|
Liaoyang Province
Manchuria under Yuan rule refers to the Yuan dynasty's rule over Manchuria, corresponding to modern Northeast China and Outer Manchuria (including Sakhalin), from 1271 to 1368. Mongol rule over Manchuria was established after the Mongol Empire's conquest of the Jin dynasty and the Eastern Xia dynasty in the early 13th century. It became a part of the Yuan dynasty of China led by Kublai Khan in 1271. During the Yuan, it was administered as Liaoyang province. Even after the overthrow of the Yuan dynasty by the Ming dynasty in 1368, Manchuria was still controlled by the Northern Yuan dynasty for almost 20 years, until it was conquered by the Ming during its campaign against Naghachu and put under Ming rule. History Conquest of Manchuria In 1211, after the conquest of Western Xia, Genghis Khan, the founder of the Mongol Empire mobilized an army to conquer the Jin dynasty, which controlled much of North China including Manchuria. They successfully destroyed the Jin forts there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan had been enthroned with the Han-style title of Emperor in 1206 and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other Mongol-led khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North China
North China, or Huabei () is a List of regions of China, geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north of the Qinling–Huaihe Line, with its heartland in the North China Plain. In modern times, the area has shifted in terms of socio-political and economic composition. Nowadays unique, embracing a North Chinese culture, it is influenced by Marxism, Soviet Union, Soviet systems of industry while preserving a traditional Chinese indigenous culture. Agriculturally, the region cultivates wheat. Most inhabitants here speak variants of Northern Chinese languages such as Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin, which includes Beijing dialect and its cousin variants. The Beijing dialect is largely the basis of Standard Chinese (or Standard Mandarin), the official language of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Jin Chinese and Mongolian language, Mongolian ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furs
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket that keeps the animal warm. The fur of mammals has many uses: protection, sensory purposes, waterproofing, and camouflaging, with the primary usage being thermoregulation. The types of hair include * ''definitive'', which may be shed after reaching a certain length; * ''vibrissae'', which are sensory hairs and are most commonly whiskers; * ''pelage'', which consists of guard hairs, under-fur, and awn hair; * '' spines'', which are a type of stiff guard hair used for defense in, for example, porcupines; * ''bristles'', which are long hairs usually used in visual signals, such as the mane of a lion; * ''velli'', often called "down fur", which insulates newborn mammals; and * ''wool'', which is long, soft, and often curly. Hair length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
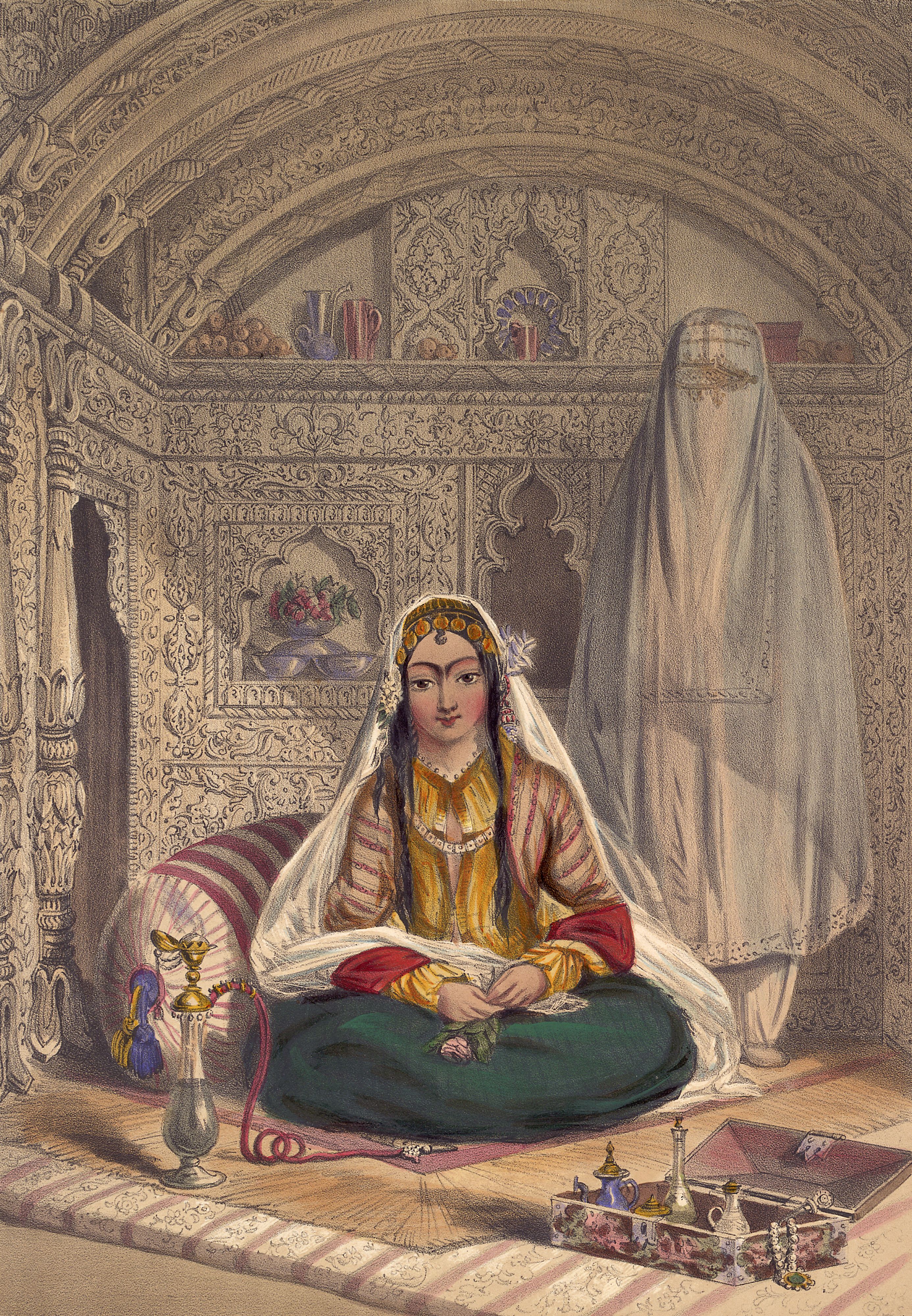
Harem
Harem (Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic servants, and other unmarried female relatives. In harems of the past, slave concubines were also housed in the harem. In former times some harems were guarded by eunuchs who were allowed inside. The structure of the harem and the extent of monogamy or polygamy has varied depending on the family's personalities, socio-economic status, and local customs. Similar institutions have been common in other Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations, especially among royal and upper-class families, and the term is sometimes used in other contexts. In traditional Persian residential architecture the women's quarters were known as ''andar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
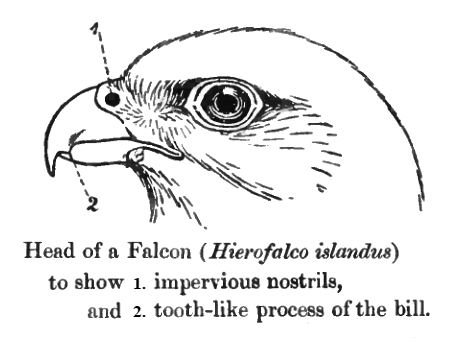
Falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene. Adult falcons have thin, tapered wings, which enable them to fly at high speed and change direction rapidly. Fledgling falcons, in their first year of flying, have longer flight feathers, which make their configuration more like that of a general-purpose bird such as a broad wing. This makes flying easier while learning the exceptional skills required to be effective hunters as adults. The falcons are the largest genus in the Falconinae subfamily of Falconidae, which itself also includes another subfamily comprising caracaras and a few other species. All these birds kill with their beaks, using a tomial "tooth" on the side of their beaks—unlike the hawks, eagles, and other birds of prey in the Accipitridae, which use their feet. The largest fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungusic Peoples
Tungusic peoples are an ethno-linguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia and Northeast Asia. The Tungusic phylum is divided into two main branches, northern (Evenic or Tungus) and southern ( Jurchen– Nanai). An intermediate group ( Oroch– Udege) is sometimes recognized. Name The name ''Tungusic'' is artificial, and properly refers just to the postulated linguistic phylum (Tungusic languages). It is derived from Russian (), a Russian exonym for the Evenks (Ewenki). English usage of ''Tungusic'' was introduced by Friedrich Max Müller in the 1850s, based on earlier use of German by Heinrich Julius Klaproth. The alternative term ''Manchu–Tungus'' is also in use ( 'Tunguso-Manchurian'). The name ''Tunguska'', a region of eastern Siberia bounded on the west by the Tunguska rivers and on the east by the Pacific Ocean, has its origin from the Tungus people (Evenks). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Güyük Khan
Güyük (also Güyug;; ''c''. March 19, 1206 – April 20, 1248) was the third Khagan-Emperor of the Mongol Empire, the eldest son of Ögedei Khan and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He reigned from 1246 to 1248. Appearance According to Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, Güyük was of "medium stature, very prudent and extremely shrewd, and serious and sedate in his manners." Early life Güyük received military training and served as an officer under his grandfather Genghis Khan and later his father Ögedei Khan (after the death of Genghis in 1227). He married Oghul Qaimish of the Merkit clan. In 1233, Güyük, along with his maternal cousin Alchidai and the Mongol general Tangghud, conquered the short-lived Dongxia Kingdom of Puxian Wannu, who was a rebellious Jin official, in a few months. After the death of Güyük's uncle Tolui, Ögedei proposed that Sorghaghtani, the widow of Tolui, marry his son Güyük. Sorghaghtani declined, saying that her prime responsibility was to he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ögedei Khan
Ögedei Khagan (also Ogodei;, Mongolian: ''Ögedei'', ''Ögüdei''; – 11 December 1241) was second khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire. The third son of Genghis Khan, he continued the expansion of the empire that his father had begun. Born in 1186 AD, Ögedei fought in numerous battles during his father's rise to power. After being granted a large appanage and taking a number of wives, including Töregene, he played a prominent role in the Mongol invasion of the Khwarazmian Empire. When his older brothers Jochi and Chagatai quarrelled over strategies when besieging Gurganj, Genghis appointed Ögedei sole commander; his successful capture of the city in 1221 ensured his military reputation. He was confirmed as heir after further infighting between his elder brothers led to both being excluded from succession plans. Genghis died in 1227, and Ögedei was elected as khagan in 1229, after a two-year regency led by his younger brother Tolui. As khan, Ögedei pursued the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaoyang
Liaoyang () is a prefecture-level city of east-central Liaoning province, China, situated on the Taizi River. It is approximately one hour south of Shenyang, the provincial capital, by car. Liaoyang is home to Liaoning University's College of Foreign Studies and a number of vocational colleges. The city hosts a limited number of professional basketball and volleyball games in a modern sports facility. According to the latest statistics in 2020, the age distribution of the population in Liaoyang is as follows: 0-14 years old account for 9.83% of the population; 15-59 years old account for 62.26% of the population; 60 years old and above account for 27.91% of the population; 65 years old and above account for 27.91% of the population 19.46% of the population. History Liaoyang is one of the oldest continuously-inhabited cities in northeast China, dating back to before the Warring States period, and the site of the city has not changed ever since. Under the Yan state and the Qin an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Xia
The Eastern Xia (), also known as Dongxia, Dongzhen (東真)Warfare in Chinese History, by H. J. Van Derven, p239 or Dazhen (大真), was a short-lived kingdom established in Manchuria (today's Northeast China and Outer Manchuria) by the Jurchen warlord Puxian Wannu in 1215 during the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty. It was eventually conquered by the Mongols and its former territories were later administered by the Liaoyang province of the Yuan dynasty. History Puxian Wannu originally served the waning Jin dynasty under pressure from the Mongol Empire. While the Mongols under Genghis Khan invaded Jin, a Khitan chief Yelü Liuge (耶律留哥) revolted against the Jin dynasty in Liaodong in 1211 and made contact with the Mongol Empire in the next year. In 1214, the Jin dynasty dispatched Puxian Wannu to Liaodong, but he was defeated around Kaiyuan. While Mukhali of the Mongol Empire invaded Northern China and captured the Jin capital Zhongdu, Puxian Wannu rebelled again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puxian Wannu
Púxiān Wànnú ({{zh, t=蒲鮮萬奴, s=蒲鲜万奴, w=P'u-hsien Wan-nu) was a Jurchen warlord who established the short-lived Eastern Xia dynasty in 13th-century China. He originally served the waning Jin dynasty under pressure from the Mongol Empire. While the Mongols under Genghis Khan invaded Jin, a Khitan chief Yelü Liuge (耶律留哥) revolted against the dynasty in Liaodong in 1211 and made contact with the Mongol Empire in the next year. In 1214 Jin dispatched Puxian Wannu to Liaodong, but he was defeated around Kaiyuan. While Mukhali of the Mongol Empire invaded Northern China, Puxian Wannu rebelled against Jin and founded the Dazhen (大眞) kingdom in Dongjing (Liaoyang) in 1215. He adopted the title of Tianwang (天王 lit. ''Heavenly King'') and named his era Tiantai (天泰). As a result of an internal strife in the Eastern Liao, Yelü Liuge was expelled and sought support from Genghis. The Khitans got a counterattack from Jin and fled to Goryeo without pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebe
Jebe (or Jebei, mn, Зэв, ''Zev''; birth name: Jirqo'adai (Modern Mongolian: Zurgadai), mn, Зургаадай, ) (death: approximately 1224) was one of the most prominent Noyans (generals) of Genghis Khan. He belonged to the Besud clan, part of the Taichud tribe, which was under Targudai Khiriltug's leadership at the time of Genghis Khan. Even though Jebe was originally an enemy soldier, Genghis Khan recruited him and turned him into one of his greatest generals. Jebe played an important role in helping to expand the territory of Genghis Khan's empire. Despite playing a large role as a general for Genghis Khan, there are relatively few sources or biographies about his life. Jebe has been described as "the greatest cavalry general in history" for his unorthodox and daring maneuvers. Origin of name In 1204, during the Battle of the Thirteen Sides, an arrow wounded Genghis Khan in the neck. His loyal subordinate, Jelme, cared for him. After winning the battle, he asked th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |