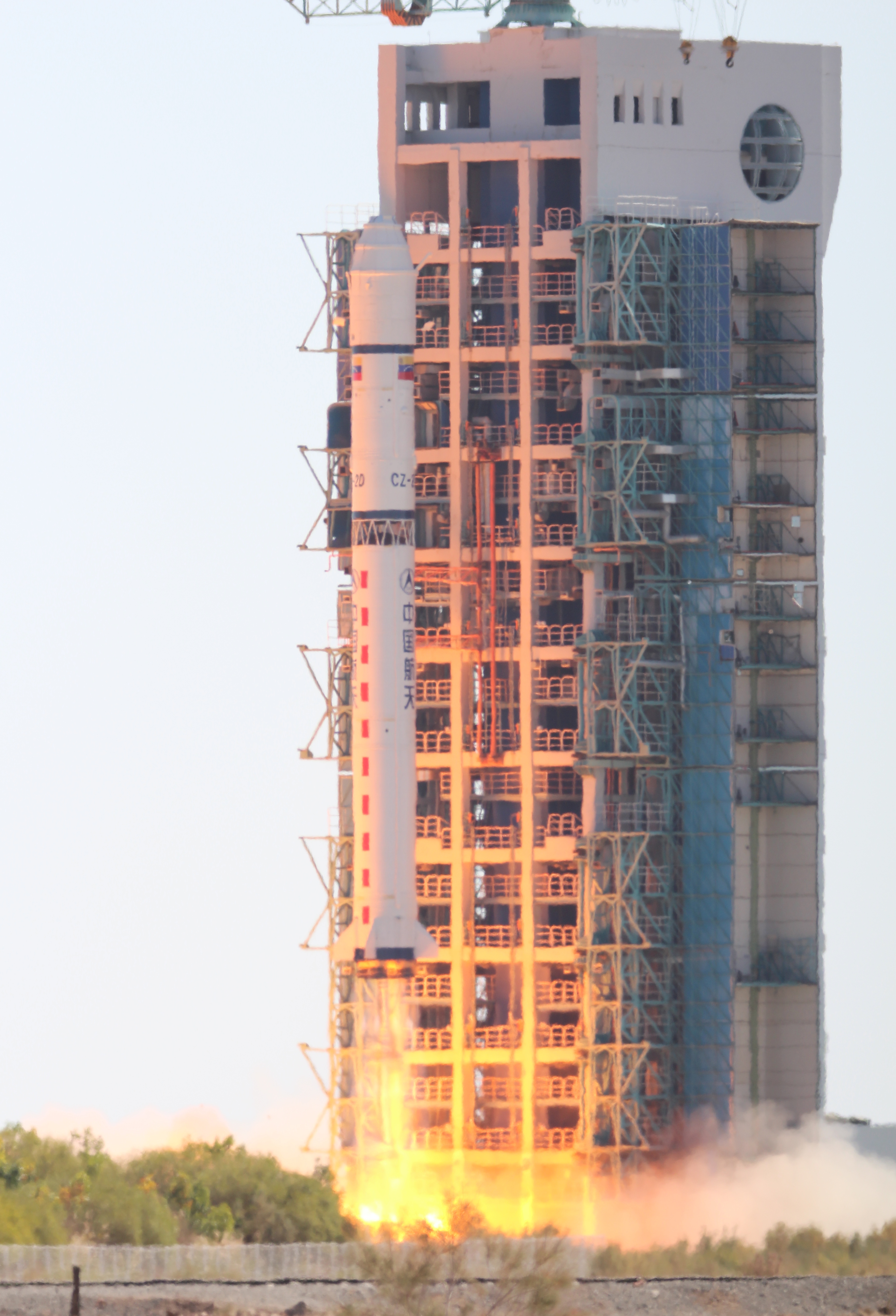
Long March 2D
The Long March 2D (), also known as the Chang Zheng 2D, CZ-2D and LM-2D, is a Chinese two-stage orbital carrier rocket mainly used for launching LEO and SSO satellites. It is manufactured by the Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology (SAST). It is mainly launched from areas LA-2B and LA-4 at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. The Long March 2D made its maiden flight on 9 August 1992. It was initially used to launch FSW-2 and FSW-3 reconnaissance satellites. Unlike all other members of the Long March 2 rocket family, the Long March 2D is a two-stage version of the Long March 4 The Long March rockets are a family of expendable launch system rockets operated by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation. The rockets are named after the Chinese Red Army's 1934–35 Long March military retreat during the Ch ... launch vehicle. Launch statistics List of launches The Long March 2D made its maiden flight on 9 August 1992. References Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VRSS-1
VRSS-1 (Venezuelan Remote Sensing Satellite-1), also known as (Satellite) Francisco Miranda, is the first Venezuelan remote sensing satellite, and the second Venezuelan satellite after VENESAT-1. It will be used to study the territory of Venezuela and help with planning, agriculture and disaster recovery. It was built and launched by the Chinese and has been named after Venezuelan revolutionary Francisco de Miranda. Satellite The satellite was built after a contract between Venezuela and China was signed in Caracas on 26 May 2011, and follows from their previous collaboration on VENESAT-1. The contract, worth $144.8 million USD, included $67.8 million for the satellite, $22m for the launch, $16m for the ground station in Venezuela and $22m for software. The main contractor is China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation and the satellite is based on the CAST 2000 bus developed by the China Academy of Space Technology. One source posits that VRSS-1 is based upon the Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never more than about one-third of the radius of Earth. The term ''LEO region'' is also used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. All crewed space stations to date have been within LEO. From 1968 to 1972, the Apollo program's lunar missions sent humans beyond LEO. Since the end of the Apollo program, no human spaceflights have been beyond LEO. Defining characteristics A wide variety of sources define LEO in terms of altitude. The altitude of an object in an elliptic orbit can vary significantly along the orbit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiyan (satellite)
Shiyan (SY, ) is a Chinese experimental satellite program consisting of a variety of test satellites. Given the Classified information, classified nature of the satellites, Chinese government statements regarding the missions of Shiyan satellites follow the common refrain of agricultural monitoring and space environment observation — the same offered for other classified programs such as the Tongxin Jishu Shiyan, Yaogan, and Shijian programs. Alternatively named Tansuo satellites, Shiyan satellites occupy varying orbits including Low Earth orbit, low Earth, Polar orbit, polar Sun-synchronous orbit, sun-synchronous, Geosynchronous orbit, geosynchronous, and Highly elliptical orbit, highly-elliptical orbits and are believed to accomplish a diverse set of missions from rendezvous proximity operations (RPO) to Satellite imagery, earth imaging. Though similarly named, the Shiyan satellite program is not to be confused with the separate Shijian, Shijian satellite program. Notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaogan
Yaogan () is the cover name used by the People's Republic of China to refer to its military reconnaissance satellites. Yaogan satellites are largely known to primarily support the People's Liberation Army's Strategic Support Force (PLASSF), formerly the Aerospace Reconnaissance Bureau of the Second Department of the General Staff. Yaogan satellites are the successor program to the Fanhui Shi Weixing ( FSW) recoverable reconnaissance satellite program but, unlike its predecessor, includes a variety of classes utilizing various means of remote sensing such as optical reconnaissance, synthetic-aperture radar (SAR), and electronic intelligence (ELINT) for maritime surveillance. Yaogan satellites have been launched from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center (TSLC) in Shanxi province, the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center (JSLC) in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, and the Xichang Satellite Launch Center (XSLC) in Sichuan province. Although individual Yaogan satellites are often refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shijian
Shijian (, abbr. "SJ") is a series of satellites built and operated by the People's Republic of China. Some Shijian-series satellites have drawn significant concerns from the United States government and space observers who cite unannounced launches, undisclosed sub-satellites deployed in orbit, unusual orbital maneuvers, and demonstrated rendezvous proximity operations (RPO) including the close inspection and towing of other satellites. Little is known about the series and what differentiates it from other experimental satellite series launched by China such as the Chuangxin () series or Shiyan () series. The China Aerospace Studies Institute of the United States Air Force asserts that Shiyan-series satellites play an earlier role in the systems development process testing various new technologies on a single bus while Shijan-series satellites are used to develop operational best practices and optimize the technologies previously tested on Shiyan-series satellites. In this regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 2D Launching VRSS-1 Afar
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France * Long, Washington, United States People * Long (surname) * Long (surname 龍) (Chinese surname) Fictional characters * Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series Sports * Long, a fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially stock markets * Lòng, name for a laneway in Shanghai * Long in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 2D Launching Off Pad With VRSS-1
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France * Long, Washington, United States People * Long (surname) * Long (surname 龍) (Chinese surname) Fictional characters * Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series Sports * Long, a fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially stock markets * Lòng, name for a laneway in Shanghai * Long in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 2
Long March 2 rocket family or Chang Zheng 2 rocket family as in Chinese pinyin is an expendable launch system operated by the People's Republic of China. The rockets use the abbreviations LM-2 family for export, and CZ-2 family within China, as "Chang Zheng" means "Long March" in Chinese pinyin. They are part of the larger Long March rocket family. Development and design falls mostly under the auspices of the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT). History Long March 2 was the original model in the Long March 2 rocket family, which was derived from China's first ICBM, the DF-5. The development work began in 1970. The first rocket was launched on November 5, 1974, but the launch failed. After the failed first launch of Long March 2, its design was slightly modified and designated as Long March 2A. Long March 2A was successfully launched in 1975. The production of the Long March 2A ended in 1979. Long March 2C and Long March 2D's first launches occurred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
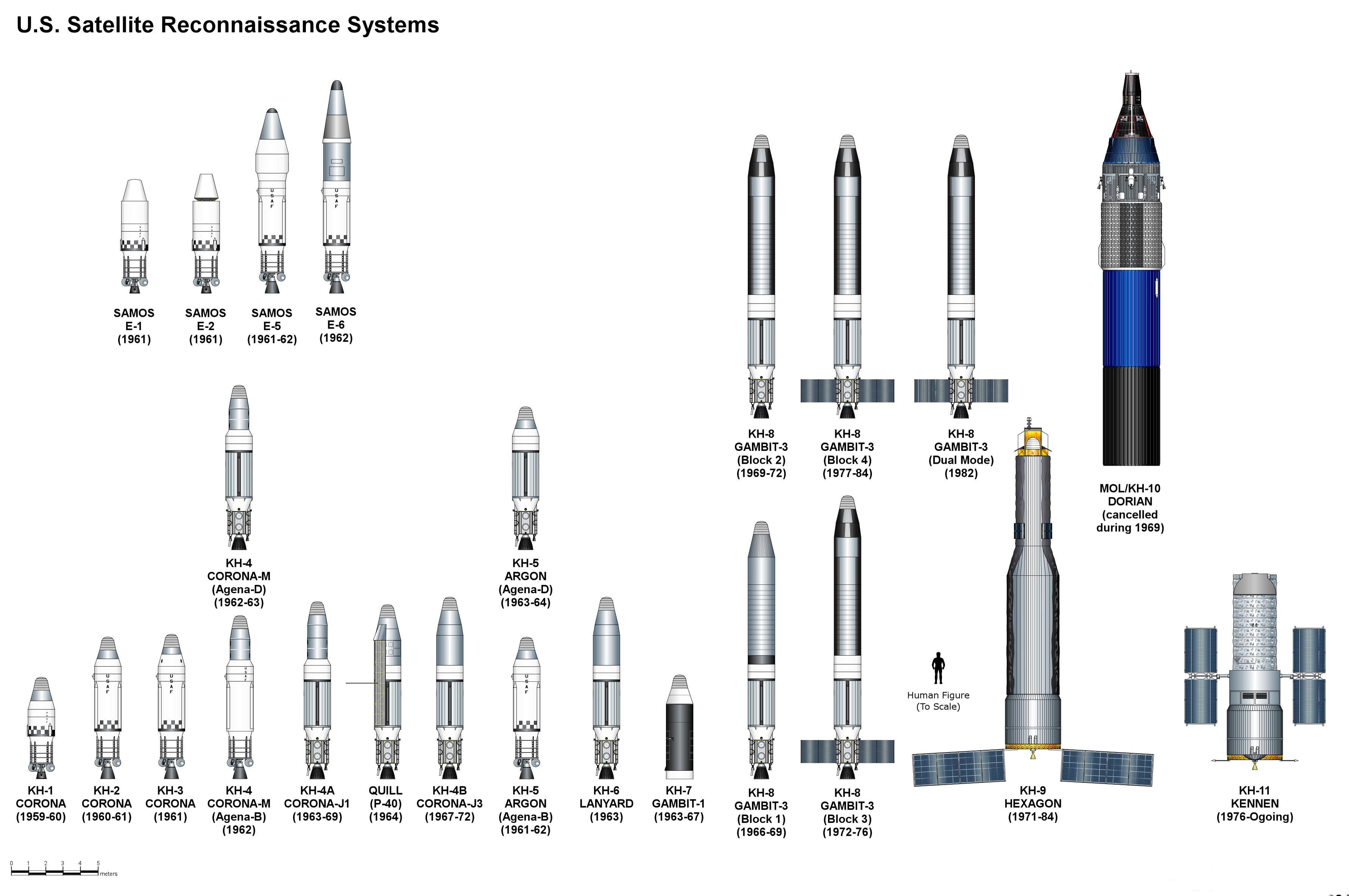
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassified o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)