|
Levantine Aurignacian
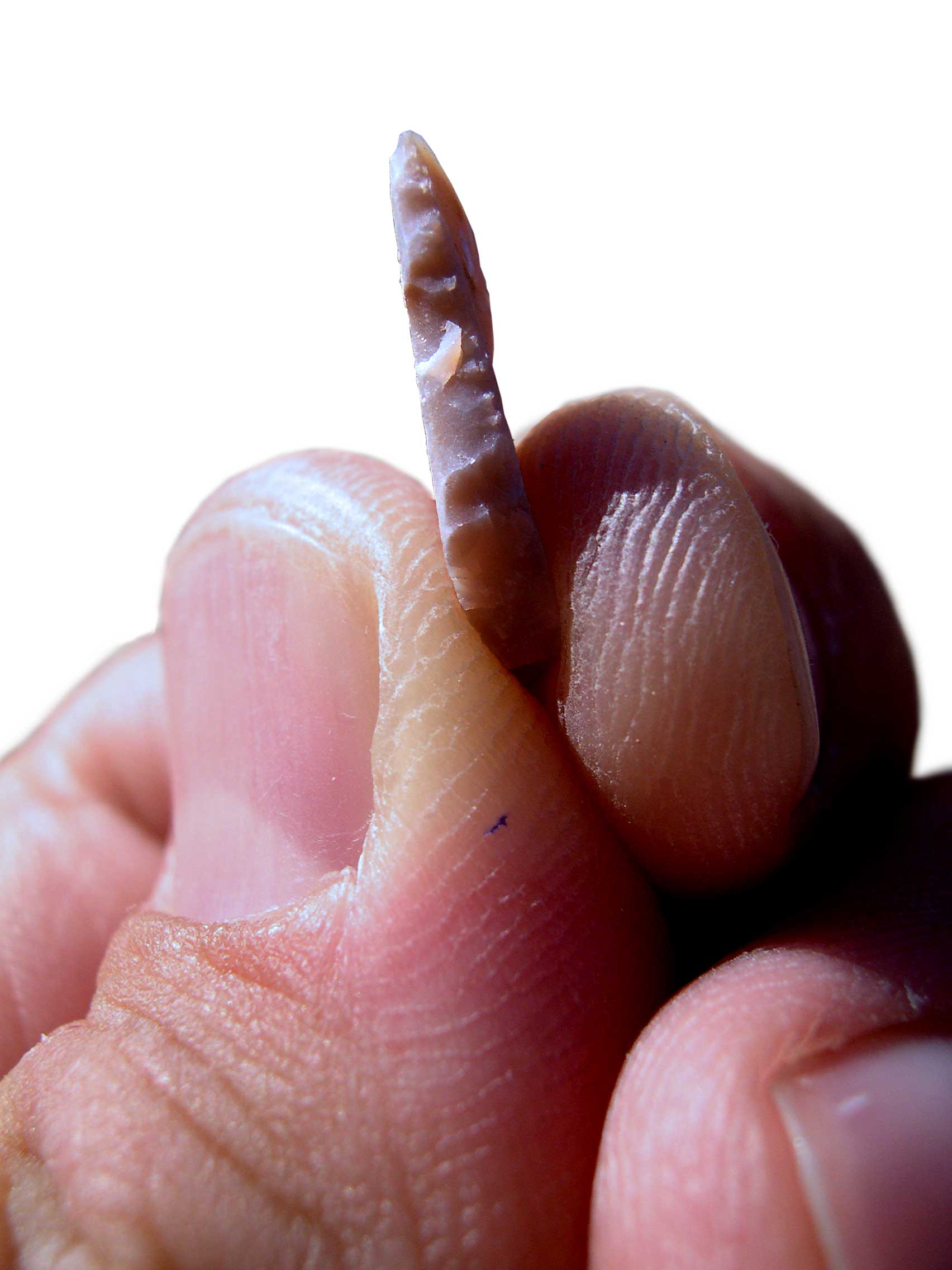
The Levantine Aurignacian (35,000-29,000 BP, calibrated, 32,000-26,000 BP, non-calibrated) is an Upper Paleolithic culture of the Near-Eastern Levant that evolved from the Emiran culture. It was named so because of the similarity of stone tools with the Aurignacian culture in Europe. The Levantine Aurignacian used to be called Lower and Upper Antelian in old sources, from the site of Wadi Antelias in Lebanon. The most important innovation in this period is the incorporation of some typical elements of Aurignacian, like some types of burins and narrow blade points that resemble the European type of Font-Yves. Levantine Aurignacian period Similarities with Aurignacian are found in the manufacture of blades and in the processing of bone tools. The Levantine Aurignacian follows chronologically the Emiran and Early Ahmarian in the same area of the Near East, and closely related to them. The carving of a horse with traces of a layer of ocher painting from HaYonim Cave, now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the French mandate over Syria and Lebanon after World War I. This is pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raqefet Cave
Raqefet Cave (''Cyclamen Cave'') is a Late Natufian archaeological site located in Mount Carmel in the north of Israel. It was discovered in 1956. The site indicates plants were already used as food at Raqefet, before the advent of agriculture. History Remains in one of the chambers of the cave suggest the production of beer during the occupation of the cave. The earliest archaeological evidence of fermentation consists of 13,000-year-old residues of a beer with the consistency of gruel, used by the semi-nomadic Natufians for ritual feasting, at the Raqefet Cave. Earlier levels at Raqefet include remains from the Levantine Aurignacian. Earlier Mousterian remains were also found at Site 187. In 2020, incised slabs were discovered at Raqefet Cave, with a human figure most likely shown as dancing. Gallery Raqefet homo18.JPG, Human remains Raqefet mortars.JPG, Rock mortars used to prepare malt for beer manufacture File:Raqefet Cave rock mortars.jpg, Raqefet Cave rock mortars. Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ksar Akil
Ksar Akil (also Ksar 'Akil or Ksar Aqil) is an archeological site northeast of Beirut in Lebanon. It is located about west of Antelias spring on the north bank of the northern tributary of the Wadi Antelias. It is a large rock shelter below a steep limestone cliff. It was first noticed by Godefroy Zumoffen in 1900 and first studied by A. E. Day in 1926 then first systematically excavated by J.G. Doherty, S.J., and J.F. Ewing, S.J., in 1937-1938 and again in 1947-1948, then later by Jacques Tixier in 1969-1975 before research was interrupted by the Lebanese Civil War. Excavations showed occupational deposits reaching down to a depth of with one of the longest sequences of Paleolithic flint industries ever found in the Middle East. The first level of contained Upper Levallois-Mousterian remains with long and triangular Lithic flakes. The level above this showed industries accounting for all six stages of the Upper Paleolithic. An Emireh point was found at the first stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kebara Cave
Kebara Cave ( he, מערת כבארה, Me'arat Kebbara, ar, مغارة الكبارة, Mugharat al-Kabara) is a limestone cave locality in Wadi Kebara, situated at above sea level on the western escarpment of the Carmel Range, in the Ramat HaNadiv preserve of Zichron Yaakov. History The cave was inhabited between 60,000 and 48,000 BP and is famous for its excavated finds of hominid remains. Dorothy Garrod and Francis Turville-Petre excavated in the cave in the early 1930s. Excavations have since yielded a large number of human remains associated with a Mousterian archaeological context. The first specimen discovered in 1965, during the excavations of M. Stekelis, was an incomplete infant skeleton (Kebara 1). The most significant discovery made at Kebara Cave was Kebara 2 in 1982, the most complete postcranial Neanderthal skeleton found to date. Nicknamed "Moshe" and dating to ''circa'' 60,000 BP, the skeleton preserved a large part of one individual's torso ( vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Bedouin towns, including Rahat and Tel Sheva and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Trans-Jordan's name". Despite th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microlith
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The microliths were used in spear points and arrowheads. Microliths are produced from either a small blade ( microblade) or a larger blade-like piece of flint by abrupt or truncated retouching, which leaves a very typical piece of waste, called a microburin. The microliths themselves are sufficiently worked so as to be distinguishable from workshop waste or accidents. Two families of microliths are usually defined: laminar and geometric. An assemblage of microliths can be used to date an archeological site. Laminar microliths are slightly larger, and are associated with the end of the Upper Paleolithic and the beginning of the Epipaleolithic era; geometric microliths are characteristic of the Mesolithic and the Neolithic. Geometric micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipalaeolithic Near East
The Epipalaeolithic Near East designates the Epipalaeolithic ("Final Old Stone Age", also known as Mesolithic) in the prehistory of the Near East. It is the period after the Upper Palaeolithic and before the Neolithic, between approximately 20,000 and 10,000 years Before Present (BP). The people of the Epipalaeolithic were nomadic hunter-gatherers who generally lived in small, seasonal camps rather than permanent villages. They made sophisticated stone tools using microliths—small, finely-produced blades that were hafted in wooden implements. These are the primary artifacts by which archaeologists recognise and classify Epipalaeolithic sites. The start of the Epipalaeolithic is defined by the appearance of microliths. Although this is an arbitrary boundary, the Epipalaeolithic does differ significantly from the preceding Upper Palaeolithic. Epipalaeolithic sites are more numerous, better preserved, and can be accurately radiocarbon dated. The period coincides with the gradual r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago (late Marine Isotope Stage 9 to late Marine Isotope Stage 7), and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. According to the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans, anatomically modern humans began migrating out of Africa during the Middle Stone Age/Middle Paleolithic around 125,000 years ago and began to repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.png)