|
Line Of Beauty
Line of beauty is a term and a theory in art or aesthetics used to describe an S-shaped curved line (a serpentine line) appearing within an object, as the boundary line of an object, or as a virtual boundary line formed by the composition of several objects. This theory originated with William Hogarth (18th-century English painter, satirist, and writer), and is an essential part of Hogarth's theory of aesthetics as described in his 1753 book '' Analysis of Beauty''. According to this theory, S-shaped curved lines signify liveliness and activity and excite the attention of the viewer as contrasted with straight lines, parallel lines, or right-angled intersecting lines, which signify stasis, death, or inanimate objects. In contrast to grand compositional lines, which are regularly found in Baroque or Rococo art, the serpentine line is not primarily dictating the whole composition of a canvas. Instead, the line should be understood as being found in specific subject matter, like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine Lines From William Hogarth's The Analysis Of Beauty
Serpentine may refer to: Shapes * Serpentine shape, a shape resembling a serpent * Serpentine curve, a mathematical curve * Serpentine, a type of riding figure Science and nature * Serpentine subgroup, a group of minerals * Serpentinite, a type of rock * Serpentine soil, soil derived from serpentinite * Serpentine (alkaloid), a chemical compound * Serpentine receptor, a protein in cellular membranes * Serpentine powder, a type of gunpowder Objects * Serpentine lock, a component of matchlock pistols * Serpentine (cannon), a military weapon * Serpentine belt, an automotive component * Serpentine streamer A serpentine streamer is a type of party accessory made out of long strips of paper, wound up in a roll, which form snakelike patterns in the air when thrown. Serpentine streamers can also be used as party decorations, usually hung up from the cei ..., a party accessory Places Australia * Serpentine, Victoria, Australia, a town * Serpentine, Western Australia, a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesthetics
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed through judgments of taste. Aesthetics covers both natural and artificial sources of experiences and how we form a judgment about those sources. It considers what happens in our minds when we engage with objects or environments such as viewing visual art, listening to music, reading poetry, experiencing a play, watching a fashion show, movie, sports or even exploring various aspects of nature. The philosophy of art specifically studies how artists imagine, create, and perform works of art, as well as how people use, enjoy, and criticize art. Aesthetics considers why people like some works of art and not others, as well as how art can affect moods or even our beliefs. Both aesthetics and the philosophy of art try to find answers for what exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine Shape
A serpentine shape is any of certain curved shapes of an object or design, which are suggestive of the shape of a snake (the adjective "serpentine" is derived from the word ''serpent''). Serpentine shapes occur in architecture, in furniture, and in mathematics. In architecture and urban design The serpentine shape is observed in many architectural settings. It may provide strength, as in serpentine walls, it may allow the facade of a building to face in multiple directions, or it may be chosen for purely aesthetic reasons. *At the University of Virginia, serpentine walls (crinkle crankle walls) extend down the length of the main lawn at the University of Virginia and flank both sides of the rotunda. They are one of the many structures Thomas Jefferson created that combine aesthetics with utility. The sinusoidal path of the wall provides strength against toppling over, allowing the wall to be only a single brick thick. *At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Baker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects", and he is perhaps best known for his series ''A Harlot's Progress'', ''A Rake's Progress'' and '' Marriage A-la-Mode''. Knowledge of his work is so pervasive that satirical political illustrations in this style are often referred to as "Hogarthian". Hogarth was born in London to a lower-middle-class family. In his youth he took up an apprenticeship with an engraver, but did not complete the apprenticeship. His father underwent periods of mixed fortune, and was at one time imprisoned in lieu of outstanding debts, an event that is thought to have informed William's paintings and prints with a hard edge. Influenced by French and Italian painting and engraving, Hogarth's works are mostly sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Beauty
''The Analysis of Beauty'' is a book written by the 18th-century artist and writer William Hogarth, published in 1753, which describes Hogarth's theories of visual beauty and grace in a manner accessible to the common man of his day. The "Line of Beauty" Prominent among Hogarth's ideas of beauty was the theory of the Line of Beauty; an S-shaped (serpentine) curved line that excited the attention of the viewer and evoked liveliness and movement. ''The Analysis of Beauty'' formed the intellectual centerpiece of what the historian Ernst Gombrich described as Hogarth's "grim campaign against the fashionable taste", which Hogarth himself described as his "War with the Connoisseurs". Six principles In ''The Analysis of Beauty'' Hogarth implements six principles that independently affect beauty. Although he concurs that those principles have an effect, he is not determinate on their specific influence. The first principle of beauty Hogarth describes is fitness, which is not in it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and ''trompe-l'œil'' frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement. The Rococo style began in France in the 1730s as a reaction against the more formal and geometric Louis XIV style. It was known as the "style Rocaille", or "Rocaille style". It soon spread to other parts of Europe, particularly northern Italy, Austria, southern Germany, Central Europe and Russia. It also came to influence the other arts, particularly sculpture, furniture, silverware, glassware, painting, music, and theatre. Although originally a secular style primarily used for interiors of private residences, the Rococo had a spiritual aspect to it which led to its widespread use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer Street And Gin Lane
''Beer Street'' and ''Gin Lane'' are two prints issued in 1751 by English artist William Hogarth in support of what would become the Gin Act. Designed to be viewed alongside each other, they depict the evils of the consumption of gin as a contrast to the merits of drinking beer. At almost the same time and on the same subject, Hogarth's friend Henry Fielding published ''An Inquiry into the Late Increase in Robbers''. Issued together with ''The Four Stages of Cruelty'', the prints continued a movement started in ''Industry and Idleness'', away from depicting the laughable foibles of fashionable society (as he had done with '' Marriage A-la-Mode'') and towards a more cutting satire on the problems of poverty and crime. On the simplest level, Hogarth portrays the inhabitants of Beer Street as happy and healthy, nourished by the native English ale, and those who live in Gin Lane as destroyed by their addiction to the foreign spirit of gin; but, as with so many of Hogarth's works, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-curve (art)
In the visual arts, an S-curve is an '' S''-shaped curve that can serves a wide variety of compositional purposes. The term is usually applied to the standing human figure bending first one way and then back the other. It may also be applied more generally, for example in landscape painting and photography. Human figure In Ancient Greek and Roman sculpture, the S-curve is a traditional art concept where the figure's body and posture is depicted like a sinuous or serpentine manner. It is related to and is an extension of the art term of contrapposto which is when a figure is depicted slouching or placing one's weight and thus center of gravity to one side. However, the S Curve involves more of the body than the contrapposto, and is therefore considered to be a more advanced technical development. The "S Curve" concept was probably invented by the famous Greek sculptor Praxiteles, son of Kifissodotos, who lived in the 4th century BC. The Indian tribhanga ("three bend") pose is si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
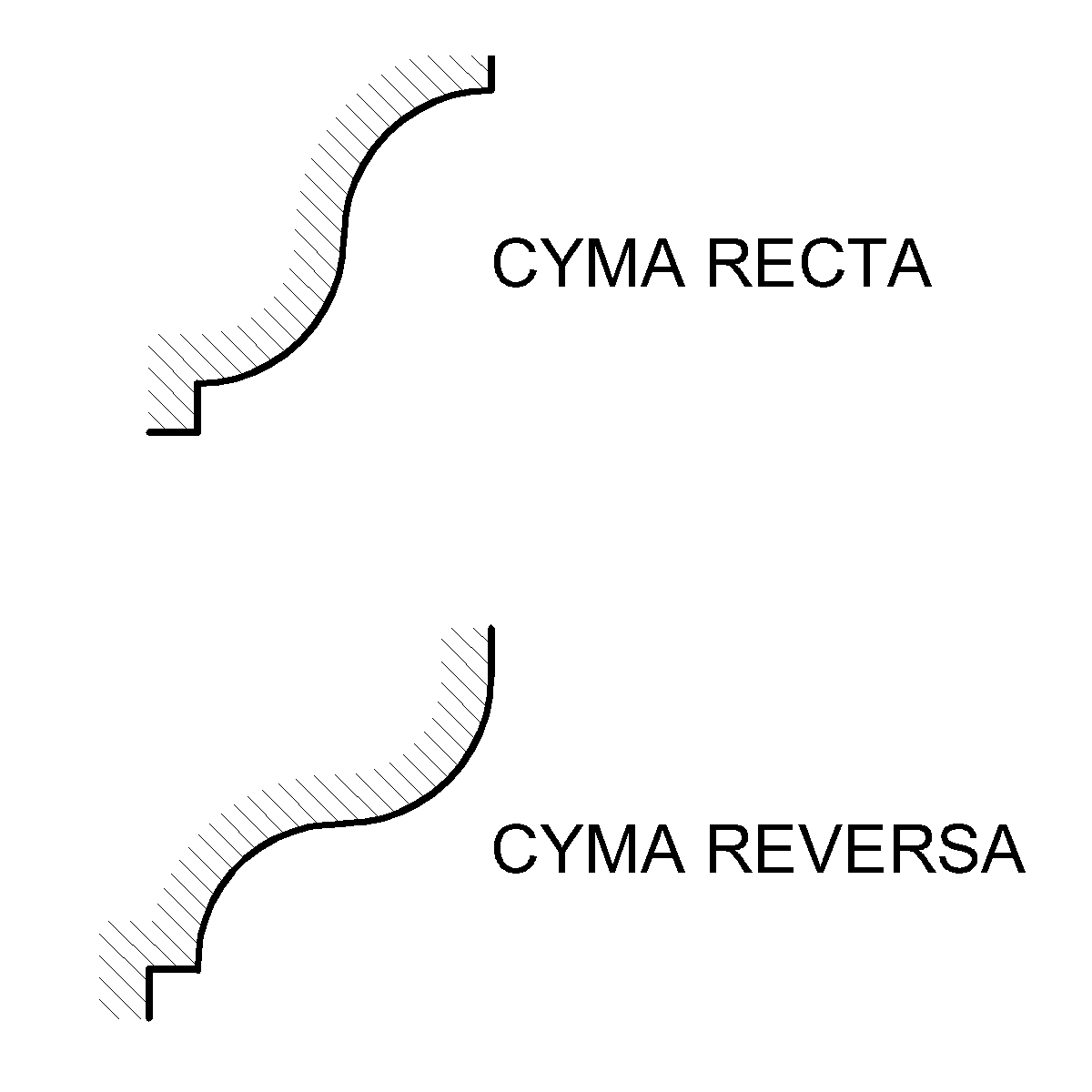
Ogee
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or ''vice versa'', have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions (and have tangents that are approximately parallel). First seen in textiles in the 12th century, the use of ogee elements—in particular, in the design of arches—has been said to characterise various Gothic and Gothic Revival architectural styles. The shape has many such uses in architecture from those periods to the present day, including in the ogee arch in these architectural styles, where two ogees oriented as mirror images compose the sides of the arch, and in decorative molding designs, where single ogees are common profiles (see opening image) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesthetic Beauty
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed through judgments of taste. Aesthetics covers both natural and artificial sources of experiences and how we form a judgment about those sources. It considers what happens in our minds when we engage with objects or environments such as viewing visual art, listening to music, reading poetry, experiencing a play, watching a fashion show, movie, sports or even exploring various aspects of nature. The philosophy of art specifically studies how artists imagine, create, and perform works of art, as well as how people use, enjoy, and criticize art. Aesthetics considers why people like some works of art and not others, as well as how art can affect moods or even our beliefs. Both aesthetics and the philosophy of art try to find answers for what exact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art History
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today, art history examines broader aspects of visual culture, including the various visual and conceptual outcomes related to an ever-evolving definition of art. Art history encompasses the study of objects created by different cultures around the world and throughout history that convey meaning, importance or serve usefulness primarily through visual representations. As a discipline, art history is distinguished from art criticism, which is concerned with establishing a relative artistic value upon individual works with respect to others of comparable style or sanctioning an entire style or movement; and art theory or "philosophy of art", which is concerned with the fundamental nature of art. One branch of this area of study is aesthetics, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |