|
Leithia
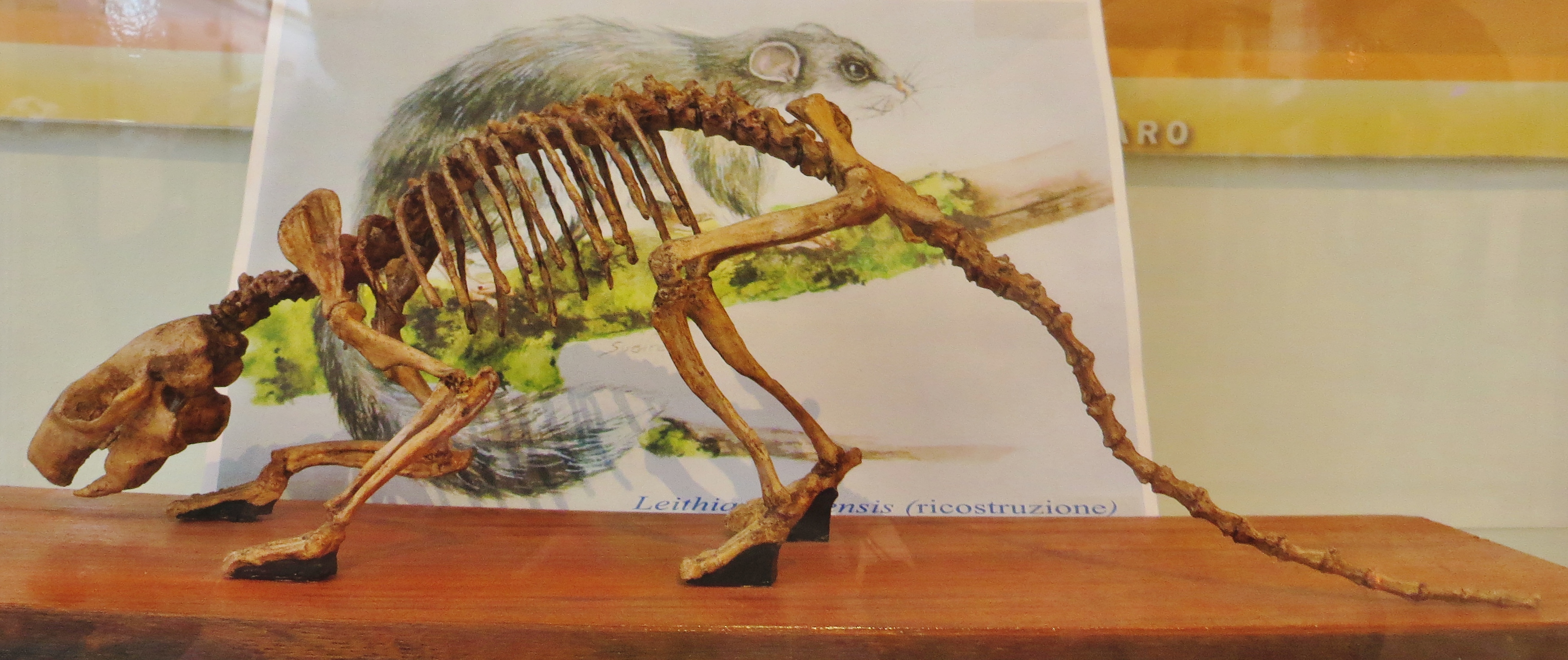
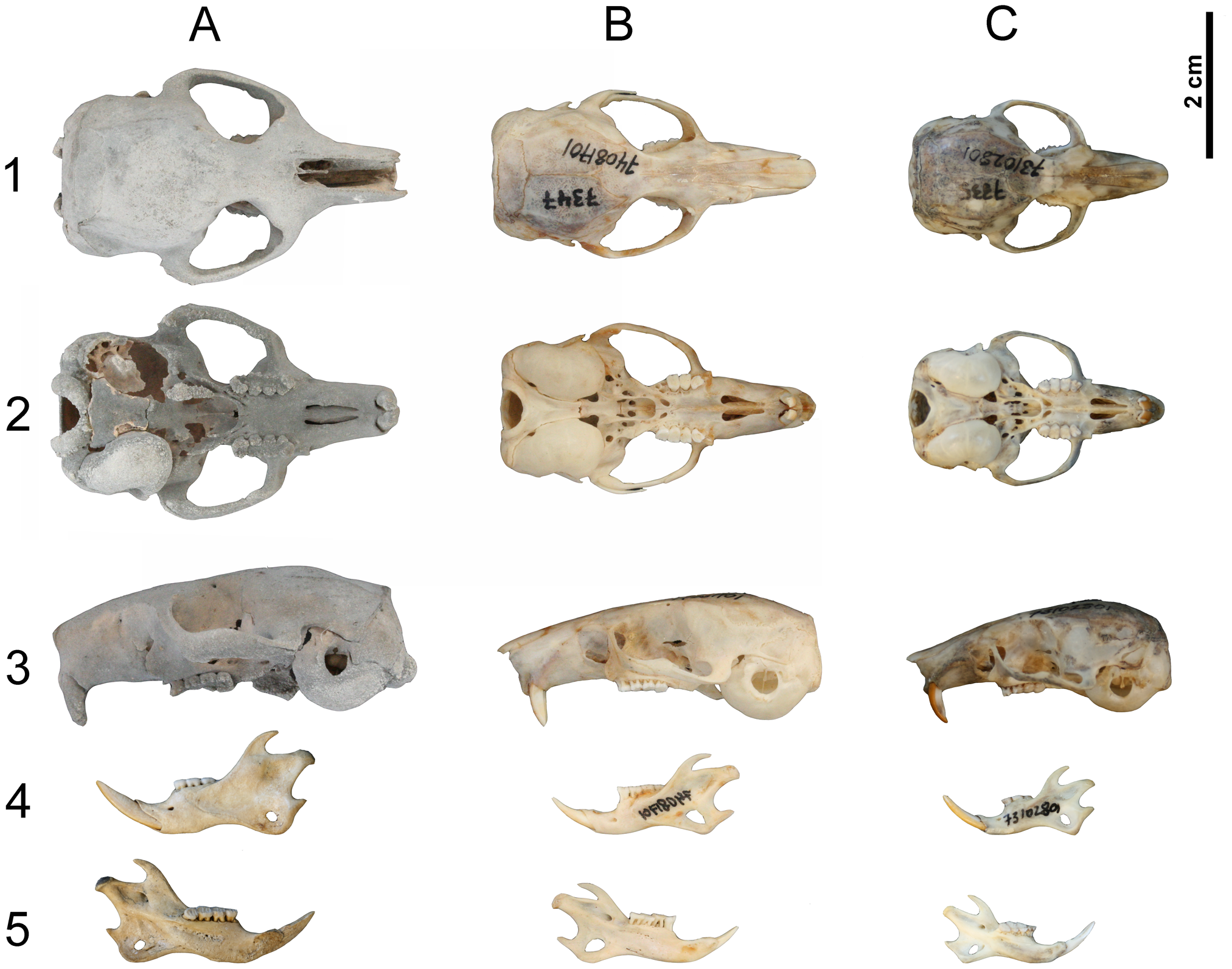
''Leithia'' is a genus of extinct giant dormice from the Mediterranean islands of Malta and Sicily. It is considered an example of island gigantism. ''Leithia melitensis'' is the largest known species of dormouse, living or extinct, being twice the size of any other known species. Discovery and taxonomy The species were first named by Andrew Leith Adams in 1863 from remains found in caves in Malta and were assigned to the living genus '' Myoxus.''Adams, A. L. (1863), ‘Observations on the Fossiliferous caves of Malta’. ''Journal of the Royal Society,'' 4 .2. pp.11–19. ''Leithia'' was proposed in 1896 by Richard Lydekker as a new genus, suggesting an arrangement currently recognised as the subfamily Leithiinae; the names honour Leith Adams. It is estimated to have weighed up to . In the time before the Mediterranean islands were colonised by humans, dozens of mammal species endemic to the area, some unusually large like ''Leithia'', some unusually small (such as pyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leithia Melitensis 7243
''Leithia'' is a genus of extinct giant dormice from the Mediterranean islands of Malta and Sicily. It is considered an example of island gigantism. ''Leithia melitensis'' is the largest known species of dormouse, living or extinct, being twice the size of any other known species. Discovery and taxonomy The species were first named by Andrew Leith Adams in 1863 from remains found in caves in Malta and were assigned to the living genus '' Myoxus.''Adams, A. L. (1863), ‘Observations on the Fossiliferous caves of Malta’. ''Journal of the Royal Society,'' 4 .2. pp.11–19. ''Leithia'' was proposed in 1896 by Richard Lydekker as a new genus, suggesting an arrangement currently recognised as the subfamily Leithiinae; the names honour Leith Adams. It is estimated to have weighed up to . In the time before the Mediterranean islands were colonised by humans, dozens of mammal species endemic to the area, some unusually large like ''Leithia'', some unusually small (such as pyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dormice
A dormouse is a rodent of the family Gliridae (this family is also variously called Myoxidae or Muscardinidae by different taxonomists). Dormice are nocturnal animals found in Africa, Asia, and Europe. They are named for their long, dormant hibernation period of six months or longer. As only one species of dormouse – the hazel dormouse – is native to the United Kingdom, in everyday English usage "dormouse" can refer either to that one species or to the family as a whole. The English name of the species derived from the French ''dormeuse'', and the latter in turn possibly from the Languedocien ''radourmeire''. Etymology Concerning the dormouse's name, etymonline says "long-tailed Old World rodent noted for its state of semi-hibernation in winter, early 15c., possibly from Anglo-French ''dormouse'' 'tending to be dormant' (from stem of ''dormir'' 'to sleep,' see ''dormant''), with the second element mistaken for ''mouse''; or perhaps it is from a Middle English dialectal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dormouse
A dormouse is a rodent of the family Gliridae (this family is also variously called Myoxidae or Muscardinidae by different taxonomists). Dormice are nocturnal animals found in Africa, Asia, and Europe. They are named for their long, dormant hibernation period of six months or longer. As only one species of dormouse – the hazel dormouse – is native to the United Kingdom, in everyday English usage "dormouse" can refer either to that one species or to the family as a whole. The English name of the species derived from the French ''dormeuse'', and the latter in turn possibly from the Languedocien ''radourmeire''. Etymology Concerning the dormouse's name, etymonline says "long-tailed Old World rodent noted for its state of semi-hibernation in winter, early 15c., possibly from Anglo-French ''dormouse'' 'tending to be dormant' (from stem of ''dormir'' 'to sleep,' see ''dormant''), with the second element mistaken for ''mouse''; or perhaps it is from a Middle English dialectal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leithiinae
Leithiinae is a subfamily of dormice. It is named after the '' Leithia'', an extinct genus of giant dormouse from the Pleistocene of Sicily. Classification Subfamily Leithiinae *Genus '' Chaetocauda'' **Chinese dormouse, ''Chaetocauda sichuanensis'' *Genus ''Dryomys'' ** Woolly dormouse, ''Dryomys laniger'' ** Balochistan forest dormouse, ''Dryomys niethammeri'' **Forest dormouse The forest dormouse (''Dryomys nitedula'') is a species of rodent in the family Gliridae found in eastern Europe, the Balkans and parts of western Central Asia. It is categorized as being of least concern in the ''IUCN List of Threatened Specie ..., ''Dryomys nitedula'' *Genus '' Eliomys'', garden dormice ** Asian garden dormouse, ''Eliomys melanurus'' ** Maghreb garden dormouse, ''Eliomys munbyanus'' ** Garden dormouse, ''Eliomys quercinus'' *Genus '' Hypnomys''† (Balearic dormouse) **'' Hypnomys morphaeus''† **'' Hypnomys mahonensis''† *Genus '' Leithia''† *Genus '' Muscardinus'' ** Hazel d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Leith Adams
Andrew Leith Adams FRSE, FRS (21 March 1827 – 29 July 1882) was a Scottish physician, naturalist and geologist. He was the father of the writer Francis Adams.Gaston, A. J. in Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Volume 1. pp. 222–223 Life and career Adams was the son of Francis Adams (1796–1861), a surgeon and Espeth Shaw. He studied medicine and joined as an army physician in 1848, serving in the 22nd Infantry Regiment in India. Between 1849–1854 he was posted in Dagshai, Rawalpindi and Peshawar. He also served in Kashmir, Egypt, Malta (1861–1868), Gibraltar and Canada. He married Bertha Jane Grundy on 26 October 1859, who later became famous as a novelist. He spent his spare time studying the natural history of these countries. He was among the first to study the interior of Ladakh and wrote about it in "The Birds of Cashmere and Ladakh". The orange bullfinch (''Pyrrhula aurantiaca'') was discovered by him as also the first breeding site of brown-headed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Gigantism
Island gigantism, or insular gigantism, is a biological phenomenon in which the size of an animal species isolated on an island increases dramatically in comparison to its mainland relatives. Island gigantism is one aspect of the more general Foster's rule, "island effect" or "Foster's rule", which posits that when mainland animals colonize islands, small species tend to evolve larger bodies, and large species tend to evolve smaller bodies (insular dwarfism). This is itself one aspect of the more general phenomenon of island syndrome which describes the differences in Morphology (biology), morphology, ecology, physiology and ethology, behaviour of insular species compared to their continental counterparts. Following the arrival of humans and associated introduced predators (dogs, cats, rats, pigs), many giant as well as other island endemics have become Extinction, extinct. A similar size increase, as well as increased woodiness, has been observed in some insular plants. Possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypnomys
''Hypnomys'', otherwise known as Balearic giant dormice, is an extinct genus of dormouse (Gliridae) in the subfamily Leithiinae. Its species are considered examples of insular gigantism. They were endemic to the Balearic Islands in the western Mediterranean from the Early Pliocene until their extinction around 4,000 years ago. They first appeared in the fossil record on Mallorca during the Early Pliocene, presumably due to the Messinian salinity crisis causing a connection with mainland Europe. They later spread to Menorca, and a possible molar is also known from Ibiza. ''Hypnomys'' became extinct during the Holocene after human arrival on the Balearics. They were one of only three native land mammals to the islands at the time of human arrival, alongside the shrew ''Nesiotites'' and goat-antelope ''Myotragus''. History of discovery The first remains of ''Hypnomys'' were discovered in 1910 on the island of Mallorca in the Balearic Islands by British palaeontologist Dorothea Bate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Lydekker
Richard Lydekker (; 25 July 1849 – 16 April 1915) was an English naturalist, geologist and writer of numerous books on natural history. Biography Richard Lydekker was born at Tavistock Square in London. His father was Gerard Wolfe Lydekker, a barrister-at-law with Dutch ancestry. The family moved to Harpenden Lodge soon after Richard's birth. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he took a first-class in the Natural Science tripos (1872). In 1874 he joined the Geological Survey of India and made studies of the vertebrate palaeontology of northern India (especially Kashmir). He remained in this post until the death of his father in 1881. His main work in India was on the Siwalik palaeofauna; it was published in ''Palaeontologia Indica''. He was responsible for the cataloguing of the fossil mammals, reptiles, and birds in the Natural History Museum (10 vols., 1891). He named a variety of taxa including the golden-bellied mangabey; as a taxon authority h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messinian
The Messinian is in the geologic timescale the last age or uppermost stage of the Miocene. It spans the time between 7.246 ± 0.005 Ma and 5.333 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago). It follows the Tortonian and is followed by the Zanclean, the first age of the Pliocene. The Messinian overlaps the Turolian European Land Mammal Mega Zone (more precisely MN 12 and 13) and the Pontian Central European Paratethys Stage. It also overlaps the late Huayquerian and early Montehermosan South American Land Mammal Ages, and falls inside the more extensive Hemphillian North American Land Mammal Age. During the Messinian, around 6 million years ago, the Messinian salinity crisis took place, which brought about repeated desiccations of the Mediterranean Sea. Definition The Messinian was introduced by Swiss stratigrapher Karl Mayer-Eymar in 1867. Its name comes from the Italian city of Messina on Sicily, where the Messinian evaporite deposit is of the same age. The base of the Messinia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1896
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Mammals Of Europe
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Rodents
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós ( latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |